Korean Diabetes J.
2009 Feb;33(1):65-72. 10.4093/kdj.2009.33.1.65.
Cause-of-Death Trends for Diabetes Mellitus over 10 Years
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Dong-A University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea. dkkim@dau.ac.kr
- 2Department of Endocrinology, Maryknoll Hospital, Busan, Korea.
- 3Department of Internal Medicine, Pusan National University School of Medicine, Busan, Korea.
- 4Department of Endocrinology, Daedong Hospital, Busan, Korea.
- 5Department of Endocrinology, Busan St. Mary's Medical Center, Busan, Korea.
- 6Department of Endocrinology, Wallace Memorial Baptist Hospital, Busan, Korea.
- KMID: 2222485
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4093/kdj.2009.33.1.65
Abstract
-
BACKGROUND: Recently, diabetic mortality is lower than ever before, likely due to dramatic improvements in diabetes care. This study set to analyze changes in the cause of death in type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) in the past 10 years.
METHODS
All subjects were T2DM patients over the age of 30 whose death certificates were issued at six hospitals in the Busan metropolitan area from 2000 to 2004. The patients were excluded if they had been clinically diagnosed with significant tuberculosis, liver, thyroid, renal, connective tissue diseases and cancers, prior to T2DM diagnosis. We classified the cause of death into several groups by KCD-4. The results were compared with published data on the period from 1990 to 1994.
RESULTS
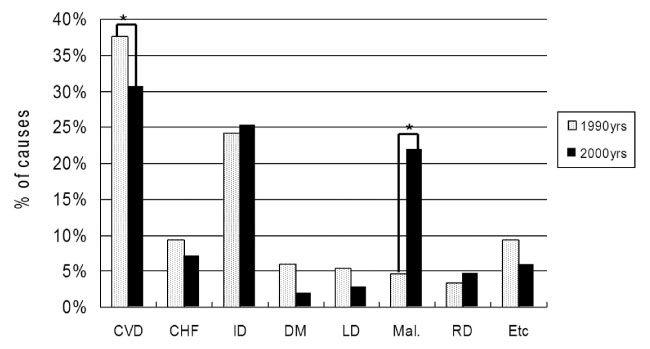
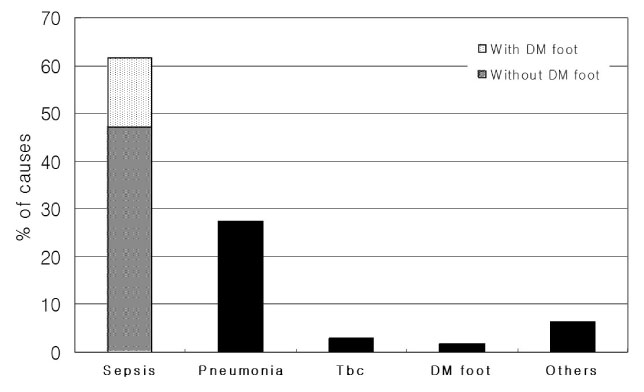
The study comprised 680 patients, of which 374 (55.0%) were male. The average age of death was 66.3 +/- 10.7 years. The most common cause of death was cardiovascular disease (30.6%), followed by infectious disease (25.3%), cancer (21.9%), congestive heart failure (7.1%), renal disease (4.7%), liver disease (2.7%), and T2DM itself (1.9%). In the study from the earlier period, the most common cause of death was also cardiovascular disease (37.6%), followed by infectious disease (24.2%), T2DM (6.0%), liver disease (5.4%), cancer (4.7%), and renal disease (3.3%).
CONCLUSION
Over both study periods, the first and second cause of death in T2DM were cardiovascular disease and infectious disease, respectively. However, death by cerebral infarction among cardiovascular disease patients was significantly lower in the latter period, while death by malignancy was markedly increased.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
The Mentors, The Social Support and Patients with Diabetes Mellitus
Yu Jeong Park
J Korean Diabetes. 2019;20(2):112-116. doi: 10.4093/jkd.2019.20.2.112.
Reference
-
1. Kim SG, Choi DS. The present state of diabetes mellitus in Korea. J Korean Med Assoc. 2008. 51:791–798.2. Cho NH. Prevalence of diabetes and management status in Korean population. Korean J Med. 2005. 68:1–3.3. Kim JH, Choi IS, Kim CW, Ku HS, Son SP, Lee KJ, Jeong CH, Choi SY, Kim IJ, Kim YK, Kang DY, Kim DK, Lim OJ. A study on the use of death for patients with non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Korean J Med. 1996. 50:530–536.4. Nick AR, Rudy WB, William FK, Nigel CU, Vincent MC. Cause-specific mortality in a population with diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2002. 25:43–48.5. Barrett-Conner E, Deborah LW. Sex differential in ischemic heart disease mortality in diabetics. Am J Epidemiol. 1983. 118:489–496.6. Masatoshi F, Yutaka N, Isao K, Takao O, Hiromitsu I, Keizo N, Susumu O, Taketo Y. Diabetes and cardiovascular disease in a prospective population survey in Japan. The Hisayama Study. Diabetes. 1996. 45:suppl 1. S14–S16.7. Joel CK, Richard PD, Maureen IH, Fanchon FF, Jenniffer HM, Dwight BB. Mortality among diabetics in national sample. Am J Epidemiol. 1988. 128:389–401.8. Marja P, Heikki M, Markku L, Kalevi P. Plasma insulin and all-cause cardiovascular, and non cardiovascular mortality. Diabetes Care. 2000. 23:1097–1102.9. Davina EW, Christoper G, Matthew WK, Timothy AW. Deaths from diabetes are under-reported in national mortality statistics. Med J Aust. 1990. 152:598–600.10. Bae KW, Ahnn YJ, Park YS, Park KS, Yang BG, Lee HK. Mortality in adults with and without diabetes in Yonchon, Korea. J Korean Diabetes Assoc. 2001. 25:384–398.11. Jenifer BM, Philip R. Cardiovascular risk in diabetes: a brief review. J Diabetes Complications. 2000. 14:108–115.12. Meigs JB. Epidemiology of cardiovascular complications in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Acta Diabetol. 2003. 40:S358–S361.13. American Diabetes Association. Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes-2007. Diabetes Care. 2007. 30:suppl 1. S4–S41.14. Korean Diabetes Association. Treatment guideline for diabetes. 2007. 1st ed. Seoul: MMK Communications;110.15. Park IB, Kim DJ, Kim JY, Kim HY, Kim HY, Min KW, Park SW, Park JH, Baik SH, Son HS, Ahn CW, Oh JY, Lee SH, Lee JY, Chung CH, Choi IJ, Choi KM. Current status of aspirin user in Korean diabetic patients using Korean health insurance database. J Korean Diabetes Assoc. 2006. 30:363–371.16. Rolka DB, Fagot-Campagna A, Narayan KM. Aspirin use among adults with diabetes: estimates from the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Diabetes Care. 2001. 24:197–201.17. Krein SL, Vijan S, Pogach LM, Hogan MM, Kerr EA. Aspirin use and counseling about aspirin among patients with diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2002. 25:965–970.18. Kim BJ, Woo JT, Kim SW, Yang IM, Kim JW, Kim YS, Choi YK. Cause of death in diabetic subject. J Kyung Hee Univ Med Cent. 1997. 13:358–365.19. Kawate R, Yamakido M, Nishimoto Y, Benett PH, Knowler EC. Diabetes mellitus and its vascular complications in Japanese migrants on the Island of Hawaii. Diabetes Care. 1979. 2:161–170.20. The ADVANCE Collaborative Group. Intensive blood glucose control and vascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2008. 358:2560–2572.21. Holman RR, Paul SK, Bethel MA, Matthew DR, Neil HA. 10-Year follow-up of intensive glucose control in type 2 Diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2008. 359:1577–1589.22. The Action to Control Cardiovascular Risk in Diabetes Study Group. Effects of intensive glucose lowering in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2008. 358:2545–2559.23. The Diabetes Control and Complications Trial Research Group. The relationship of glycemic exposure (HbA1c) to the risk of development and progression of retinopathy in the diabetes control and complications trial. Diabetes. 1995. 44:968–983.24. UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Group. Intensive blood-glucose control with sulphonylureas or insulin compared with conventional treatment and risk of complications in patients with type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 33). UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Group. Lancet. 1998. 352:837–853.25. Holman RR, Paul SK, Bethel MA, Neil HA, Matthews DR. Long-term follw-up after tight control of blood pressure in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2008. 359:1565–1576.26. Kim SA, Park WS, Ohrr HC, Kang HY, Lee DH, Yi SW, Kwak YH, Song JS. Prevalence and management status of diabetes mellitus in Korea. Korean J Med. 2005. 68:10–17.27. Gaede P, Vedel P, Larsen N, Jensen GV, Parving HH, Pedersen O. Multifactorial intervention and cardiovascular disease in patients with type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2003. 348:383–393.28. Ken GU, Catherine CC, Maureen IH. Mortality in adults with and without diabetes in a national cohort of the U.S. population, 1971-1993. Diabetes Care. 1998. 21:1138–1145.29. Ioacara S, Ionescu-Tirgoviste C, Sabau S, Enachescu C, Farcasiu E, Bradescu O. Mortality trends in noninsulin-treated type 2 diabetes mellitus patients in the 1943-2000 period. Rom J Int Med. 2007. 45:371–377.30. Inoue M, Iwasaki M, Otani T, Sasazuki S, Tsugane S. Diabetes mellitus and the risk of cancer: results from a large-scale population-based cohort study in Japan. Arch Intern Med. 2006. 166:1871–1877.31. Chung YW, Han DS, Park KH, Eun CS, Yoo KS, Park CK. Insulin therapy and colorectal adenoma risk among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a case-control study in Korea. Dis Colon Rectum. 2008. 51:593–597.32. Barone BB, Yeh HC, Snyder CF, Peairs KS, Stein KB, Derr RL, Wolff AC, Brancati FL. Long-term all-cause mortality in cancer patients with preexisting diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA. 2008. 300:2754–2764.34. A statistical table of the cause of death. Korea National Statistical Office. 2008. http://www.nso.go.kr.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Cause-of-Death Trends for Diabetes Mellitus over 10 Years (Korean Diabetes J 33(1):65-72, 2009)
- Cause-of-Death Trends for Diabetes Mellitus over 10 Years (Korean Diabetes J 33(1):65-72, 2009)
- The Link Between Sleep and Diabetes Mellitus: A Literature Review
- Treatment guideline for diabetes
- A Clinical Study of Pulmonary Tuberculosis Associated with Diabetes Mellitus