Korean Diabetes J.
2009 Feb;33(1):58-64. 10.4093/kdj.2009.33.1.58.
Effects of 'Ubiquitous Healthcare' on the Ability of Self-Management in Elderly Diabetic Patients
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul.Korea. janghak@sn.ac.kr
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Medical Informatics, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Radiology, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2222484
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4093/kdj.2009.33.1.58
Abstract
-
BACKGROUND: The need for a new healthcare system is growing due to the paradigm shift from health supervision to health maintenance. Previously, we performed a pilot study that examined the effectiveness of a ubiquitous healthcare (U-healthcare) diabetes management program which consists of self-monitoring of blood glucose (SMBG) and mobile phone services for elderly patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. In this study, we investigated the effect of a diabetes management program using U-healthcare based on the self-care skills of elderly patients with diabetes mellitus.
METHODS
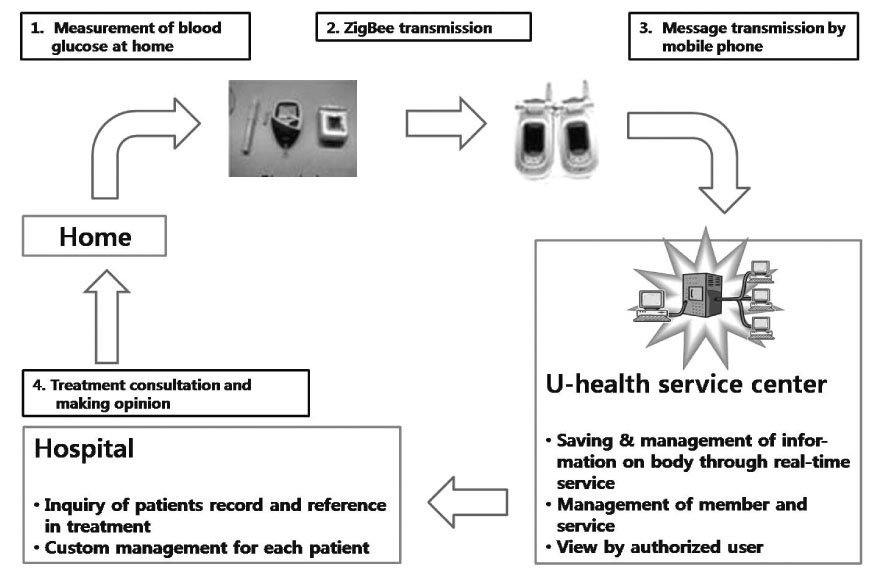
From July to October 2005, 17 patients were recruited and provided with a blood glucometer with the ZigBee module and a mobile phone. In addition, the patients' understanding of diabetes self-care skills was examined at the beginning and end of the study. At the end of the study, we determined the level of patient satisfaction regarding U-healthcare services.
RESULTS
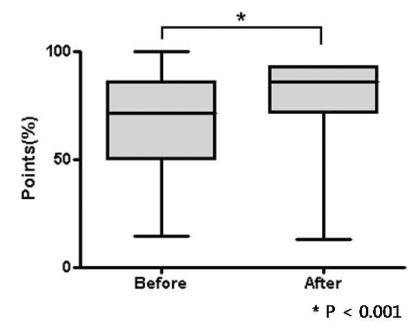
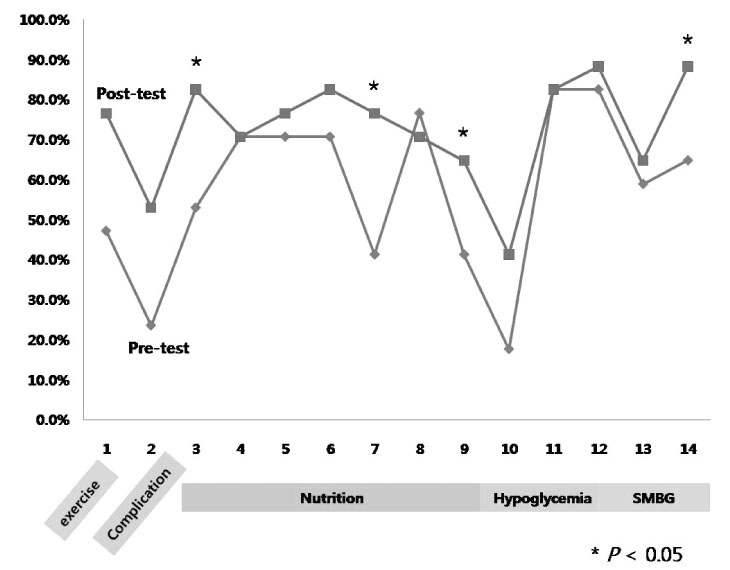
The patients' test scores on their understanding of diabetes mellitus improved from 57.2 +/- 20.7 to 72.7 +/- 13.4%. Specifically, patient knowledge of the basic principles for a proper diabetic diet (52.9% vs. 82.4%, P = 0.046), foods that influence blood sugar level (41.2% vs. 76.5%, P = 0.007) and the influence of beverage choice (41.2% vs. 64.7%, P = 0.007), all increased. In addition, a significant increase in knowledge of living standards regarding diabetes mellitus was observed (64.7% vs. 88.2%, P = 0.0032).
CONCLUSION
We conclude that the U-healthcare incorporating SMBG could be promising, as it improves self-management skills of diabetes mellitus patients, as well as their understanding of the disease.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Effectiveness of the Smart Care Service for Diabetes Management
Young-Soon Chung, Yongsuk Kim, Chang Hee Lee
Healthc Inform Res. 2014;20(4):288-294. doi: 10.4258/hir.2014.20.4.288.Self-management of Chronic Conditions Using mHealth Interventions in Korea: A Systematic Review
Jae Yoon Yi, Yujin Kim, Yoon-Min Cho, Hongsoo Kim
Healthc Inform Res. 2018;24(3):187-197. doi: 10.4258/hir.2018.24.3.187.
Reference
-
1. Tate DF, Jackvony EH, Wing RR. Effects of internet behavioral counseling on weight loss in adults at risk for type 2 diabetes: a randomized trial. JAMA. 2003. 289:1833–1836.2. McMahon GT, Gomes HE, Hickson Hohne S, Hu TM, Levine BA, Conlin PR. Web-based care management in patients with poorly controlled diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2005. 28:1624–1629.3. Lee HJ, Lee SH, Ha KS, Jang HC, Chung WY, Kim JY, Chang YS, Yoo DH. Ubiquitous healthcare service using Zigbee and mobile phone for elderly patients. Int J Med Inform. 2008.4. Cho JH, Kwon HS, Yoon KH. Perspectives of "Ubiquitous Health Care System" for diabetes management. J Korean Diabetes Assoc. 2006. 30:87–95.5. Baik SH, Choi KM. Diabetes mellitus in elderly Korean. J Korean Diabetes Assoc. 2003. 27:229–303.6. Kim HJ, Ahn CW. Elderly diabetes mellitus. Korean Clinical Diabetes J. 2007. 8:6–7.7. Nam HW. Clinical characteristics of Elderly Diabetes. Korean Clinical Diabetes J. 2007. 8:11–15.8. Hogan P, Dall T, Nikolov P. Economic costs of diabetes in the US in 2002. Diabetes Care. 2003. 26:917–932.9. American Diabetic Association. Economic costs of diabetes in the U.S. In 2007. Diabetes Care. 2008. 31:596–615.10. Kollmann A, Riedl M, Kastner P, Schreier G, Ludvik B. Feasibility of a mobile phone-based data service for functional insulin treatment of type 1 diabetes mellitus patients. J Med Internet Res. 2007. 9:e36.11. Lee SH, Ha KS, Jang HC, Lee HJ, Chung WY, Kim JY, Yoo DH, Lee SB, Lee SJ. A Study on U-Healthcare Service using Mobile Phone for elderly patients. J Kor Soc Med Informatics. 2007. 11:98–102.12. Lee KU, Choi YA, Lee YH, Park SW, Yoo HJ, Kim SY, Lee HK, Min HK. Development of a Diabetes Knowledge Test. J Korean Diabetes Assoc. 1985. 9:89–93.13. Cho JH, Chang SA, Kwon HS, Choi YH, Ko SH, Moon SD, Yoo SJ, Song KH, Son HS, Kim HS, Lee WC, Cha BY, Son HY, Yoon KH. Long-term effect of the Internet-based glucose monitoring system on HbA1c reduction and glucose stability: a 30-month follow-up study for diabetes management with a ubiquitous medical care system. Diabetes Care. 2006. 29:2625–2631.14. Kim JH. Guidelines for education of diabetes in the eldery. J Korean Diabetes Assoc. 2006. 30:suppl 2. S297–S301.15. Franciosi M, Pellegrini F, De Berardis G, Belfiglio M, Di Nardo B, Greenfield S, Kaplan SH, Rossi MC, Sacco M, Tognoni G, Valentini M, Nicolucci A. Self-monitoring of blood glucose in non-insulin-treated diabetic patients: a longitudinal evaluation of its impact on metabolic control. Diabet Med. 2005. 22:900–906.