Dement Neurocogn Disord.
2013 Mar;12(1):9-20. 10.12779/dnd.2013.12.1.9.
Neurologists' Awareness and Preparedness on Prion Diseases in Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurology, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea. neuroksy@snu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Neurology, Seoul National University Boramae Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Neurology, Yonsei University Severance Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Social and Preventive Medicine, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea.
- KMID: 2222356
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12779/dnd.2013.12.1.9
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD) is very rare human prion disease. But, neurologists take a key role in diagnosis, surveillance and management of the cases because of its complexity and difficulty in diagnosis of the disease. The aim of this study is to investigate the level of awareness and preparedness of Korean neurologists on this rare disease.
METHODS
Survey sheets of self-administered questionnaire were given to Korean neurologists who participated in the 31st Annual Meeting of the Koran Neurological Association. Data from 133 respondents were conducted by descriptive analysis.
RESULTS
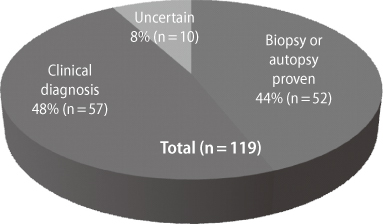
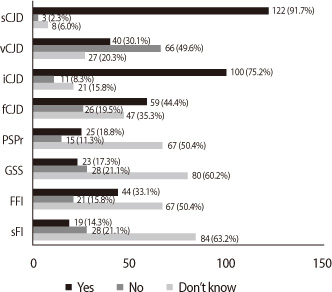
Their answers were as follows: About 62% of neurologists have experienced patients of CJD. Forty-four percent of the patients were confirmed by brain biopsy. Most of neurologists (44%) were not confident to diagnose CJD and the reason why they felt hard to diagnose was due to the variable initial clinical manifestations (45.1%) and the lack of clinical experience (51.9%). Heidenheim variant CJD, proteinase sensitive prionopathy, molecular subtypes of sporadic CJD, diagnostic criteria was not familiar term to Korean neurologists (76.7%, 53.4%, 58.6%, and 62.4% respectively). Opinion for the most useful diagnostic tool was brain MRI (45.1%), CSF 14-3-3 protein (30.1%), typical EEG finding (36.8%) and gene (PRNP) test (42.9%). And they consider none of them are specific for the diagnosis of CJD (89.5%, 73.7%, 83.5%, 91.7%, respectively). Most of the neurologist in this survey answered that the opportunity for education of CJD should be increased (67.7%).
CONCLUSIONS
Most of neurologists have encountered CJD patients although it is very rare disease. Some of the important and fundamental concepts of CJD were not correctly recognized to Korean neurologists, necessitating a persistent support for updating knowledge and information.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Neurosyphilis Mimicking Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease
Jae-Won Jang, Jeong Hoon Park, Yong Jun Eo, Seong Heon Kim, Kyung Ho Choi, SangHak Yi, Young Ho Park, SangYun Kim
Dement Neurocogn Disord. 2016;15(4):170-173. doi: 10.12779/dnd.2016.15.4.170.Neurosyphilis Mimicking Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease
Jae-Won Jang, Jeong Hoon Park, Yong Jun Eo, Seong Heon Kim, Kyung Ho Choi, SangHak Yi, Young Ho Park, SangYun Kim
Dement Neurocogn Disord. 2016;15(4):170-173. doi: 10.12779/dnd.2016.15.4.170.
Reference
-
1. Global surveillance, diagnosis and therapy of human transmissible spongiform encephalopathies: report of a WHO consultation. 9-11 February 1998; Geneva, Switzerland.2. Kim HL, Do JY, Cho HJ, Jeon YC, Park SJ, Ma HI, et al. Dura mater graft-associated Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease: the first case in Korea. J Korean Med Sci. 2011. 26:1515–1517. PubMed PMID: 22065911. Pubmed Central PMCID: 3207058.
Article3. Current status of laboratory diagnosis for Creutzfeldt Jakob Disease [2005-2010] and introduction of the active surveillance system for CJD patients. Public Health Wkly Rep. 2011. 4:73–80.4. Haywood AM. Transmissible spongiform encephalopathies. N Engl J Med. 1997. 337:1821–1828. PubMed PMID: 9400041. Epub 1997/12/18. eng.
Article5. National Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease Surveillance Diagnositic Criteria. 2010. Available from: http://www.cjd.ed.ac.kr.6. Zerr I, Kallenberg K, Summers DM, Romero C, Taratuto A, Heinemann U, et al. Updated clinical diagnostic criteria for sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Brain. 2009. 132:2659–2668. PubMed PMID: 19773352. Pubmed Central PMCID: 2759336.
Article7. Vitali P, Maccagnano E, Caverzasi E, Henry RG, Haman A, Torres-Chae C, et al. Diffusion-weighted MRI hyperintensity patterns differentiate CJD from other rapid dementias. Neurology. 2011. 76:1711–1719. PubMed PMID: 21471469. Pubmed Central PMCID: 3100134. Epub 2011/04/08. eng.
Article8. Zerr I, Pocchiari M, Collins S, Brandel JP, de Pedro Cuesta J, Knight RS, et al. Analysis of EEG and CSF 14-3-3 proteins as aids to the diagnosis of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Neurology. 2000. 55:811–815. PubMed PMID: 10994001. Epub 2000/09/20. eng.
Article9. Steinhoff BJ, Zerr I, Glatting M, Schulz-Schaeffer W, Poser S, Kretzschmar HA. Diagnostic value of periodic complexes in Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Ann Neurol. 2004. 56:702–708. PubMed PMID: 15449324. Epub 2004/09/28. eng.
Article10. Sanchez-Juan P, Green A, Ladogana A, Cuadrado-Corrales N, Saanchez-Valle R, Mitrovaa E, et al. CSF tests in the differential diagnosis of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Neurology. 2006. 67:637–643. PubMed PMID: 16924018. Epub 2006/08/23. eng.
Article11. Satoh K, Shirabe S, Eguchi H, Tsujino A, Eguchi K, Satoh A, et al. 14-3-3 protein, total tau and phosphorylated tau in cerebrospinal fluid of patients with Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease and neurodegenerative disease in Japan. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2006. 26:45–52. PubMed PMID: 16633900. Epub 2006/04/25. eng.
Article12. Satoh J, Kurohara K, Yukitake M, Kuroda Y. The 14-3-3 protein detectable in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with prion-unrelated neurological diseases is expressed constitutively in neurons and glial cells in culture. Eur Neurol. 1999. 41:216–225. PubMed PMID: 10343153. Epub 1999/05/27. eng.
Article13. Rabinovici GD, Wang PN, Levin J, Cook L, Pravdin M, Davis J, et al. First symptom in sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Neurology. 2006. 66:286–287. PubMed PMID: 16434680. Epub 2006/01/26. eng.
Article14. Will RG. Acquired prion disease: iatrogenic CJD, variant CJD, kuru. Br Med Bull. 2003. 66:255–265. PubMed PMID: 14522863. Epub 2003/10/03. eng.
Article15. Boesenberg C, Schulz-Schaeffer WJ, Meissner B, Kallenberg K, Bartl M, Heinemann U, et al. Clinical course in young patients with sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Ann Neurol. 2005. 58:533–543. PubMed PMID: 16037975. Epub 2005/07/23. eng.
Article16. Kim SY, Cheong HW, An SS. Human Prion Diseases. J Korean Med Assoc. 2008. 51:1125–1138.
Article