J Korean Ophthalmol Soc.
2014 Mar;55(3):374-378. 10.3341/jkos.2014.55.3.374.
Magnification Effect of the Capsulorhexis by the Cornea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology and Visual Science, Seoul St. Mary's Hospital, The Catholic University of Korea College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Ophthalmology, Chuncheon Sacred Heart's Hospital, Hallym University College of Medicine, Chuncheon, Korea. huanghs@daum.net
- KMID: 2218265
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/jkos.2014.55.3.374
Abstract
- PURPOSE
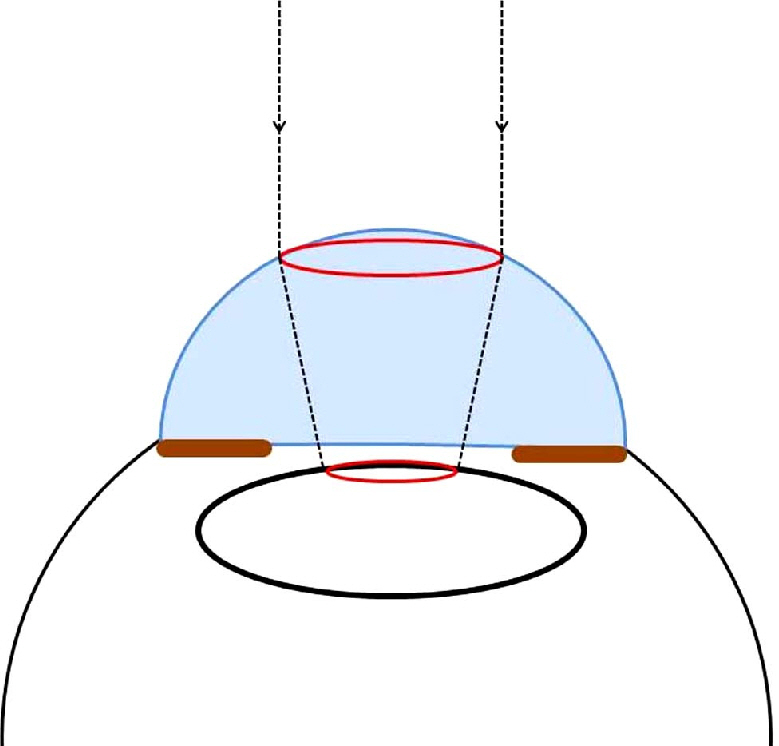
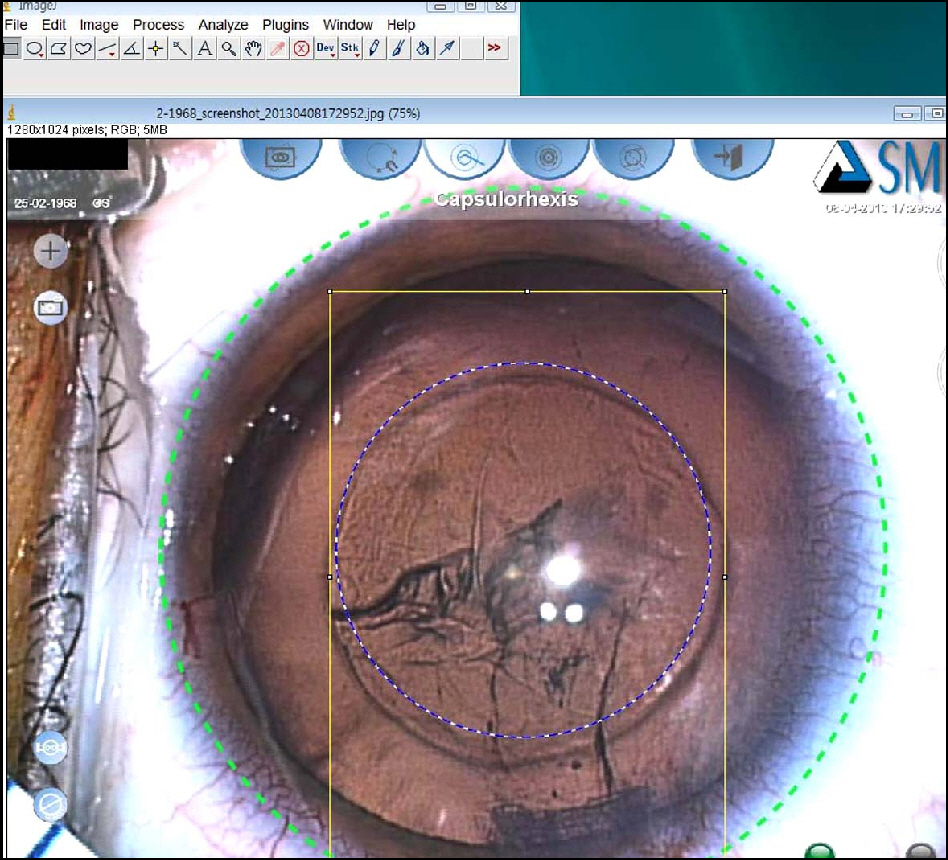
The purpose of this study is to measure the magnification of the capsulorhexis by the cornea using open ring guided capsulorhexis (ORGC) during cataract surgery. The study also investigated the magnification changes according to anterior chamber depth and corneal power.
METHODS
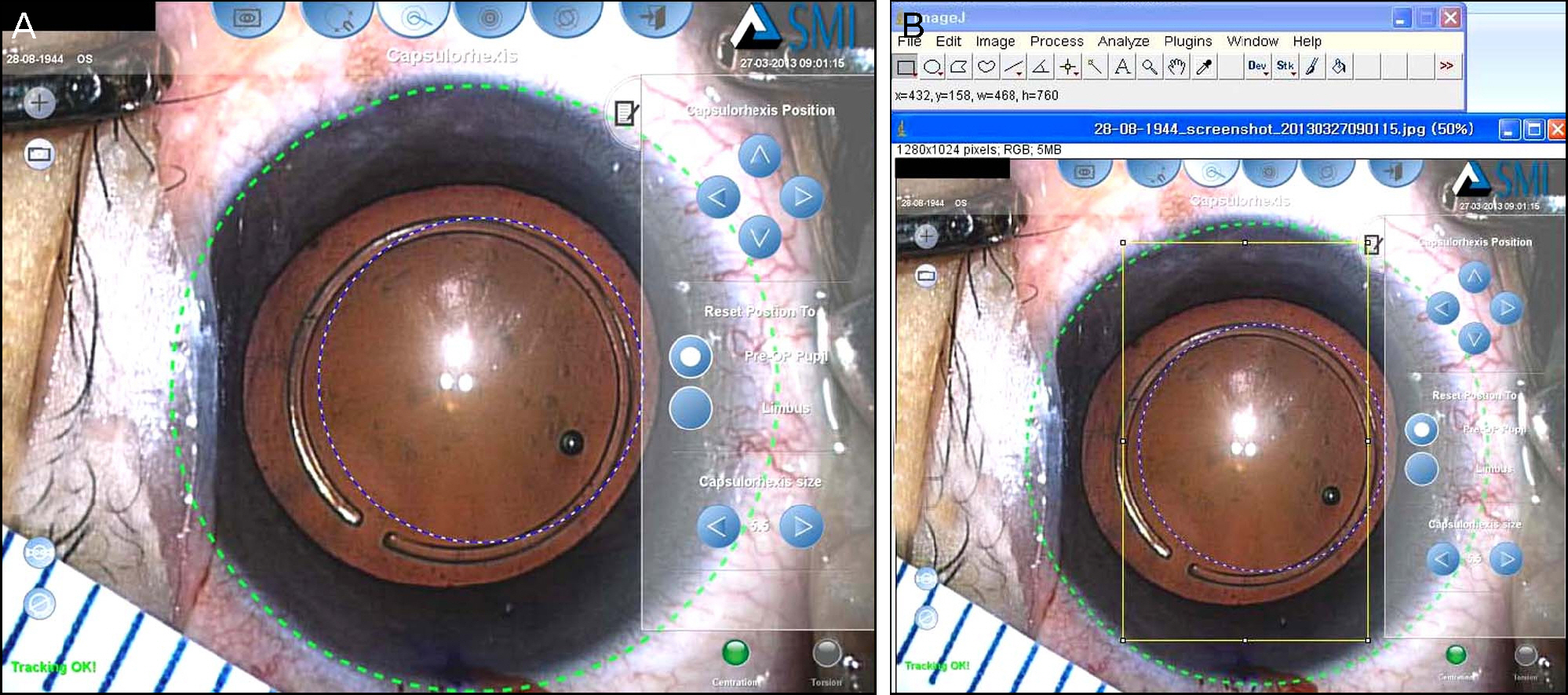
The subjects comprised 40 eyes from 37 patients whose astigmatism was lower than 0.25 D and who had cataract surgery using ORGC from December 2011 to April 2012. ORGC was set on the anterior capsule and photographs were obtained using a camera connected to a surgical microscope after attaching a ruler around the limbus. The pixel number of 5 mm gradations on a ruler and the inner diameter of ORGC were measured using ImageJ. The inner diameter of ORGC was known to be 5.30 mm and the size of ORGC in the snapshot was therefore calculated by proportional expression. After corneal power and anterior chamber depth were identified, the magnification effect was evaluated.
RESULTS
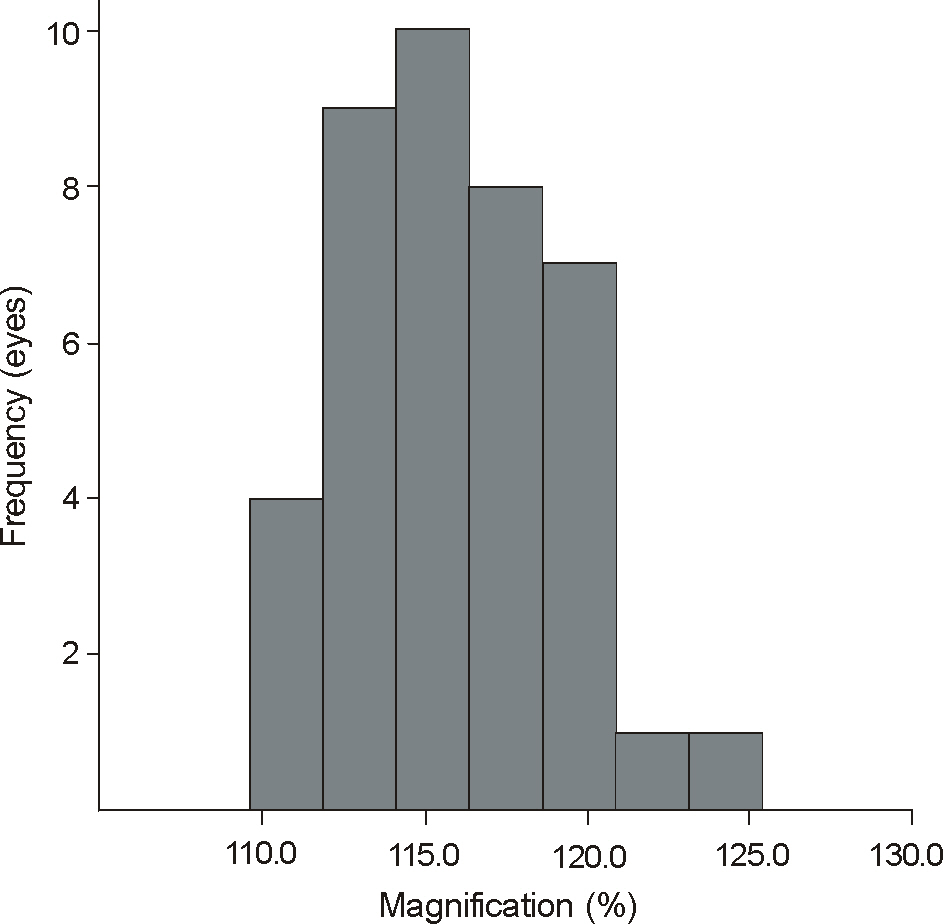
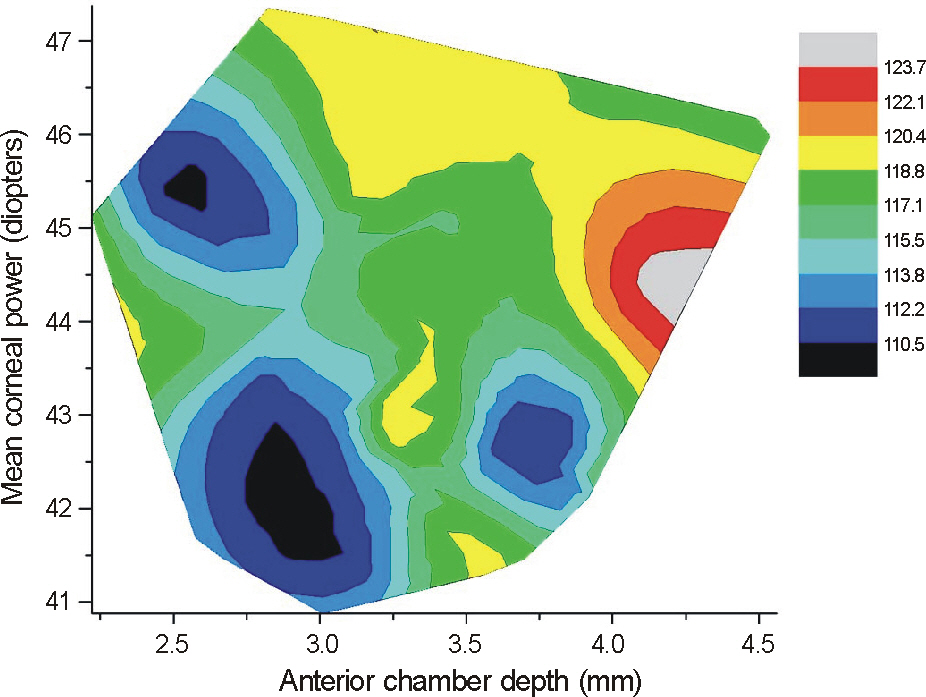
The 37 subjects were composed of 19 males and 21 females, and their average age was 64.8 years. The average depth of the anterior chamber was 3.28 mm, and the average corneal power was 43.534 D. The measured inner diameter of ORGC was 6.14 mm (SD: +/-0.16 mm) and the average magnification of the capsulorhexis was 115.9% (SD: +/-3.1%). The results showed that in the case of shallow anterior depth and low corneal power, the magnification was low equivalent to 110%. However, when the anterior chamber was deep and the corneal power was high, the magnification was greatly increased to 120%.
CONCLUSIONS
The capsulorhexis was magnified to an average of 115.9% by the cornea during cataract surgery. In particular, it is necessary to consider capsulorhexis size in cases with deep anterior chamber and high corneal power, because the magnification will be greater in those cases.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Kim EC, Hwang HS, Kim MS. Anterior capsular phimosis occluding the capsulorhexis opening after cataract surgery in a diabetic patient with high hemoglobin A1C. Semin Ophthalmol. 2013; 28:68–71.
Article2. Wallace RB 3rd. Capsulotomy diameter mark. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2003; 29:1866–8.
Article3. Waltz KL, Rubin ML. Capsulorhexis and corneal magnification. Arch Ophthalmol. 1992; 110:170.
Article4. Bali SJ, Hodge C, Lawless M, et al. Early experience with the femtosecond laser for cataract surgery. Ophthalmology. 2012; 119:891–9.
Article5. He L, Sheehy K, Culbertson W. Femtosecond laser-assisted cataract surgery. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2011; 22:43–52.
Article6. Nagy Z, Takacs A, Filkorn T, Sarayba M. Initial clinical evaluation of an intraocular femtosecond laser in cataract surgery. J Refract Surg. 2009; 25:1053–60.
Article7. Palanker DV, Blumenkranz MS, Andersen D, et al. Femtosecond laser-assisted cataract surgery with integrated optical coherence tomography. Sci Transl Med. 2010; 2:58ra85.
Article8. Friedman NJ, Palanker DV, Schuele G, et al. Femtosecond laser capsulotomy. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2011; 37:1189–98.
Article9. Nagy ZZ, Kránitz K, Takacs AI, et al. Comparison of intraocular lens decentration parameters after femtosecond and manual capsulotomies. J Refract Surg. 2011; 27:564–9.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Clinical Outcomes of Manual Continuous Curvilinear Capsulorhexis and Precision Pulse Capsulotomy
- A Laboratory Study of Diathermy Capsulorhexis
- Extraction of the Leris Nucleus with the Continuous Circular Capsulorhexis in Planned Extracapsular Cataract Extraction
- A Case of Capsule Contraction Syndrome following Continuous Curvilinear Capsulorhexis
- Magnification Error in Digital Radiographs of the Cervical Spine Against Magnetic Resonance Imaging Measurements