J Korean Ophthalmol Soc.
2014 Sep;55(9):1272-1276. 10.3341/jkos.2014.55.9.1272.
Optic Canal Location Using Computed Tomography (CT)
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. shbaek6534@korea.ac.kr
- 2Department of Ophthalmology, Dongguk University Ilsan Hospital, Dongguk University College of Medicine, Goyang, Korea.
- 3Nune Eye Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2217108
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/jkos.2014.55.9.1272
Abstract
- PURPOSE
In this study we evaluated the location and shape of the optic canal using computed tomography (CT) for diagnosis and treatment of posterior orbital diseases.
METHODS
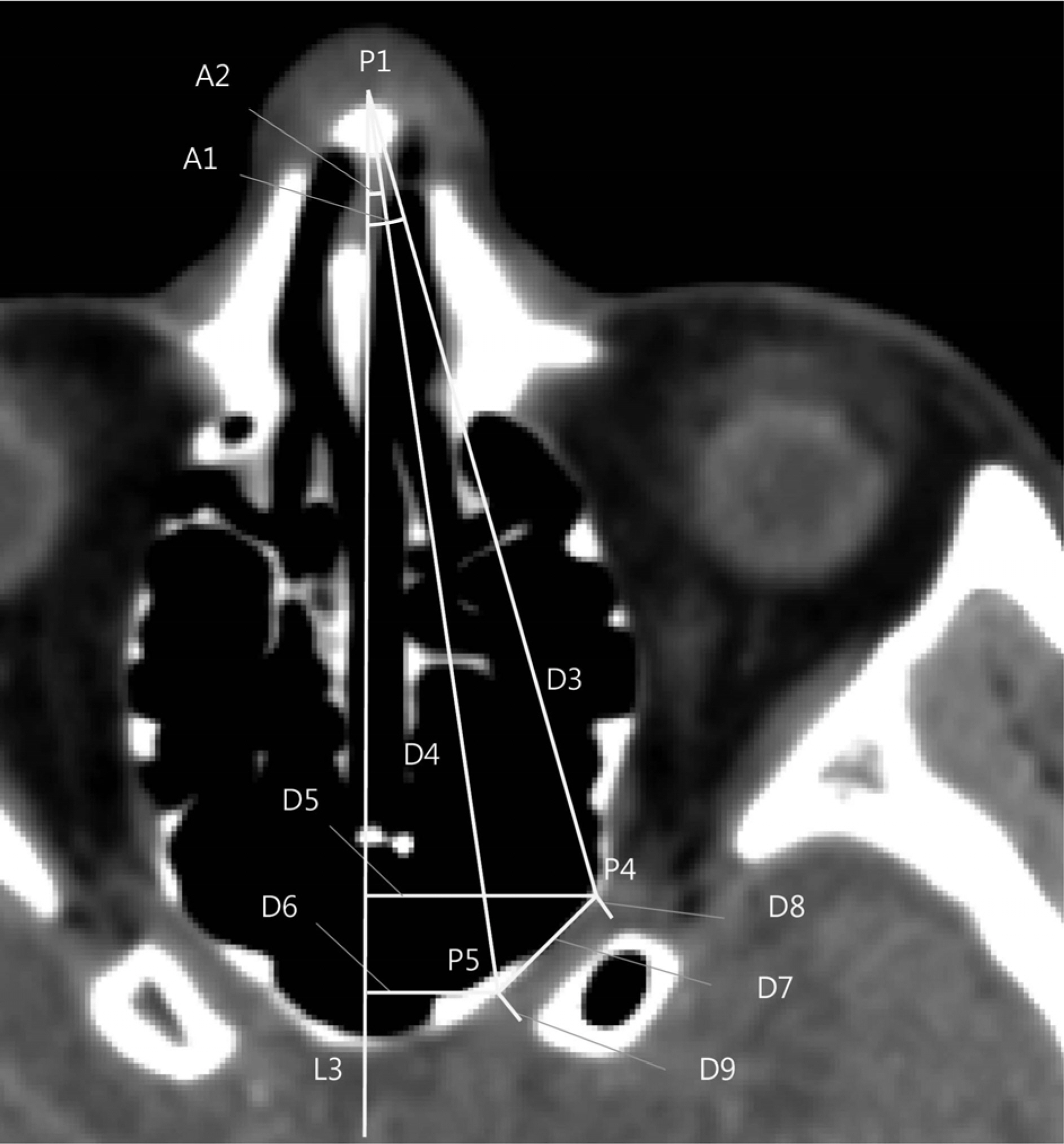
Fifty patients, who had received a facial bone CT between November 2012 and June 2013 at Korea University Hospital were included in the present study. The location and shape of the optic canal was evaluated using 9 parameters on CT (P1: nasal bone tip; P2: middle point of tuberculum sellae; P3: root of columella nasi; P4: orbit end of the optic canal; P5: cranium end or the optic canal; P6: P1's projection on L2; L1: line that links P1 and P2; L2: goes through P3 and parallel to L1; L3: bisector of right and left and goes through P1).
RESULTS
The distance between P3 and P4 was 81.5 mm and 75.6 mm in males and females, respectively (p = 0.001). The distance between P3 and P5 was 88.5 mm and 82.1 mm in, males and females, respectively (p = 0.001). The width of the orbital end and cranium end of the optic canal, the length of the optic canal was 2.4 mm, 4.1 mm, 10.9 mm in males and 2.3 mm, 3.6 mm, 10.2 mm, in females, respectively.
CONCLUSIONS
By determining the location and shape of the optic canal, these results can facilitate endoscopic approaches to diagnose and manage posterior orbital diseases as well as manage and prevent disorders associated with the optic canal.
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Hart CK, Theodosopoulos PV, Zimmer LA. Anatomy of the optic canal: a computed tomography study of endoscopic nerve decompression. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 2009; 118:839–44.
Article2. Hart CK, Zimmer LA. Computed tomography anatomy of the optic canal. Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery. 2008; 139:74.
Article3. Zhang J, Liao J, Yang Y, et al. [Applied anatomy study of optic canal by transnasal endoscopy]. Lin Chung Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2009; 23:346–8.4. Metson R, Pletcher SD. Endoscopic orbital and optic nerve decompression. Otolaryngol Clin North Am. 2006; 39:551–61. ix.
Article5. Akdemir G, Tekdemir I, Altin L. Transethmoidal approach to the optic canal: surgical and radiological microanatomy. Surg Neurol. 2004; 62:268–74. discussion 274.
Article6. Locatelli M, Caroli M, Pluderi M, et al. Endoscopic transsphenoidal optic nerve decompression: an anatomical study. Surg Radiol Anat. 2011; 33:257–62.
Article7. Liu S, Chen Y, Song J, et al. Optic canal location by computed tomography. J Craniofac Surg. 2013; 24:284–6.
Article8. Liu X, Zhou C, Zhang G, et al. [CT anatomic measurement of the optic canal and its clinical significance]. Zhonghua Er Bi Yan Hou Ke Za Zhi. 2000; 35:275–7.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- High Dose Steroid and Optic Canal Decompression in the Treatment of Traumatic Optic Neuropathy
- The remodeling of the posterior edentulous mandible as illustrated by computed tomography
- Clinical Evaluation of Treatment of the Optic Nerve Damage
- Assessment of the relationship between the mandibular third molar and the mandibular canal using panoramic radiograph and cone beam computed tomography
- A cone-beam computed tomography study of the prevalence and location of the second mesiobuccal root canal in maxillary molars