J Korean Ophthalmol Soc.
2014 Nov;55(11):1714-1720. 10.3341/jkos.2014.55.11.1714.
A Case of Double Depressor Palsy due to Bilateral Thalamic Infarction
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, Maryknoll Medical Center, Busan, Korea. pearlsj@hanmail.net
- 2Department of Ophthalmology, Kosin University Gospel Hospital, Kosin University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea.
- KMID: 2216624
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/jkos.2014.55.11.1714
Abstract
- PURPOSE
We report a rare case of double depressor palsy after bilateral thalamus infarction.
CASE SUMMARY
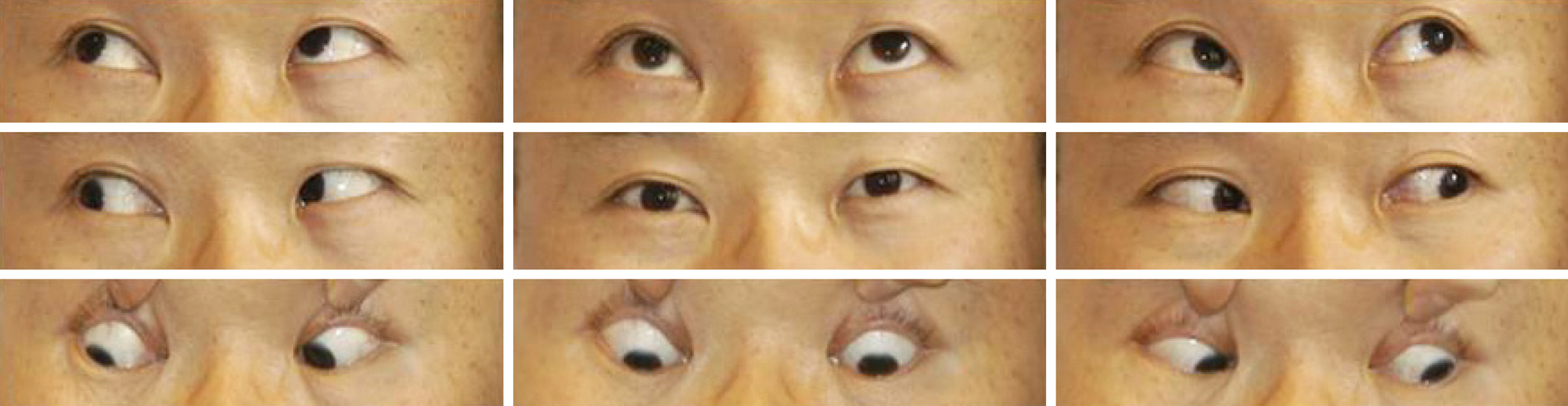
A 47-year-old male presented with complaints of diplopia upon awakening. He had atrial fibrillation, mitral valve regurgitation, aortic valve regurgitation and a history of spleen infarction 1 year prior. His right eye was hypertrophic and right eye downgaze was limited unilaterally of equal degree in adduction and abduction. Right eye horizontal and upward movements were intact. Left eye movement was intact in all directions. Pupillary light reflex response and convergence test were normal. Nystagmus was not observed. The patient was diagnosed with double depressor palsy of the right eye. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) of the brain showed an old infarction of the left thalamus and diffusion MRI showed acute infarction of the right thalamus. The patient's daily warfarin dose was 2 mg and was increased to 5 mg with cilostazol 75 mg two times a day. Seven weeks later, the patient's ocular movement revealed near normal muscle action and, subjectively, the patient was diplopia-free.
CONCLUSIONS
Double depressor palsy is a extremely rare disease and can be caused by bilateral thalamic infarction.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Rosenbaum AL, Santiago AP. Clinical strabismus management: principles and surgical techniques. Philadelphia: W.B. Saunders Company;1999; 223. 280, 389-90.2. Congress of pediatric ophthalmology and strabismus. Current concepts in strabismus. 3rd ed.Seoul: Naewae-haksool;2013; 281–319. 342-8.3. Gentilini M, De Renzi E, Crisi G. Bilateral paramedian thalamic artery infarcts: report of eight cases. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1987; 50:900–9.
Article4. Green JP, Nancy JN, Jacqueline SW. Paralysis of downgaze in two patients with clinical-radiologic correlation. Arch Ophthalmol. 1993; 111:219–22.
Article5. Halmagyi GM, Evans WA, Hallinan JM. Failure of downward gaze: the site and nature of the lesion. Arch Neurol. 1978; 35:22–6.6. Jacobs L, Anderson PJ, Bender MB. The lesions producing paralysis of downward but not upward gaze. Arch Neurol. 1973; 28:319–23.
Article7. Jacobs L, Heffner RR Jr, Newman RP. Selective paralysis of downward gaze caused by bilateral lesions of the mesencephalic periaqueductal gray matter. Neurology. 1985; 35:516–21.
Article8. Kim JS, Hwang JM. Clinical neuro-ophthalmology. Seoul: E-public. 2010; chap. 5.9. Lee WT, Park KA. Medical neuroanatomy. 2nd ed.Seoul: Korea medical books publisher;2008. p. 439.10. Bae CS, Baek SY, Cho HJ, et al. Core text of neuroanatomy. Seoul: Ko Moon Sa;1993. p. 241–80.11. Lazzaro NA, Wright B, Castillo M, et al. Artery of percheron infarction: imaging patterns and clinical spectrum. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2010; 31:1283–9.
Article12. Castaigne P, Lhermitte F, Buge A, et al. Paramedian thalamic and midbrain infarct: clinical and neuropathological study. Ann Neurol. 1981; 10:127–48.13. Aziz RN, Apio CM, Fernando MB, et al. The posterior thalamoperforating artery (the main perforating trunk from P1) micro-surgical study. J Bras Neurocirurg. 1992; 3:103–7.14. George AE, Raybaud C, Salamon G, Kricheff II. Anatomy of the thalamoperforating arteries with special emphasis on arteriography of the third ventricle: Part I. Am J Roentgenol Radium Ther Nucl Med. 1975; 124:220–30.
Article15. Saeki N, Rhoton AL Jr. Microsurgical anatomy of the upper basilar artery and the posterior circle of Willis. J Neurosurg. 1977; 46:563–78.
Article16. Park SQ, Bae HG, Yoon SM, et al. Morphological characteristics of the thalamoperforating arteries. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2010; 47:36–41.
Article17. Heubner. Zur topographie der Ernährungsgabiete der einzelnen hirnarterien. Zbl Med Wiss. 1872; 52:817–21.18. Duret H. Recherches anatomiques sur la circulation de l'encéphale. Arch Phys Norm Path. 1874; 1:60–91.19. Westberg G. Arteries of the basal ganglia. Acta radiol. 1966; 5:581–96.
Article20. Percheron G. The anatomy of the arterial supply of the human thalamus and its use for the interpretation of the thalamic vascular pathology. Z Neurol. 1973; 205:1–13.
Article21. Shea YF, Lin OY, Chang RS, Luk JK. Artery of Percheron infarction. Hong Kong Med J. 2012; 18:446.e1–2.22. Pal S, Ferguson E, Madill SA, Al-Shahi Salman R. Neurological picture. Double depressor palsy caused by bilateral paramedian thalamic infarcts. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2009; 80:1328–9.23. Ozdemir N, Haciyakupoğlu S, Ersöz TR, et al. Down gaze palsy due to periaqueductal lesion diagnosed by magnetic resonance imaging. Ophthalmologica. 1995; 209:225–7.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Acute Pseudobulbar Palsy After Bilateral Paramedian Thalamic Infarction: A Case Report
- Two Cases of Bilateral Thalamic Infarction
- Asymmetric Asterixis Induced by Phenytoin in a Patient with Thalamic Infarction
- Bilateral Thalamic Infarction Related to Artery of Percheron with Microembolic Signal
- A Case of Ocular Myasthenia Gravis Presenting as Double Depressor Palsy