J Korean Ophthalmol Soc.
2012 Jul;53(7):1027-1029. 10.3341/jkos.2012.53.7.1027.
A Case of Eyelid Steatocystoma
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. resourceful@hanmail.net
- 2Department of Ophthalmology, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Ophthalmology, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea.
- 4Department of Pathology, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea.
- 5Department of Ophthalmology, Seoul Metropolitan Government-Seoul National University Boramae Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2215864
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/jkos.2012.53.7.1027
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To report a case of eyelid steatocystoma.
CASE SUMMARY
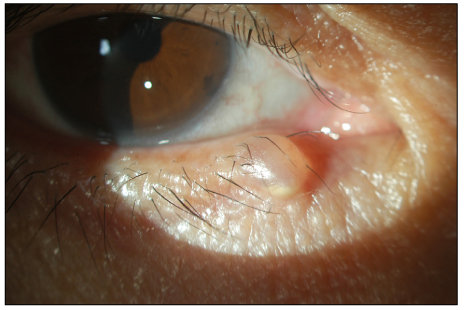
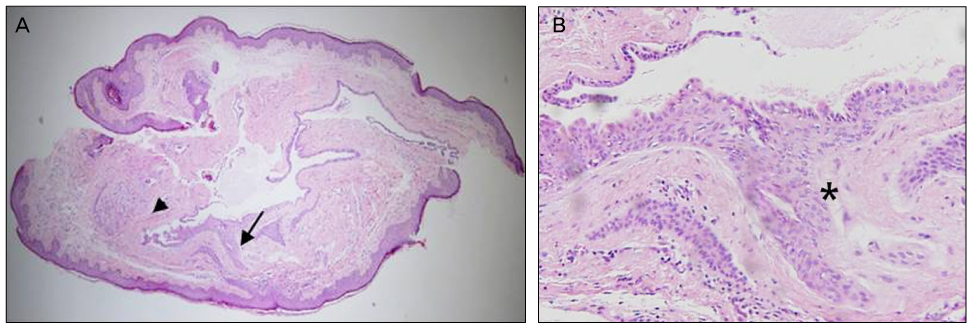
A 65-year-old woman presented with a mass around the punctum in the right lower eyelid margin, which developed several years earlier. The mass was a light yellowish cystic nodule and there were no other ocular abnormalities. Under local anesthesia, the mass was completely excised. Histopathologic examination showed a cyst surrounded by stratified squamous epithelium and a sebaceous duct which entered the hair follicle, compatible with the diagnosis of steatocystoma.
CONCLUSIONS
Steatocystoma should be considered as a differential diagnosis of a solitary cystic eyelid tumor.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 3 articles
-
A Case of Steatocystoma Simplex and Sebaceous Gland Hyperplasia of the Bilateral Lacrimal Caruncle
Junkyu Chung, Shin-Myeong Choi, Ji Sang Han, Jae-Ho Shin, Tae Gi Kim
J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2018;59(9):871-875. doi: 10.3341/jkos.2018.59.9.871.Removal of Eyelid Epidermal Cyst Using High-Frequency Radio-Wave Electrosurgery
Jong Yeop Park, Ho Chang Kim, Eok Soo Suh
J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2014;55(12):1727-1733. doi: 10.3341/jkos.2014.55.12.1727.A Case of Steatocystoma Simplex of the Orbit
Yu jeong Kim, Yong Shick Lee, Mi jung Chi
J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2015;56(11):1794-1797. doi: 10.3341/jkos.2015.56.11.1794.
Reference
-
1. Requena L, Sánchez Yus E. Follicular hybrid cysts. An expanded spectrum. Am J Dermatopathol. 1991. 13:228–233.2. Brownstein MH. Steatocystoma simplex. A solitary steatocystoma. Arch Dermatol. 1982. 118:409–411.3. Plewig G, Wolff HH, Braun-Falco O. Steatocystoma multiplex: anatomic reevaluation, electron microscopy, and autoradiography. Arch Dermatol Res. 1982. 272:363–380.4. Procianoy F, Golbert MB, Golbspan L, et al. Steatocystoma simplex of the eyelid. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg. 2009. 25:147–148.5. Tirakunwichcha S, Vaivanijkul J. Steatocystoma simplex of the eyelid. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg. 2009. 25:49–50.6. Nakamura S, Nakayama K, Hoshi K, Onda S. A case of steatocystoma simplex on the head. J Dermatol. 1988. 15:347–348.7. Kim NJ, Moon KC, Khwarg SI. Steatocystoma simplex of the caruncle. Can J Ophthalmol. 2006. 41:83–85.8. Pamoukian VN, Westreich M. Five generations with steatocystoma multiplex congenita: a treatment regimen. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1997. 99:1142–1146.9. Feinstein A, Friedman J, Schwach-Millet M. Pachyonychia congenita. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1988. 19:705–711.