J Korean Ophthalmol Soc.
2015 Apr;56(4):573-579. 10.3341/jkos.2015.56.4.573.
Evaluation of Prognostic Factors and Outcomes of Single-Stage Adjustable Strabismus Surgery in Thyroid Eye Disease
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Ophthalmology, Dongtan Sacred Heart Hospital, Hallym University College of Medicine, Hwaseong, Korea. soolienah99@naver.com
- KMID: 2215708
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/jkos.2015.56.4.573
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To evaluate the prognostic factors that contribute to favorable surgical outcomes of single-stage adjustable strabismus surgery in thyroid eye disease.
METHODS
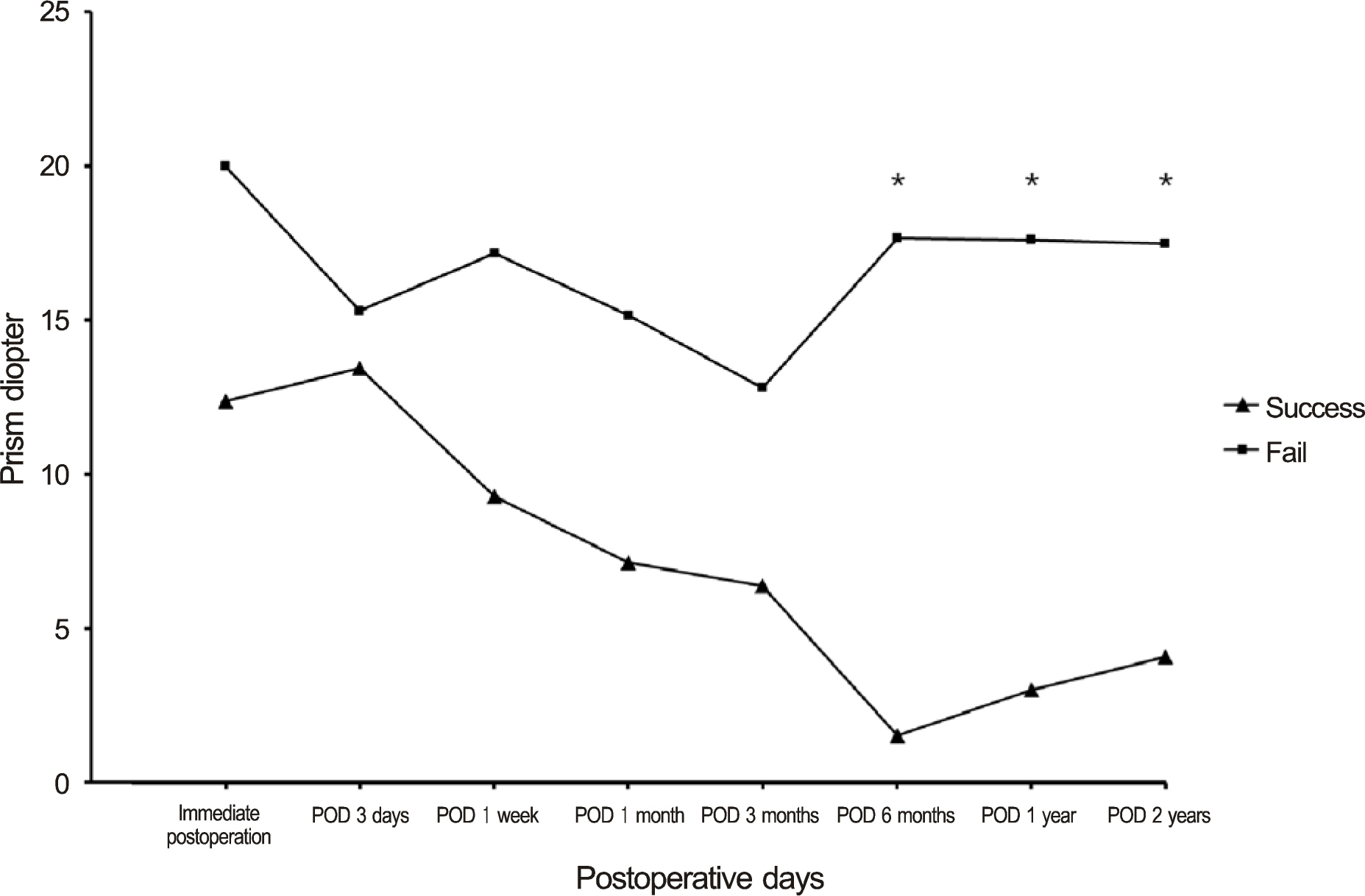
Retrospective review of clinical case notes were done of all patients who had surgical treatment for strabismus related to thyroid eye disease under the care of a single hospital between January 2005 and December 2012 (n = 30). Factors that possibly influenced the outcome were statistically analyzed for significance. "Successful" surgical outcome was defined as patients whose residual deviation was within 8 prism diopters and free from diplopia in the primary position on postoperative 1 year.
RESULTS
Mean preoperative vertical deviation was 17.5 prism diopters (PD) and horizontal deviation was 20.3 PD. Mean follow-up time was 12.4 months. Twenty-four patients (80.0%) had successful surgical results. Four patients (13.3%) needed further surgery due to recurrence of previous strabismus and two patients (6.7%) needed prism glasses due to remaining strabismus. Previous history of proptosis (p = 0.02), optic neuropathy (p = 0.01), intravenous (IV) steroid pulse therapy (p = 0.02), number of times of IV steroid pulse therapy (p = 0.01), and orbital decompression surgery (p = 0.03) were different between success and failure groups.
CONCLUSIONS
Single-stage adjustable strabismus surgery under topical anesthesia showed a success rate of 80% for strabismus patients with thyroid eye disease. Patients who previously had proptosis, optic neuropathy, IV steroid pulse therapy, and orbital decompression surgery significantly showed unsuccessful results after strabismus surgery.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Rajendram R, Bunce C, Adams GG, et al. Smoking and strabismus surgery in patients with thyroid eye disease. Ophthalmology. 2011; 118:2493–7.
Article2. Nassar MM, Dickinson AJ, Neoh C, et al. Parameters predicting outcomes of strabismus surgery in the management of Graves' ophthalmopathy. J AAPOS. 2009; 13:236–40.
Article3. Schotthoefer EO, Wallace DK. Strabismus associated with thyroid eye disease. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2007; 18:361–5.
Article4. Mills MD, Coats DK, Donahue SP, Wheeler DT; American Academy of Ophthalmology. Strabismus surgery for adults: a report by the American Academy of Ophthalmology. Ophthalmology. 2004; 111:1255–62.5. Scott WE, Thalacker JA. Diagnosis and treatment of thyroid myopathy. Ophthalmology. 1981; 88:493–8.
Article6. Choy YJ, Park SE. To compare long-term follow-up adjustable and nonadjustable surgery success rates in horizontal strabismus surgery. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2012; 53:316–22.
Article7. Koc F, Durlu N, Ozal H, et al. Single-stage adjustable strabismus surgery under topical anesthesia and propofol. Strabismus. 2005; 13:157–61.
Article8. Rauz S, Govan JA. One stage vertical rectus muscle recession using adjustable sutures under local anaesthesia. Br J Ophthalmol. 1996; 80:713–8.
Article9. Sharma P, Reinecke RD. Single-stage adjustable strabismus surgery for restrictive strabismus. J AAPOS. 2003; 7:358–62.
Article10. Zou L, Liu R, Liu H, et al. Single-stage surgery for symptomatic small-angle strabismus under topical anaesthesia. Can J Ophthalmol. 2014; 49:222–7.
Article11. Karaba VL, Elibol O. One-stage vs. two-stage adjustable sutures for the correction of esotropia. Strabismus. 2004; 12:27–34.
Article12. Looi AL, Luu CD, Wong TY, et al. Factors associated with decompression and strabismus surgery in thyroid eye disease. Ann Acad Med Singapore. 2005; 34:154–7.13. Ruttum MS. Effect of prior orbital decompression on outcome of strabismus surgery in patients with thyroid ophthalmopathy. J AAPOS. 2000; 4:102–5.
Article14. Goldberg RA. The evolving paradigm of orbital decompression surgery. Arch Ophthalmol. 1998; 116:95–6.
Article15. Gilbert J, Dailey RA, Christensen LE. Characteristics and outcomes of strabismus surgery after orbital decompression for thyroid eye disease. J AAPOS. 2005; 9:26–30.
Article16. Kim MH, Park KA, Oh SY. The effect of previous orbital decompression on results of strabismus surgery in patients with Graves' ophthalmopathy. J AAPOS. 2013; 17:188–91.
Article17. Oh HS, Chang YH, Lee JB. Strabismus surgery for thyroid ophthalmopathy. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2002; 43:1718–23.18. Peragallo JH, Velez FG, Demer JL, Pineles SL. Postoperative drift in patients with thyroid ophthalmopathy undergoing unilateral inferior rectus muscle recession. Strabismus. 2013; 21:23–8.
Article19. Kraus DJ, Bullock JD. Treatment of thyroid ocular myopathy with adjustable and nonadjustable suture strabismus surgery. Trans Am Ophthalmol Soc. 1993; 91:67–79. discussion 79-84.20. Gardner TA, Kennerdell JS. Treatment of dysthyroid myopathy with adjustable suture recession. Ophthalmic Surg. 1990; 21:519–21.
Article21. Zhang MS, Hutchinson AK, Drack AV, et al. Improved ocular alignment with adjustable sutures in adults undergoing strabismus surgery. Ophthalmology. 2012; 119:396–402.
Article22. Kushner BJ. An evaluation of the semiadjustable suture strabismus surgical procedure. J AAPOS. 2004; 8:481–7.
Article23. Park JM, Kim JH, Lee SJ, Choi HY. Surgical results of intraoperative adjustable suture strabismus surgery under local anesthesia. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2007; 48:405–10.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Strabismus Surgery for Thyroid Ophthalmopathy
- The Effect of Intraoperative Adjustable Suture Strabismus Surgery in Adult Strabismus Patients
- Effects of 5-Fluorouracil on Delayed Adjustment in Experimental Strabismus Surgery
- Relationship between Thyrotropin Binding Inhibitory Immunoglobulin and Strabismus-associated Thyroid Eye Disease Stability
- The Effect of Cyclosporin A on Delayed Adjustable Strabismus Surgery in Rabbits