J Korean Ophthalmol Soc.
2011 Dec;52(12):1455-1460. 10.3341/jkos.2011.52.12.1455.
Diverse Types of Glaucoma in Patients with Pseudoexfoliation Syndrome: Normal Pressure Glaucoma
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, Hallym University College of Medicine, Anyang, Korea. eyechung90@hanmail.net
- KMID: 2215149
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/jkos.2011.52.12.1455
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To evaluate the types of glaucoma in patients with pseudoexfoliation syndrome (PXS) and analyze the glaucomatous changes in patients with normal intraocular pressure (IOP).
METHODS
A retrospective chart analysis of patients diagnosed with PXS was performed. The types of glaucoma were classified based on the IOP, optic disc examination, visual field test results, and optical coherence tomography (OCT) results. Other than those with pseudoexfoliative glaucoma (PXG), the normal IOP patients with PXS were divided into glaucomatous and non-glaucomatous groups. Later, the glaucomatous group was clinically compared to the non-glaucomatous group.
RESULTS
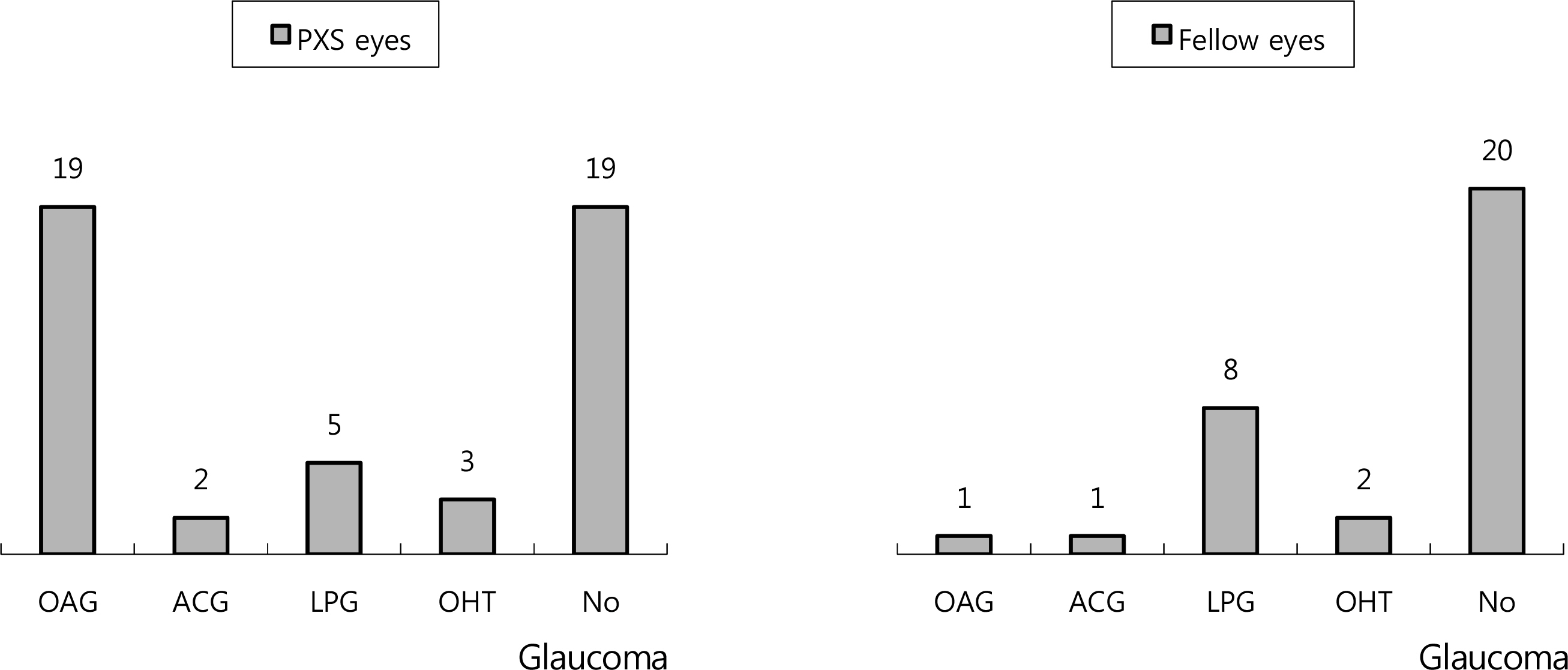
The records of 40 patients with PXS were evaluated. Among the 48 PXS eyes, high pressure glaucoma was found in 21 eyes (43.75%), low pressure glaucoma in 5 eyes (10.42%), and non-glaucoma in 19 eyes (39.58%). However, in the 32 fellow eyes without PXS, 2 eyes (6.25%), 8 eyes (25%), and 20 eyes (62.5%) showed the above diseases, respectively. In result, PXS affected the glaucomatous change (odds ratio = 2.544, p = 0.045). By contrast, in PXS patients with normal IOP, PXS did not affect the glaucomatous change (p = 0.519).
CONCLUSIONS
Diverse types of glaucoma including low pressure glaucoma may exist in patients with PXS. Considering the possibility of low pressure glaucoma in patients with PXS is necessary.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 3 articles
-
Comparison of Anterior Segment Features between Groups with or without Glaucoma in Pseudoexfoliation Syndrome
Bon Hyeok Gu, Sangkyung Choi
J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2018;59(11):1049-1055. doi: 10.3341/jkos.2018.59.11.1049.Central Corneal Thickness and Corneal Endothelial Cells in Pseudoexfoliation Syndrome
In Boem Chang, Dong Won Paik, Tai Jin Kim, Hyo Shin Ha, Jung Hyun Park
J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2013;54(7):1060-1065. doi: 10.3341/jkos.2013.54.7.1060.Central Corneal Thickness in Korean Subjects with Primary Angle-Closure Glaucoma
In Boem Chang, Min Byung Chae, Jung Hyun Park, Tai Jin Kim, Jae Suk Kim
J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2014;55(3):402-407. doi: 10.3341/jkos.2014.55.3.402.
Reference
-
References
1. Jeng SM, Karger RA, Hodge DO, et al. The risk of glaucoma in pseudoexfoliation syndrome. J Glaucoma. 2007; 16:117–21.
Article2. Ritch R, Schlötzer-Schrehardt U. Exfoliation syndrome. Surv Ophthalmol. 2001; 45:265–315.
Article3. Kozart DM, Yanoff M. Intraocular pressure status in 100 consecutive patients with exfoliation syndrome. Ophthalmology. 1982; 89:214–8.
Article4. Henry JC, Krupin T, Schmitt M, et al. Long-term followup of pseudoexfoliation and the development of elevated intraocular pressure. Ophthalmology. 1987; 94:545–52.
Article5. Aasved H. Intraocular pressure in eyes with and without fi-brillopathia epitheliocapsularis (so-called senile exfoliation or pseudoexfoliation). Acta Ophthalmol(Copenh). 1971; 49:601–10.6. Cashwell LF Jr, Shields MB. Exfoliation syndrome. Prevalence in a southeastern United States population. Arch Ophthalmol. 1988; 106:335–6.
Article7. Hiller R, Sperduto RD, Krueger DE. Pseudoexfoliation, intraocular pressure, and senile lens changes in a population-based survey. Arch Ophthalmol. 1982; 100:1080–2.
Article8. Kivelä T, Hietanen J, Uusitalo M. Autopsy analysis of clinically unilateral exfoliation syndrome. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1997; 38:2008–15.9. Layden WE, Shaffer RN. Exfoliation syndrome. Am J Ophthalmol. 1974; 78:835–41.
Article10. Roth M, Epstein DL. Exfoliation syndrome. Am J Ophthalmol. 1980; 89:477–81.
Article11. Brooks AM, Gillies WE. The presentation and prognosis of glaucoma in pseudoexfoliation of the lens capsule. Ophthalmology. 1988; 95:271–6.
Article12. Gillies WE, Brooks AM. The presentation of acute glaucoma in pseudoexfoliation of the lens capsule. Aust N Z J Ophthalmol. 1988; 16:101–6.
Article13. Choi J, Park KH. Clinical characteristics of Korean patients with pseudoexfoliation syndrome. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2006; 47:577–86.14. Koz OG, Turkcu MF, Yarangumeli A, et al. Normotensive glaucoma and risk factors in normotensive eyes with pseudoexfoliation syndrome. J Glaucoma. 2009; 18:684–8.
Article15. Puska P, Vesti E, Tomita G, et al. Optic disc changes in normotensive persons with unilateral exfoliation syndrome: a 3-year followup study. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 1999; 237:457–62.
Article16. Yarangümeli A, Davutluoglu B, Köz OG, et al. Glaucomatous damage in normotensive fellow eyes of patients with unilateral hypertensive pseudoexfoliation glaucoma: normotensive pseudoexfoliation glaucoma? Clin Experiment Ophthalmol. 2006; 34:15–9.17. Anderson DR. Automated Static Perimetry. St. Louis: Mosby Year Book;1992. p. 123.18. Slagsvold JE. The followup in patients with pseudoexfoliation of the lens capsule with and without glaucoma. 2. The development of glaucoma in persons with pseudoexfoliation. Acta Ophthalmol (Copenh). 1986; 64:241–5.19. Yüksel N, Karabaş VL, Arslan A, et al. Ocular hemodynamics in pseudoexfoliation syndrome and pseudoexfoliation glaucoma. Ophthalmology. 2001; 108:1043–9.
Article20. Ocakoglu O, Koyluoglu N, Kayiran A, et al. Microvascular blood flow of the optic nerve head and peripapillary retina in unilateral exfoliation syndrome. Acta Ophthalmol Scand. 2004; 82:49–53.
Article21. Pena JD, Netland PA, Vidal I, et al. Elastosis of the lamina cribrosa in glaucomatous optic neuropathy. Exp Eye Res. 1998; 67:517–24.
Article22. Borazan M, Karalezli A, Kucukerdonmez C, et al. Aqueous humor and plasma levels of vascular endothelial growth factor and nitric oxide in patients with pseudoexfoliation syndrome and pseudoexfoliation glaucoma. J Glaucoma. 2010; 19:207–11.
Article23. Altintaş O, Yüksel N, Karabaş VL, Qağ lar Y. Diurnal intraocular pressure variation in pseudoexfoliation syndrome. Eur J Ophthalmol. 2004; 14:495–500.
Article24. Nenciu A, Stefan C, Melinte D, et al. IOP diurnal fluctuations in patients presenting pseudoexfoliative syndrome. Oftalmologia. 2006; 50:121–5.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Cases of Pseudophakic Pseudoexfoliation in Glaucoma Patients
- Association with Systemic and Ophthalmic Disease in Korean Pseudoexfoliation Syndrome Patients
- Comparison of Serum Homocysteine, Vitamin B12, Vitamin B6 and Folate Levels in Different Glaucoma Types
- Comparison of Anterior Segment Features between Groups with or without Glaucoma in Pseudoexfoliation Syndrome
- Refractive Outcomes of Uneventful Cataract Surgery in Pseudoexfoliation Syndrome and Pseudoexfoliation Glaucoma