J Korean Ophthalmol Soc.
2011 Aug;52(8):910-915. 10.3341/jkos.2011.52.8.910.
Botulinum Toxin A Treatment for Patients with Periorbital Spasm after Facial Nerve Paresis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, Bundang CHA Medical Center, CHA University, Seongnam, Korea. eye@cha.ac.kr
- KMID: 2214766
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/jkos.2011.52.8.910
Abstract
- PURPOSE
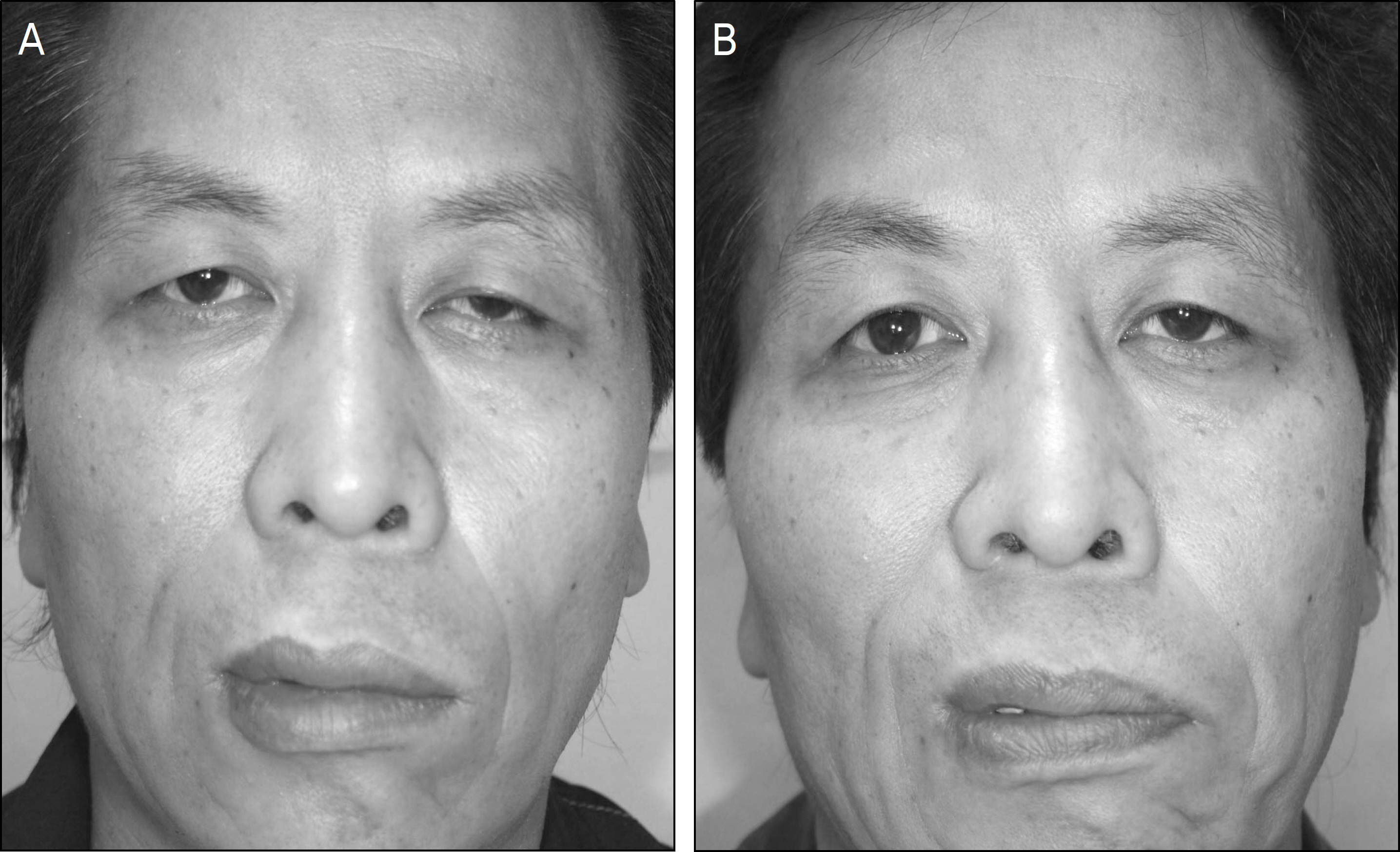
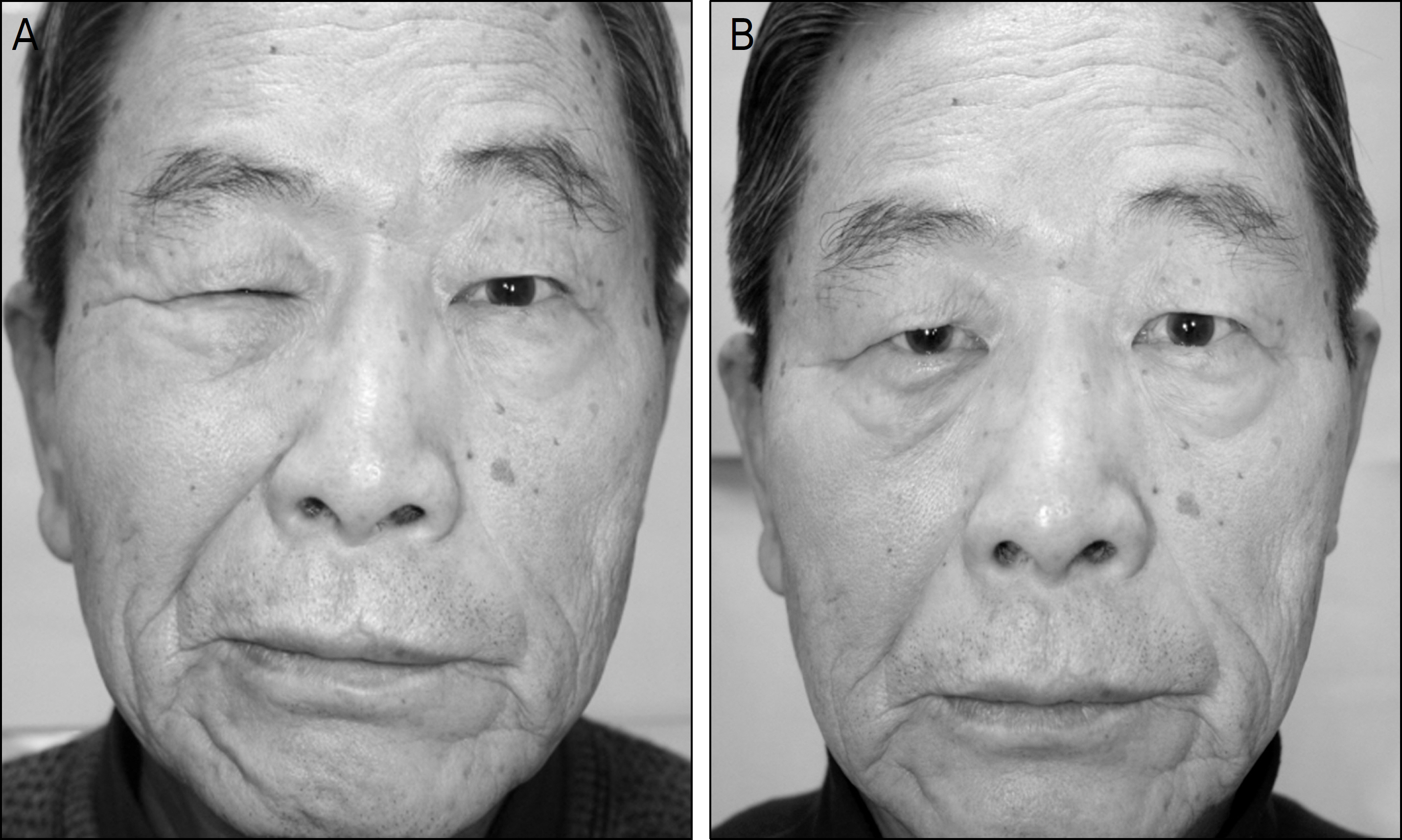
To evaluate clinical features of periorbital spasm and facial asymmetry in the patients who recovered poorly from Bell's palsy and facial trauma and to investigate the effect of Botulinum toxin A as a treatment for periorbital spasm and facial asymmetry.
METHODS
Between November 2001 and January 2010, Botulinum toxin injection was performed in 17 patients who had blepharospasm and facial asymmetry following poor recovery from facial palsy. The past history, trauma history, clinical manifestation of blepharospasm, Botulinum toxin A injection dose, injection site, frequency of injection, and duration of effect was evaluated. Data was analyzed using the Mann-Whitney U test, SPSS 12.0.
RESULTS
The mean number of injections was 2.7 +/- 2.4 times and the mean dose per injection unit was 12.2 +/- 1.2 units. The Botulinum toxin effect lasted 6.9 +/- 5.5 months in Bell's palsy patients, and 8.0 +/- 4.2 months in trauma patients. There was no significant difference between the 2 groups. Most patients reported improvement of periorbital spasm and facial asymmetry. After treatment, 1 patient complained of epiphora and 1 patient complained of ptosis; conservative treatment was performed for these patients.
CONCLUSIONS
Blepharospasm can be treated and a cosmetic improvement in facial symmetry can be achieved by Botulinum toxin A injection in the patients who recover poorly from facial palsy.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Choi D, Dunn LT. Facial nerve repair and regeneration: an overview of basic principles for neurosurgeons. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2001; 143:107–14.2. Wang HC, Lu CH, Lee RJ, et al. Post-traumatic hemifacial spasm. J Clin Neurosci. 2006; 13:681–3.
Article3. Borodic G, Bartley M, Slattery W, et al. Botulinum toxin for aberrant facial nerve regeneration: double-blind, placebo-controlled trial using subjective endpoints. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2005; 116:36–43.
Article4. Scott AB, Kennedy RA, Stubbs HA. Botulinum A toxin injection as a treatment for blepharospasm. Arch Ophthalmol. 1985; 103:347–50.
Article5. Lee HD, Jang JW, Lee SY. Management of essential blepharospasm: botulinum toxin a treatment and orbicularis myectomy operation. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1999; 40:3246–52.6. Borodic GE, Pearce LB, Cheney M, et al. Botulinum A toxin for treatment of aberrant facial nerve regeneration. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1993; 91:1042–5.
Article7. Putterman AM. Botulinum toxin injections in the treatment of sev-enth nerve misdirection. Am J Ophthalmol. 1990; 110:205–6.
Article8. Mehta RP, Hadlock TA. Botulinum toxin and quality of life in patients with facial paralysis. Arch Facial Plast Surg. 2008; 10:84–7.
Article9. Kahn JB, Gliklich RE, Boyev KP, et al. Validation of a patient-graded instrument for facial nerve paralysis: the FaCE scale. Laryngoscope. 2001; 111:387–98.
Article10. Yu SB, Lew H, Yun YS. Therapeutic effect of botulinum toxin injection in eyelid myokymia patients. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2007; 48:749–54.11. Shin JH, Jeon C, Woo KI, Kim YD. Clinical comparability of dys-port and botox in essential blepharospasm. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2009; 50:331–5.
Article12. McLoon LK, Bauer G, Wirtschafter J. Quantification of muscle loss in the doxorubicin-treated orbicularis oculi of the monkey. Effect of local injection of doxorubicin into the eyelid. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1991; 32:1667–73.13. McCord CD Jr, Coles WH, Shore JW, et al. Treatment of essential blepharospasm. I. Comparison of facial nerve avulsion and eye-brow-eyelid muscle stripping procedure. Arch Ophthalmol. 1984; 102:266–8.14. Frueh BR, Callahan A, Dortzbach RK, et al. The effects of differential section of the VIITH nerve on patients with intractable blepharospasm. Trans Sect Ophthalmol Am Acad Ophthalmol Otolaryngol. 1976; 81:595–602.15. Jones TW Jr, Waller RR, Samples JR. Myectomy for essential blepharospasm. Mayo Clin Proc. 1985; 60:663–6.
Article16. Bates AK, Halliday BL, Bailey CS, et al. Surgical management of essential blepharospasm. Br J Ophthalmol. 1991; 75:487–90.
Article17. Frueh BR, Musch DC, Bersani TA. Effects of eyelid protractor excision for the treatment of benign essential blepharospasm. Am J Ophthalmol. 1992; 113:681–6.
Article18. Anderson RL, Patrinely JR. Surgical management of blepharospasm. Adv Neurol. 1988; 49:501–20.19. Lee TS, Choi JS, Kim JS. Clinical effect of limited myectomy for the treatment of essential blepharospasm. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2004; 45:1783–9.20. Borodic GE. Orbicularis oculi myo-osseous fixation: a new treatment for benign essential blepharospasm and blepharospasm associated with diffuse facial dystonia (meige syndrome). Ophthalmic Surg Lasers Imaging. 2010; 41:360–9.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Botulinum Toxin Injection Treatment for Facial Spasm
- Electrophysiologic Study of the Hemifacial Spasm
- A clinical study on the use of botulinum toxin type a in maxillofacial area
- Botulinum Toxin A for Spasmodic Torticollis, Hemifacial Spasm and Facial Synkinesis
- The Effects of Botulinum Toxin (BTXA(R)) Dermal Injections on Facial Wrinkle Lines