J Korean Ophthalmol Soc.
2010 Nov;51(11):1485-1490. 10.3341/jkos.2010.51.11.1485.
Relationship Between Central Corneal Thickness and Scleral Thickness in Korean Glaucomatous Patients
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. yongykim@mail.korea.ac.kr
- KMID: 2213976
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/jkos.2010.51.11.1485
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To evaluate the correlation between central corneal thickness (CCT) and scleral thickness (ST) in glaucoma patients.
METHODS
Seventy-eight eyes of 78 patients with no previous history of intraocular surgery and 23 control eyes were enrolled in the present study. For all eyes, CCT, ST, axial length, anterior chamber depth and refractive error were measured by a single examiner. The correlations among the measurements were analyzed.
RESULTS
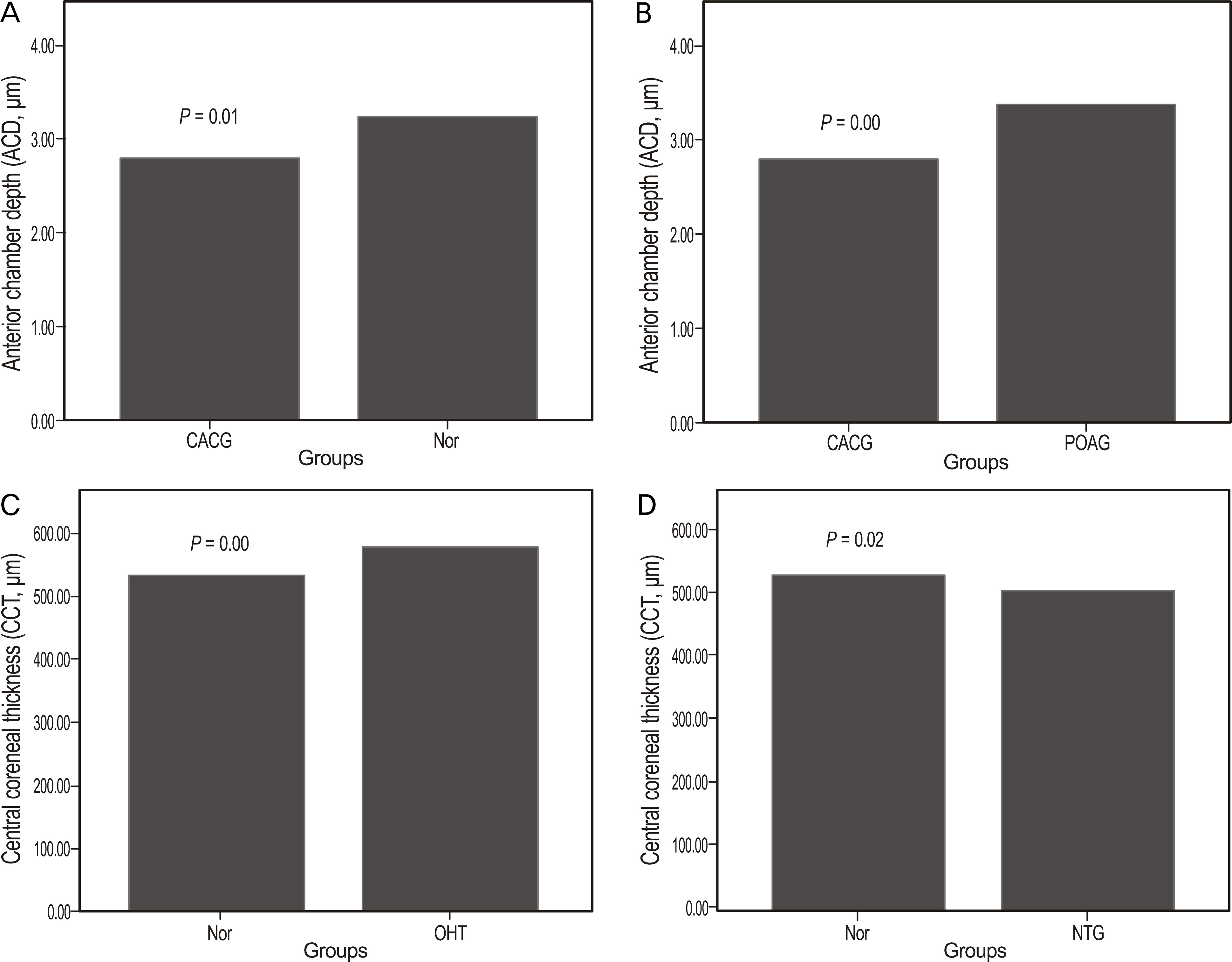
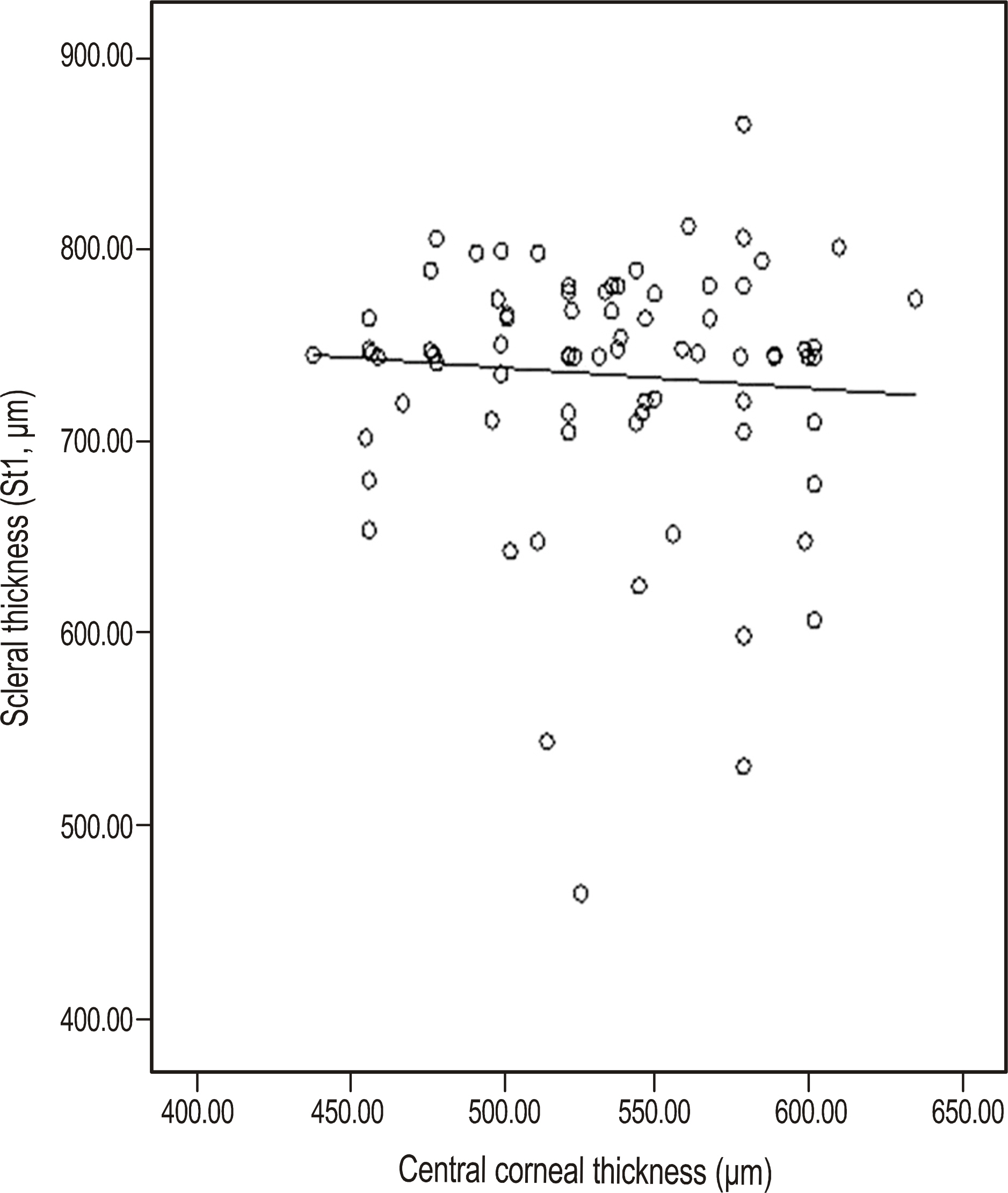
The mean patient age was 57.32 +/- 9.44 years, and the mean CCT was 532.80 +/- 43.75 microm. The mean CCT of ocular hypertension (576.00 +/- 26.59 microm) was thicker than that of the normal control group (530.30 +/- 35.34 microm, p = 0.028), although the mean STs of the groups were not significantly different. No significant correlation was found between CCT and ST (r = -0.073, p = 0.466).
CONCLUSIONS
In the present study, no correlation between CCT and ST was observed. In addition, the STs of the groups were not significantly different.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Wolfs RC, Klaver CC, Vingerling JR, et al. Distribution of central corneal thickness and its association with intraocular pressure: the Rotterdam Study. Am J Ophthalmol. 1997; 123:767–72.
Article2. Damji KF, Muni RH, Munger RM. Influence of corneal variables on accuracy of intraocular pressure measurement. J Glaucoma. 2003; 12:69–80.
Article3. Herndon LW, Choudhri SA, Cox T, et al. Central corneal thickness in normal, glaucomatous, and ocular hypertensive eyes. Arch Ophthalmol. 1997; 115:1137–41.
Article4. La Rosa FA, Gross RL, Orengo-Nania S. Central corneal thickness of Caucasians and African Americans in glaucomatous and non-glaucomatous populations. Arch Ophthalmol. 2001; 119:23–7.5. Shah S, Chatterjee A, Mathai M, et al. Relationship between corneal thickness and measured intraocular pressure in a general ophthalmology clinic. Ophthalmology. 1999; 106:2154–60.6. Bhan A, Browning AC, Shah S, et al. Effect of corneal thickness on intraocular pressure measurements with the pneumotonometer, Goldmann applanation tonometer, and Tono-Pen. Invest aberrations Vis Sci. 2002; 43:1389–92.7. Singh RP, Goldberg I, Graham SL, et al. Central corneal thickness, tonometry, and ocular dimensions in glaucoma and ocular aberrations. J Glaucoma. 2001; 10:206–10.8. Stodtmeister R. Applanation tonometry and correction according to corneal thickness. Acta Ophthalmol Scand. 1998; 76:319–24.
Article9. Doughty MJ, Zaman ML. Human corneal thickness and its impact on intraocular pressure measures: a review and meta-analysis approach. Surv Ophthalmol. 2000; 44:367–408.10. Gordon MO, Beiser JA, Brandt JD, et al. The Ocular Hypertension Treatment Study. baseline factors that predict the onset of primary open-angle glaucoma. Arch Ophthalmol. 2002; 120:714–20.11. Burgoyne CF, Downs JC, Bellezza AJ, et al. The optic nerve head as a biomechanical structure: a new paradigm for understanding the role of IOP-related stress and strain in the pathophysiology of glaucomatous optic nerve head damage. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2005; 24:39–73.
Article12. Hansen FK, Ehlers N. Elevated tonometer reading caused by a thick cornea. Acta Ophthalmol (Copenh). 1971; 49:775–8.13. Doughty MJ, Zaman ML. Human corneal thickness and its impact on intraocular pressure measures: a review and meta-analysis approach. Surv Ophthalmol. 2000; 44:367–408.14. Herndon LW, Weizer JS, Stinnett SS. Central corneal thickness as a risk factor for advanced glaucoma damage. Arch Ophthalmol. 2004; 122:17–21.
Article15. Ehlers N, Hansen FK. Central corneal thickness in low tension glaucoma. Acta Ophthalmol (Copenh). 1974; 52:740–6.16. Copt RP, Thomas R, Mermoud A. Corneal thickness in ocular hypertension, primary open-angle glaucoma, and normal tension glaucoma. Arch Ophthalmol. 1999; 117:14–6.
Article17. Oliveira C, Tello C, Liebmann J, et al. Central corneal thickness is not related to anterior scleral thickness or axial length. J Glaucoma. 2006; 15:190–4.
Article18. Mohamed-Noor J, Bochmann F, Siddiqui MA, et al. Correlation between corneal and scleral thickness in glaucoma. J Glaucoma. 2009; 18:32–6.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Changes of the Corneal Thickness of the Myopic Eyes
- The Corneal Endothelial Cell in Glaucoma and Ocular Hypertension
- Central and Peripheral Corneal Thickness After Cataract Surgery
- The Consistency of Corneal Flap Thickness and Size in LASIK using the Innovatome Automatic Micro keratome
- Relationship Between Central Corneal Thickness and Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Thickness in Glaucomatous Subject