J Korean Ophthalmol Soc.
2009 Dec;50(12):1873-1876. 10.3341/jkos.2009.50.12.1873.
The Change of Vertical Deviation in the Seated and Supine Position
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, College of Medicine, Catholic University of Daegu, Daegu, Korea. kimsy@cu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2213001
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/jkos.2009.50.12.1873
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To evaluate the change in hyperdeviation according to position change in patients with vertical strabismus.
METHODS
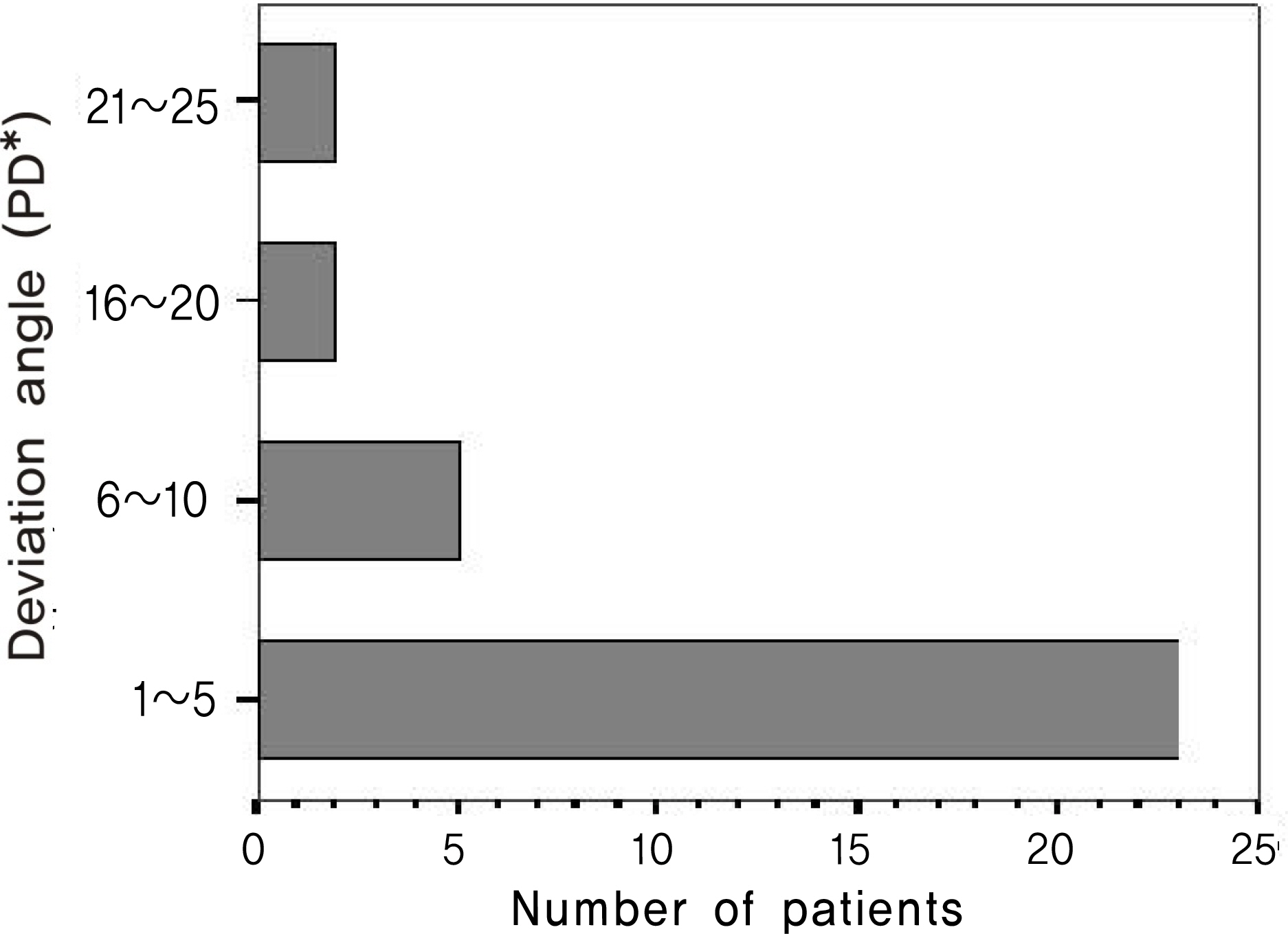
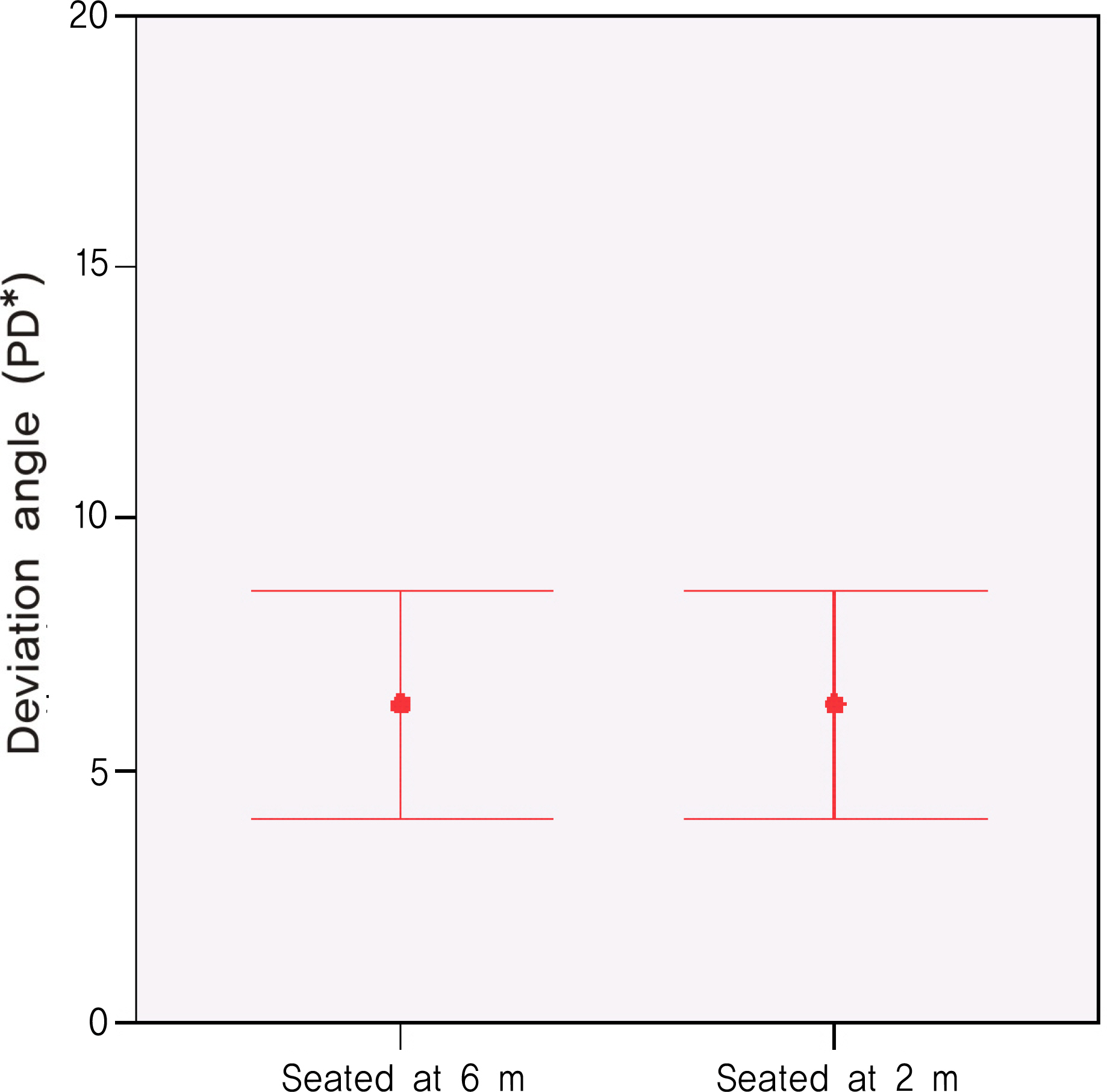
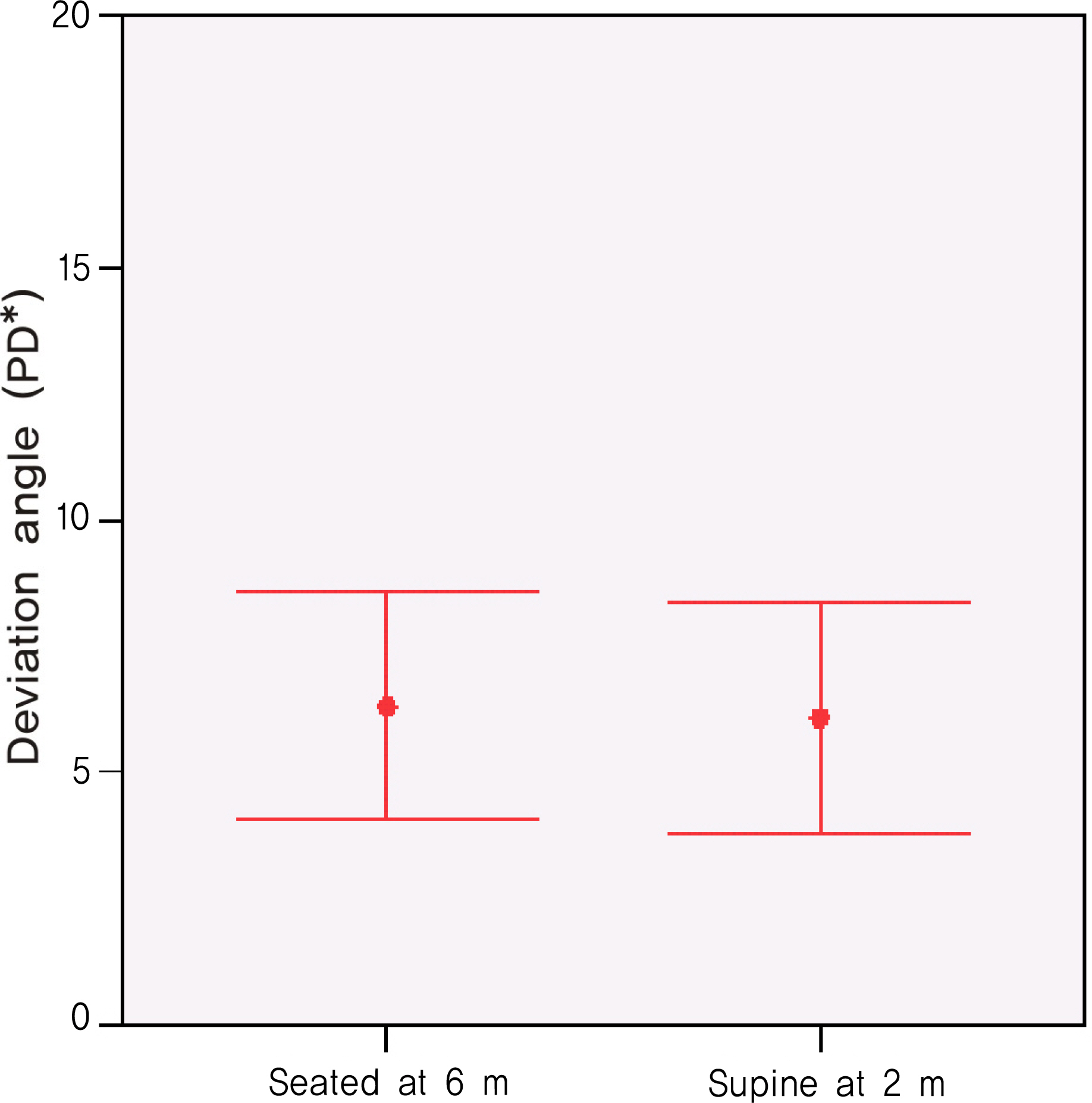
The authors measured the hyperdeviation in 32 patients with vertical strabismus at 6 m, 2 m, and 33 cm in the seated position and at 2 m and 33 cm in the supine position using the alternate prism cover test.
RESULTS
The mean amount of hyperdeviation in the seated position was 6.31+/-6.27 PD at 6 m, 6.31+/-6.27 PD at 2 m, and 3.69+/-6.65 PD at 33 cm. The mean hyperdeviation in the supine position was 6.09+/-6.37 PD at 2 m and 3.55+/-6.36 PD at 33 cm. There was no significant difference in hyperdeviation according to the change of position at the same measuring distance. No significant difference between the hyperdeviation at 6 m in the seated position and 2 m in the supine position was found (P>0.05).
CONCLUSIONS
The hyperdeviation at 6 m and 33 cm in the seated position can be replaced by hyperdeviation at 2 m and 33 cm in the supine position during adjustable suture surgery for vertical strabismus.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. von Noorden GK, Campos EC. Binocular vision and ocular motility: Theory and management of strabismus. 6th ed.St. Louis: Mosby;2002. p. 591–3.2. Jeon YH, Kim SY. The change of exodeviation in the seated and supine position. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2006; 47:264–8.3. Becker R, Krizizok TH, Wassill H. Use of preoperative assessment of positionally induced cyclotorsion: a video-oculographic study. Br J Ophthalmol. 2004; 88:417–21.
Article4. Gordes RS, Vaseghi S, Pansell T, et al. Influence of the body position to cyclorotation in healthy probands. Ophthalmologe. 2002; 99:142.5. Swami AU, Steinert RF, Osborne WE, White AA. Rotational malposition during laser in situ keratomileusis. Am J Ophthalmol. 2002; 133:561–2.
Article6. Cho HH, Sohn MA. The ocular cyclotorsion induced by the positional change. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1999; 40:2911–7.7. Jwa WB, Hong SJ, Lee JH, Lee JM. Evaluation of the ocular cyclotorsion during laser in situ keratomileusis. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2003; 44:2099–104.8. Jun JY, Hun D, Chang HR. Position-induced cyclotorsion under monocular fixation. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2005; 46:111–6.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Change of Exodeviation in the Seated and Supine Position
- The Ocular Cyclotorsion Induced by the Positional Change
- Adaptive responses of cardiac function to fetal postural change as gestational age increases
- Change in Intraocular Pressure According to Sleeping Posture in Normal People
- Spirometry on Supine position in Young Healthy Students