J Korean Ophthalmol Soc.
2009 Dec;50(12):1831-1839. 10.3341/jkos.2009.50.12.1831.
The Effect of Positional Changes during Heavy Weight Lifting on Intraocular Pressure
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, Wallace Memorial Baptist Hospital, Busan, Korea. kjdeye@naver.com
- KMID: 2212995
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/jkos.2009.50.12.1831
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To measure intraocular pressure (IOP) as a function of positional changes of the head during heavy weight lifting.
METHODS
The subjects of this study were 30 healthy adult males in their twenties to forties. This study investigated their ophthalmic examinations, BMI (body mass index), and 1RM (one repetition maximum) according to the three bench press positions.
RESULTS
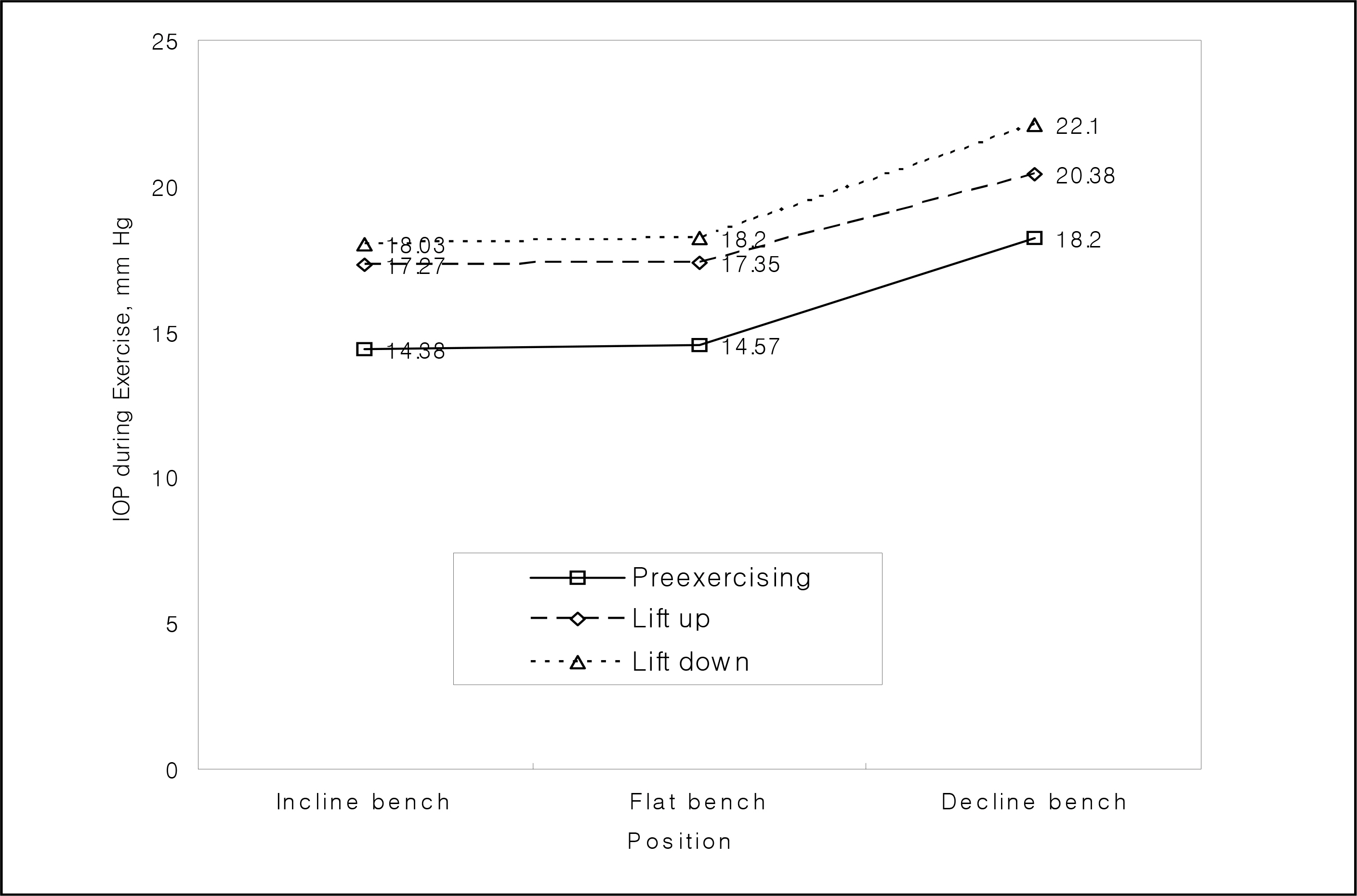
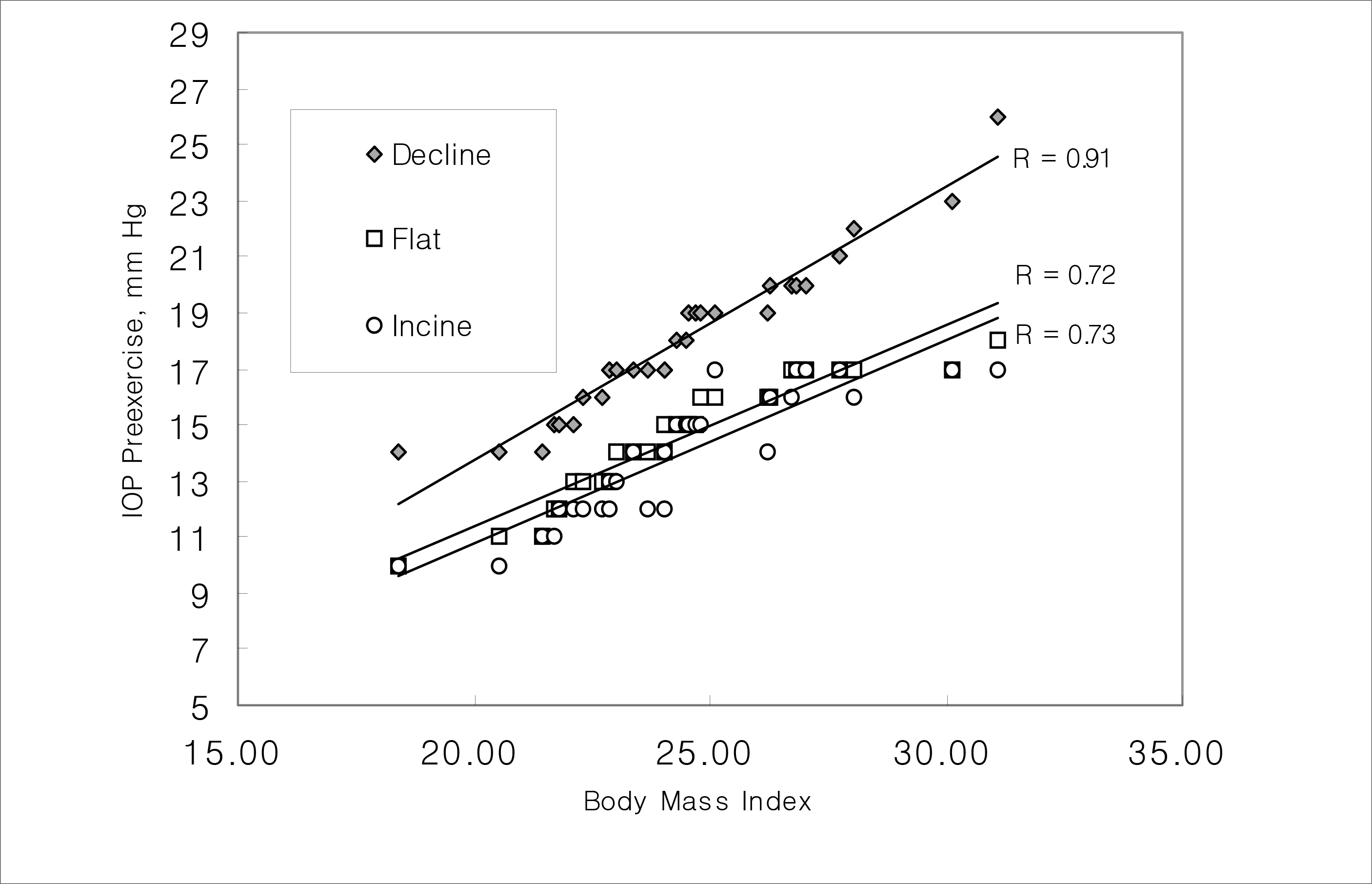
Before exercising, the IOP was higher in the lowered head position in the decline bench press (18.20+/-2.89 mmHg) than in the incline bench press (14.38+/-2.32 mmHg) (p<0.001). The IOP increased significantly during the bench press exercise, relative to during the pre-exercise (p<0.001). Upon lift down, IOP increased by 3.72+/-1.85 mmHg greater than upon lift up, and mean IOP increased by 2.61+/-1.63 mmHg (p<0.001). In our experiments, IOP increased to a maximum of 22.10+/-2.79 mmHg, measured during lift down in the decline bench press configuration. The BMI and the IOP before exercise showed significant correlation (p<0.05).
CONCLUSIONS
IOP increased more during exercise involving a lower head position. Further study is needed to know the extent to which this result is relevant for glaucoma patients and which activities and head positions during exercise may worsen glaucoma. In the meantime, patients with severe glaucoma may need to avoid lifting heavy objects with a lowered head position.
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Fleck SJ, Kraemer WJ. Designing resistance training programs. 3rd ed.Champaign II: Human Kinetics;2004. p. 13–51.2. Barnett C, Kippers V, Turner P. Effect of variations of the bench press exercise on the EMG activity of five shoulder muscles. J Strength Cond Res. 1995; 9:222–7.3. Narloch JA, Brandstater ME. Influence of breathing technique on arterial blood pressure during heavy weight lifting. Arch Phys Med Rehebil. 1995; 76:457–62.
Article4. Hughes LO, Heb er ME, Lahiri A, et al. Haemodynamic advantage of the valsalva manoeuvre during heavy resistance training. Eur Heart J. 1989; 10:896–902.
Article5. Biro I, Botar Z. Ueber das verhalten den augendrucks bei verschiedenen sportsleistugen. Klin Monatsbl Augenheikd. 1967; 140:123–30.6. Dickerman RD, Smith GH, Langham-Roof L, et al. Intraocular pressure changes during maximal isometric contraction: does this reflect intracranial pressure or retinal venous pressure? Neurol Res. 1999; 21:243–6.
Article7. Vieira GM, Oliveira HB, de Andrade DT, et al. Intraocular pressure variation during weight lifting. Arch Ophthalmol. 2006; 124:1251–4.
Article8. Galin MA, Mclvor JW, Magruder GB. Influence of position on intraocular pressure. Am J Ophthalmol. 1963; 55:720–9.9. Baskaran M, Raman K, Ramani KK, et al. Intraocular pressure changes and ocular biometry during Sirsasana (headstand posture) in yoga practitioners. Ophthalmology. 2006; 113:1327–32.
Article10. Van Herick W, Shaffer RN, Schwartz A. Estimation of width of the angle of the anterior chamber. Am J Ophthalmol. 1969; 68:626–9.11. Hodapp E, Parrish RK, Andersson DR. Clinical decisions in glaucoma. St. Louis: CV Mosby;1993. p. 204.12. Earle RW. Applying exercise prescription principle. Thomas RB, Earle RW, editors. Essentials of strength training and condition. 3rd ed.Hong Kong: Human kinetics;2008. chap. 19.13. Stone MH, Collins D, Plisk S, et al. Training principles: Evaluation of modes and methods of resistance training. Strength and Conditioning Journal. 2000; 22:65–76.
Article14. Kuling K, Andrews JG, Hay JG. Human strength curves. Exerc Sports Sci. 1984; 12:417–66.15. Kim DM. Postural change of intraocular pressure in normal persons and in patients with hypertension and diabetes. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1986; 27:577–80.16. Krieglstein G, Langhan ME. Influence of body position on the intraocular pressure of normal and glaucomatous eyes. Ophthalmologica. 1975; 171:32–45.
Article17. Jain MR, Marmion VJ. Rapid pneumatic and Mackary-Marg applanation tonometry to evaluate the postural effect on intraocular pressure. Br J Ophthalmol. 1976; 60:687–93.18. Kim DM, Yun DH. Postural change of intraocular pressure. J Korea Ophthalmol Soc. 1979; 20:511–5.19. Tsukahara S, Sasaka T. Postural change of IOP in normal persons and in patients with primary wide open-angle glaucoma and low-tension glaucoma. Br J Ophthalmol. 1984; 68:389–92.
Article20. Lieth AB. Episcleral venous pressure in tonography. Br J Ophthalmol. 1963; 47:271–8.21. Hvidberg A, Kessing SV. Fernandes A. Effect of changes in PCO2 and body positions on intraocular pressure during general anaesthesia. Acta Ophthalmol. 1981; 59:465–75.22. Viestenz A, Lausen B, Junemann AM, Mardin CY. Comparison of precision of the TonoPenXL with the Goldmann and Draeger applanation tonometer in a sitting and recumbent position of the patients – a clinical study on 251 eyes. Klin Monatsbl Augenheilkd. 2002; 219:785–90.23. Carlson KH, McLaren JW, Topper JE, Brubaker RF. Effect of body position on intraocular pressure and aqueous flow. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1987; 28:1346–52.24. Mader TH, Taylor GR, Hunter N, et al. Intraocular pressure, retinal vascular, and visual acuity changes during 48 hours of 10 degrees head-down tilt. Aviat Space Environ Med. 1990; 61:810–3.25. Frey MA, Mader TH, Bagian JP, et al. Cerebral blood velocity and other cardiovascular responses to 2 days of head-down tilt. J Appl Physiol. 1993; 74:319–25.
Article26. Linder BJ, Trick GL, Wolf ML. Altering body position affects intraocular pressure and visual function. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1988; 29:1492–7.27. Christophe C, Marc-Antoine C, Anne P, et al. Changes in intraocular pressure during prolonged (7-day) head-down tilt bedrest. J Glaucoma. 2003; 12:204–8.28. Watenpaugh DE, Hargens AR. The cardiovascular system in microgravity. Fregly MJ, Blatteis CM, editors. Handbook of Physiology: Environmental Physiology. New-York: Oxford;1996. 3:chap. 29.
Article29. Smith TJ, Lewis J. Effect of inverted body position intraocular pressure. Am J Ophthalmol. 1985; 99:617–8.30. Friberg TR, Sanborn G, Weinreb RN. Intraocular and episcleral venous pressure increase during inverted posture. Am J Ophthalmol. 1987; 103:523–6.
Article31. Lanigan LP, Clark CV, Allawi J, et al. Intraocular pressure responses to systemic autonomic stimulation in diabetes mellitus. Eye. 1989; 72:141–53.
Article32. Vieira GM, Penna EP, Bottaro M, Bezerra RF. The acute effects of isotonic exercise on intraocular pressure [in Portuguese]. Arq Bras Oftalmol. 2003; 66:431–5.33. Chromiak JA, Abadie BR, Braswell RA, et al. Resistance training exercises acutely reduce intraocular pressure in physically active men and women. J Strength Cond Res. 2003; 17:715–20.
Article34. Van meurs JC, van den Bosch WA. Suprachoroidal hemorrhage following a valsalva maneuver. Arch Ophthalmol. 1993; 111:1025–6.
Article35. Rosen DA, Johnston VC. Ocular pressure patterns in the valsalva maneuver. Arch Ophthalmol. 1959; 62:810–6.
Article36. Rushmer RF. Circulatory effects of three modifications of the valsalva experiment. Am Heart J. 1946; 32:399.
Article37. Lee JK, Lee JS, Kim YK. The relationship between intraocular pressure and health parameters. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2009; 50:105–12.
Article38. Lee JS, Kim CM, Choi HY, Oum BS. A relationship between intraocular pressure and age and body mass index in a Korean population. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2003; 44:1559–66.39. Carel RS, Korczyn AD, Rock M, Goya I. Association between ocular pressure and certain health parameters. Ophthalmology. 1984; 91:311–4.
Article40. Klein BE, Klein R, Linton KL. Intraocular pressure in an American community. The Beave Dam Eye study. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1992; 33:2224–8.41. Bulpitt CJ, Hodes C, Everott MG. Intraocular pressure and systemic blood pressure in the elderly. Br J Ophthalmol. 1975; 59:717–20.
Article42. Shiose Y, Kawase Y. A new approach to stratified normal intraocular pressure in a general population. Am J Ophthalmol. 1986; 101:714–21.
Article43. Lim KC. The relationship of one repetition maximum between flat bench press exercise and incline bench press exercise. Korean Journal of Sport Biomechanics. 2006; 16:189–94.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Glaucoma pathogenesis and lifestyle modification
- Occupational Lifting Tasks and Retinal Detachment in Non-Myopics and Myopics: Extended Analysis of a Case-Control Study
- Effect of Weight Lifting on Electroglottography
- Effect of Digital Massage en Intraeeular Pressure
- Normal Intraocular Pressure of Neonates Measured with Tono-pen