J Korean Ophthalmol Soc.
2009 Sep;50(9):1308-1312. 10.3341/jkos.2009.50.9.1308.
Clinical Result After Implantation of Minus Diopter Intraocular Lens in the High Myopia Patients
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology and Visual Science, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea. ckjoo@catholic.ac.kr
- KMID: 2212612
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/jkos.2009.50.9.1308
Abstract
- PURPOSE
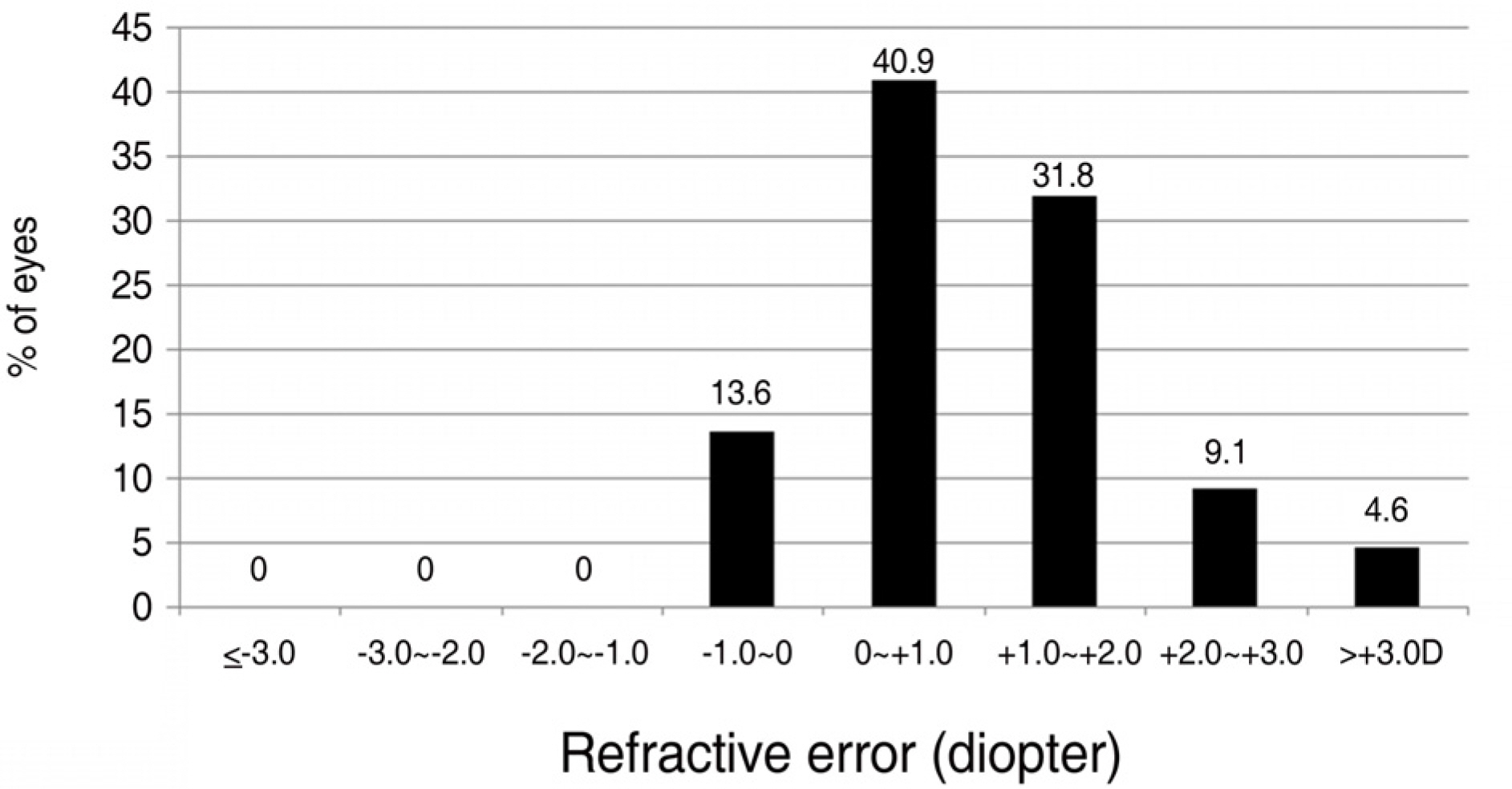
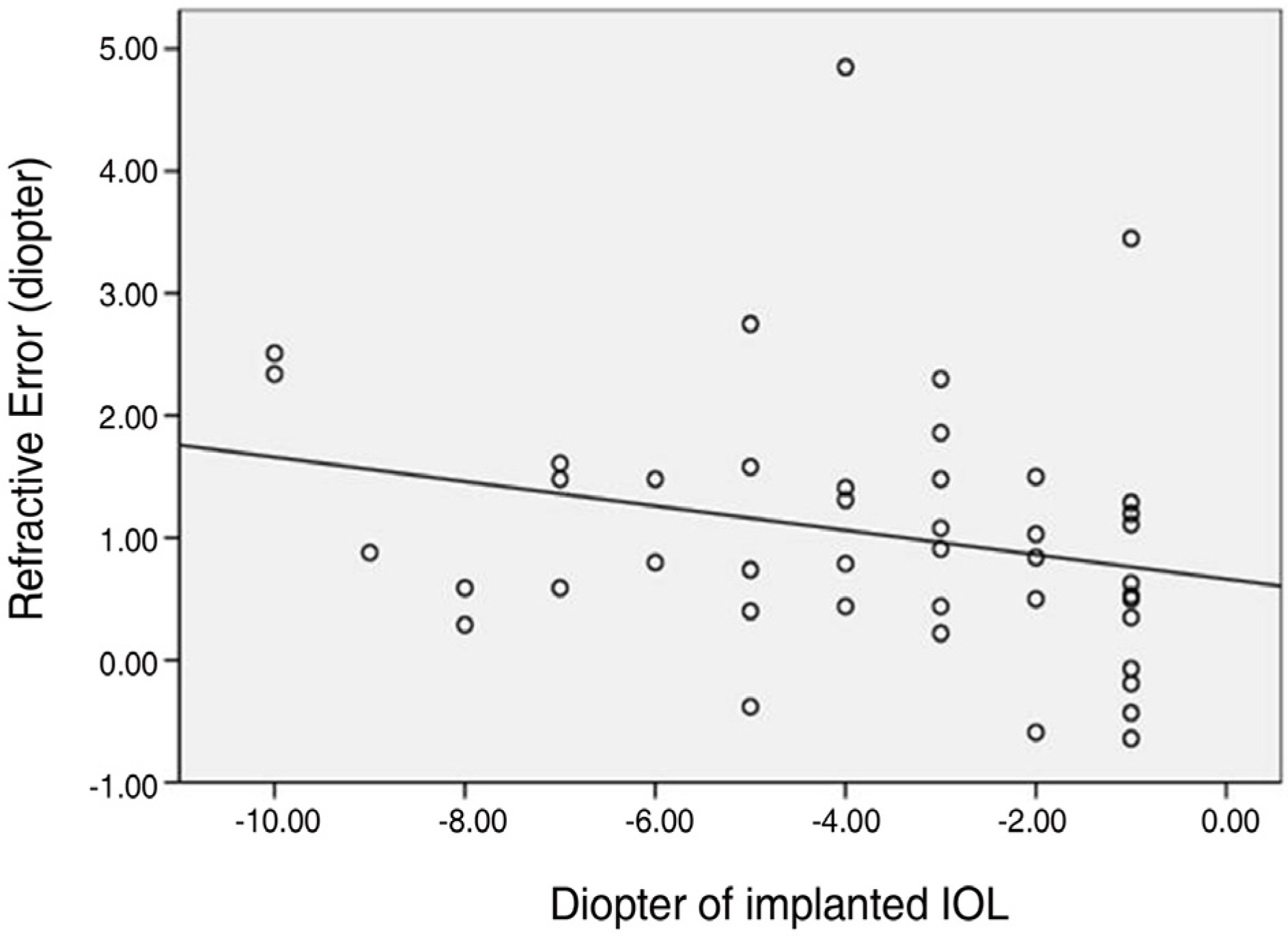
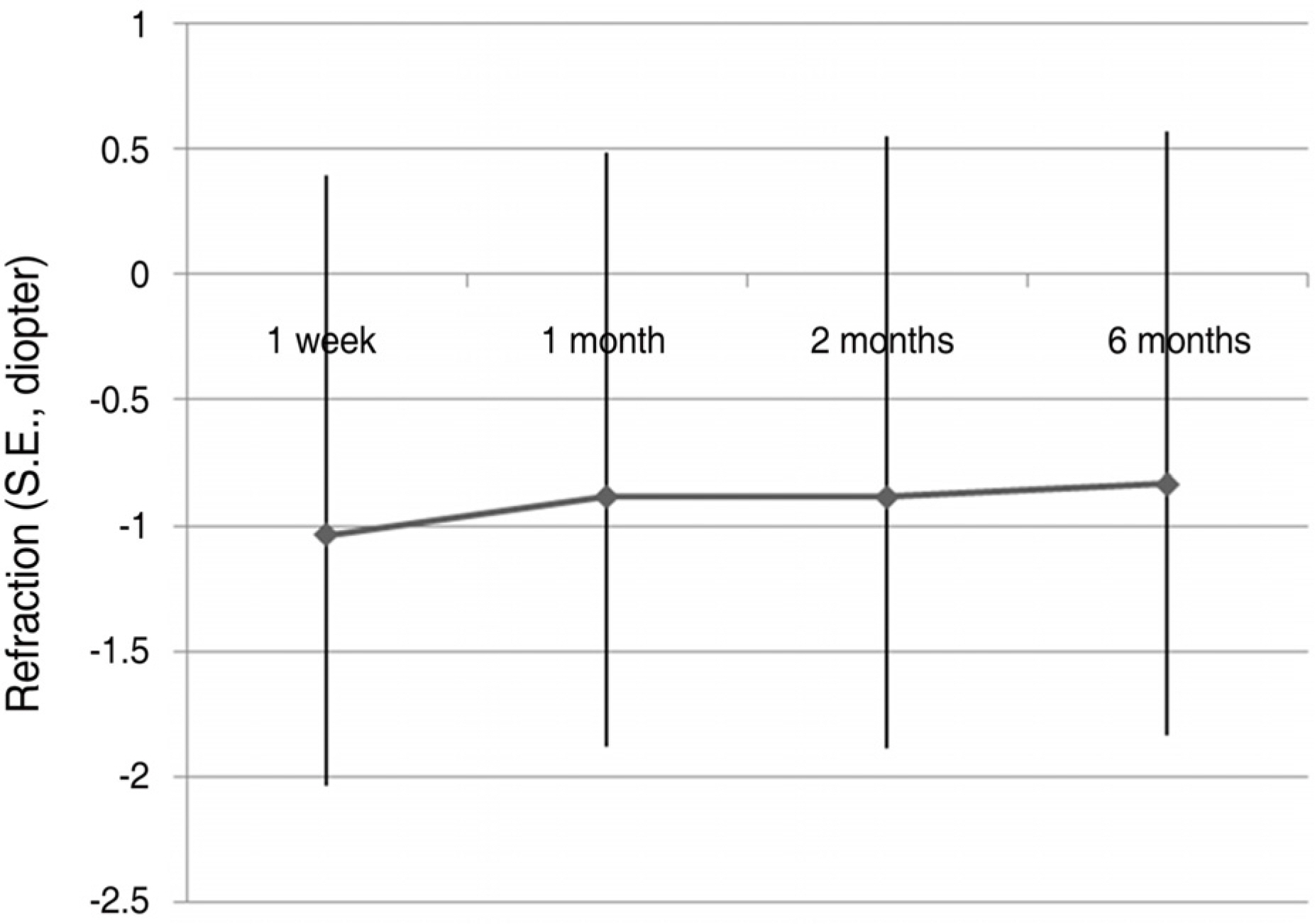
To investigate the clinical results of 44 high myopic eyes with cataracts which had minus diopter IOLs (Intraocular lenses) implanted during cataract surgery. METHODS: A retrospective chart review was done on 44 eyes in 33 patients who had undergone cataract extraction and minus diopter posterior chamber lens implantation. The IOL power was calculated using the SRK-T formula, and ACR6D SE(R) (Corneal SA, France) IOL was implanted in all cases. We evaluated pre-operative target refraction, post-operative refraction at six months, pre-operative visual acuity with and without correction, and post-operative visual acuity with and without correction. The relationships between axial length and refractive error and between the diopter of IOLs and refractive error were analyzed. RESULTS: The mean postoperative hyperopic refractive error compared to the preoperative target refraction was +1.04+/-1.05D, which was statistically significant (p<0.01). The longer the axial length and the larger the minus diopter lens inserted, the larger the hyperopic error. However, there were no statistically significant differences between them. CONCLUSIONS: Satisfactory results in visual acuity were obtained after cataract surgery in high myopic patients. However, when choosing the IOL power in high myopic patients, the possible development of postoperative hyperopic error should be considered.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Drews RC. Reliability of lens implant power formulas in hyperopes and myopes. Ophthalmic Surg. 1988; 19:11–5.
Article2. Huber C. Effectiveness of intraocular lens calculation in high ametropia. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1989; 15:667–72.
Article3. Kalogeropoulos C, Aspiotis M, Stefaniotou M, Psilas K. Factors influencing the accuracy of the SRK formula in the intraocular lens power calculation. Doc Ophthalmol. 1994; 85:223–42.
Article4. Olsen T, Thim K, Corydon L. Accuracy of the newer generation intraocular lens power calculation formulas in long and short eyes. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1991; 17:187–93.
Article5. Holladay JT, Prager TC, Chandler TY, et al. A three part system for refining intraocular lens power calculations. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1988; 14:17–24.6. Hoffer KJ. The Hoffer Q formula: a comparison of theoretic and regression formulas. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1993; 19:700–12.
Article7. Hoffer KJ. The effect of axial length on posterior chamber lenses and posterior capsule position. Current Concepts of Ophthalmic Surgery. 1984; 1:20–22.8. Retzlaff JA, Sanders DR, Kraff MC. Development of the SRK/T intraocular lens implant power calculation formula. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1990; 16:333–40.
Article9. Sanders DR, Retzlaff JA, Kraff MC, et al. Comparison to the SRK/T formula and other theoretical and regression formulas. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1990; 16:341–46.10. Tsang CS, Chong GS, Yiu EP, Ho CK. Intraocular lens power calculation formulas in Chinese eyes with high axial myopia. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2003; 29:1358–64.
Article11. Cho YT, Lee EH. Evaluation for the accuracy of the SRK/T Formula in PCL Implanted Patients(I). J Korean Opthalmol Soc. 1991; 32:752–60.12. Lee EH, Lee HS. Comparisions of the SRK, SRK 2 and Holladay Formulas In Pseudophakic Patients. J Korean Opthalmol Soc. 1990; 31:1514–9.13. Zaldivar R, Shultz MC, Davidorf JM, Holladay JT. Intraocular lens power calculations in patients with extreme myopia. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2000; 26:668–74.
Article14. Olsen T, Corydon L, Gimbel H. Intraocular lenspower calculation with an improved anterior chamber depth prediction algorithm. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1995; 21:313–9.15. Packer M, Fine IH, Hoffman RS, et al. Immersion A-scan compared with partial coherence interferometry. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2002; 28:239–42.
Article16. Chang YH, Lim SJ, Kim TH, Kim HB. Prediction of the Refractive Power after Cataract Surgery on Myopic Eyes. J Korean Opthalmol Soc. 1999; 40:424–9.17. Olsen T. Sources of error in intraocular lens power calculation. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1992; 18:125–29.
Article18. Ripandelli G, Scassa C, Parisi V, et al. Cataract Surgery as a Risk Factor for Retinal Detachment in Very Highly Myopic Eyes. Ophthalmology. 2003; 110:2355–61.
Article19. Nasisse MP, Dykstra MJ, Cobo LM. Lens capsule opacification in aphakic and pseudophakic eyes. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 1995; 233:63–70.
Article20. Gris O, Güell JL, Manero F, Müller A. Clear lens extraction to correct high myopia. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1996; 22:686–9.
Article21. Lee KH, Lee JH. The surgical outcome of clear lens extraction for correction of severe high myopia. J Korean Opthalmol Soc. 1996; 37:63–69.22. Hwang SY, Na KS, Choi GJ. A clinical study on cataract surgery in high myopia. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1997; 38:956–61.23. Xu L, Li Y, Wang S, et al. Characteristics of Highly Myopic Eyes: The Beijing Eye Study. Ophthalmology. 2007; 114:121–6.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Clinical Outcome of Minus Diopter Posterior Chamber Lens
- Clinical Results of Cataract Operations using Piggy-back Method
- Posterior Chamber Intraocular Lens Implantation in High Myopia
- Clear Lens Extraction for the Correction of High Myopia
- Postoperative Refractive Error in Combined Operation of Vitrectomy and Intraocular Lens Implantation