J Korean Surg Soc.
2012 Sep;83(3):149-154. 10.4174/jkss.2012.83.3.149.
Laparoscopic left hemihepatectomy for left intrahepatic duct stones
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Gyeongsang National University School of Medicine, Jinju, Korea. drjej@gnu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2212287
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4174/jkss.2012.83.3.149
Abstract
- PURPOSE
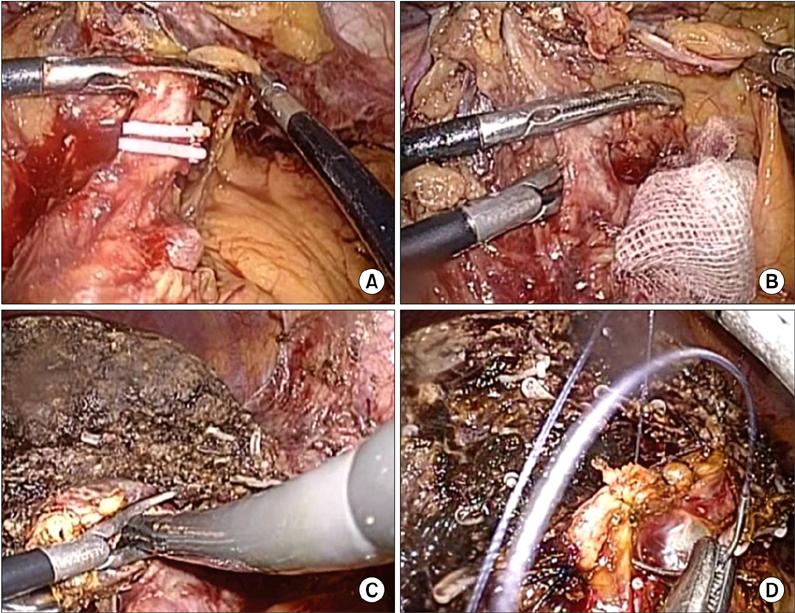
The feasibility of laparoscopic left hemihepatectomy for the management of intrahepatic duct (IHD) stones was evaluated.
METHODS
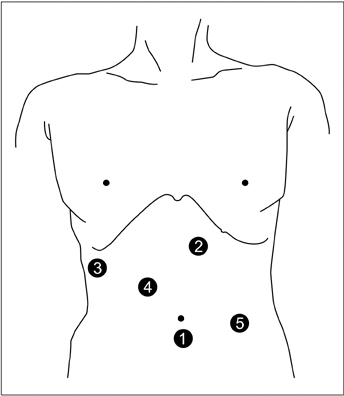
The clinical data of 26 consecutive patients who underwent total laparoscopic left hemihepatectomy for IHD stones at Gyeongsang National University Hospital between January 2009 and June 2011 were reviewed retrospectively.
RESULTS
The mean operation time was 312.1 +/- 63.4 minutes and the mean postoperative hospital stay was 11.8 +/- 5.0 days. There were 2 cases of postoperative bile leakage and 3 cases of intra-abdominal fluid collection, which were successfully managed conservatively. Remnant stones were detected in 2 patients. The initial success rate of stone clearance was 92.3% (24 of 26). The remnant stones were located in the common bile duct in both cases and were removed by endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography and endoscopic sphincterotomy. Therefore, the final success rate of stone clearance was 100% (26 of 26). During a mean follow-up of 22 months (range, 7 to 36 months), there was no patient with recurrent stone.
CONCLUSION
Laparoscopic surgery could be an effective treatment modality for the management of IHD stones in select patients.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Huang MH, Chen CH, Yang JC, Yang CC, Yeh YH, Chou DA, et al. Long-term outcome of percutaneous transhepatic cholangioscopic lithotomy for hepatolithiasis. Am J Gastroenterol. 2003. 98:2655–2662.2. Lee SK, Seo DW, Myung SJ, Park ET, Lim BC, Kim HJ, et al. Percutaneous transhepatic cholangioscopic treatment for hepatolithiasis: an evaluation of long-term results and risk factors for recurrence. Gastrointest Endosc. 2001. 53:318–323.3. Jan YY, Chen MF, Wang CS, Jeng LB, Hwang TL, Chen SC. Surgical treatment of hepatolithiasis: long-term results. Surgery. 1996. 120:509–514.4. Cheung MT, Kwok PC. Liver resection for intrahepatic stones. Arch Surg. 2005. 140:993–997.5. Han HS, Yi NJ. Laparoscopic treatment of intrahepatic duct stone. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech. 2004. 14:157–162.6. Nguyen KT, Gamblin TC, Geller DA. World review of laparoscopic liver resection-2,804 patients. Ann Surg. 2009. 250:831–841.7. Park YH, Park SJ, Jang JY, Ahn YJ, Park YC, Yoon YB, et al. Changing patterns of gallstone disease in Korea. World J Surg. 2004. 28:206–210.8. Gagner M, Rogula T, Selzer D. Laparoscopic liver resection: benefits and controversies. Surg Clin North Am. 2004. 84:451–462.9. Cherqui D, Husson E, Hammoud R, Malassagne B, Stephan F, Bensaid S, et al. Laparoscopic liver resections: a feasibility study in 30 patients. Ann Surg. 2000. 232:753–762.10. Yoon YS, Han HS, Shin SH, Cho JY, Min SK, Lee HK. Laparoscopic treatment for intrahepatic duct stones in the era of laparoscopy: laparoscopic intrahepatic duct exploration and laparoscopic hepatectomy. Ann Surg. 2009. 249:286–291.11. Tu JF, Jiang FZ, Zhu HL, Hu RY, Zhang WJ, Zhou ZX. Laparoscopic vs open left hepatectomy for hepatolithiasis. World J Gastroenterol. 2010. 16:2818–2823.12. Cai X, Wang Y, Yu H, Liang X, Peng S. Laparoscopic hepatectomy for hepatolithiasis: a feasibility and safety study in 29 patients. Surg Endosc. 2007. 21:1074–1078.13. Lai EC, Ngai TC, Yang GP, Li MK. Laparoscopic approach of surgical treatment for primary hepatolithiasis: a cohort study. Am J Surg. 2010. 199:716–721.14. Descottes B, Glineur D, Lachachi F, Valleix D, Paineau J, Hamy A, et al. Laparoscopic liver resection of benign liver tumors. Surg Endosc. 2003. 17:23–30.15. Lesurtel M, Cherqui D, Laurent A, Tayar C, Fagniez PL. Laparoscopic versus open left lateral hepatic lobectomy: a case-control study. J Am Coll Surg. 2003. 196:236–242.16. Dulucq JL, Wintringer P, Stabilini C, Berticelli J, Mahajna A. Laparoscopic liver resections: a single center experience. Surg Endosc. 2005. 19:886–891.17. Haberstroh J, Ahrens M, Munzar T, Waninger J, Salm R, Matern U, et al. Effects of the Pringle maneuver on hemodynamics during laparoscopic liver resection in the pig. Eur Surg Res. 1996. 28:8–13.18. Malassagne B, Cherqui D, Alon R, Brunetti F, Humeres R, Fagniez PL. Safety of selective vascular clamping for major hepatectomies. J Am Coll Surg. 1998. 187:482–486.19. Cai XJ, Wang YF, Liang YL, Yu H, Liang X. Laparoscopic left hemihepatectomy: a safety and feasibility study of 19 cases. Surg Endosc. 2009. 23:2556–2562.20. Yang T, Lau WY, Lai EC, Yang LQ, Zhang J, Yang GS, et al. Hepatectomy for bilateral primary hepatolithiasis: a cohort study. Ann Surg. 2010. 251:84–90.21. Sun WB, Han BL, Cai JX. The surgical treatment of isolated left-sided hepatolithiasis: a 22-year experience. Surgery. 2000. 127:493–497.22. Chen DW, Tung-Ping Poon R, Liu CL, Fan ST, Wong J. Immediate and long-term outcomes of hepatectomy for hepatolithiasis. Surgery. 2004. 135:386–393.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Feasibility of Left Hemi-hepatectomy for the Treatment of Left Intrahepatic Duct Stones
- Intrahepatic Duct Stones in Young Patients
- The Feasibility of Laparoscopic Hepatectomy for the Patients with Left Intrahepatic Stones
- Surgical Clip Moved into the Extrahepatic Bile Duct after Laparoscopic Hepatectomy
- Intraoperative cholangiographic findings of intrahepatic duct stones