J Korean Surg Soc.
2010 Nov;79(5):411-414. 10.4174/jkss.2010.79.5.411.
Extraskeletal Ewing's Sarcoma of the Breast, Mimicking Cyst
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, Inha University School of Medicine, Incheon, Korea.
- 2Department of Radiology, Inha University School of Medicine, Incheon, Korea. kimyj@inha.ac.kr
- 3Department of Pathology, Inha University School of Medicine, Incheon, Korea.
- 4Department of Surgery, Inha University School of Medicine, Incheon, Korea.
- KMID: 2212055
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4174/jkss.2010.79.5.411
Abstract
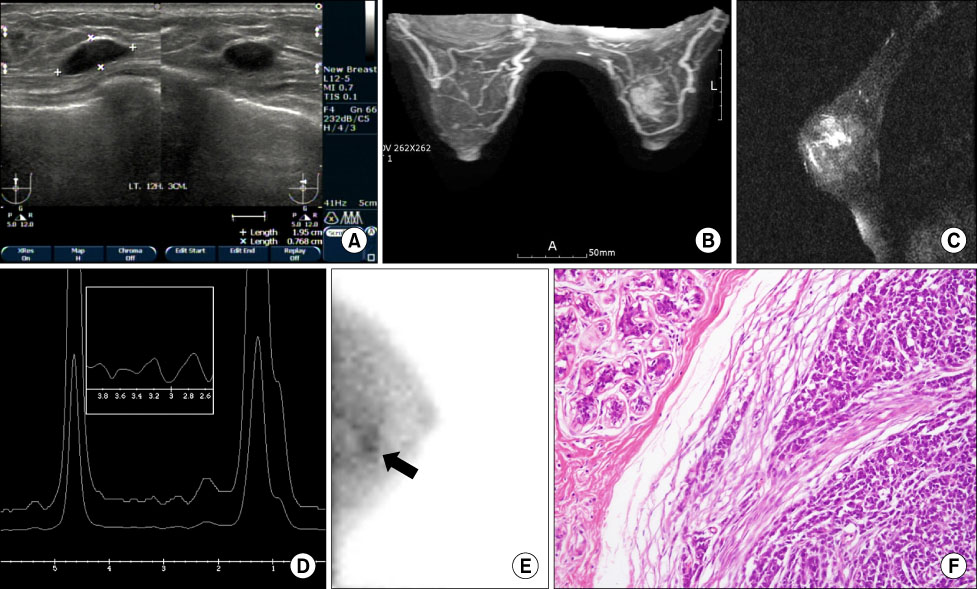
- Extraskeletal Ewing' sarcoma (EES) is a rare soft tissue tumor morphologically indistinguishable from the osseous Ewing's sarcoma (ES). We report a case of recurrent EES of the breast that, to the best of our knowledge, has rarely been reported. It was initially confused for a cyst on ultrasound. In addition, MRI and breast-specific gamma imaging (BSGI) in our case have complementary value over conventional imaging.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Maxwell RW, Ghate SV, Bentley RC, Soo MS. Primary primitive neuroectodermal tumor of the breast. J Ultrasound Med. 2006. 25:1331–1333.2. da Silva BB, Lopes-Costa PV, Pires CG, Borges RS, da Silva RG Jr. Primitive neuroectodermal tumor of the breast. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2008. 137:248–249.3. Popli MB, Popli V, Bahl P, Solanki Y. Extraskeletal Ewing's sarcoma of the breast. Eur J Radiol Extra. 2009. 70:e65–e67.4. Ahmad R, Mayol BR, Davis M, Rougraff BT. Extraskeletal Ewing's sarcoma. Cancer. 1999. 85:725–731.5. Ryu BY, Kim TH, Kim HS, Hwang DJ, Cho JW, Lee HW, et al. Osteogenic sarcoma of the breast. J Korean Surg Soc. 2001. 61:441–444.6. Ko K, Kim EA, Lee ES, Kwon Y. Primary primitive neuroectodermal tumor of the breast: a case report. Korean J Radiol. 2009. 10:407–410.7. Enzinger FM, Weiss SW. Enzinger FM, Weiss SW, editors. Extraskeletal Ewing's sarcoma/primitive neuroectodermal tumor family. Soft Tissue Sarcoma. 2001. 4th ed. St. Louis: Mobis;1289–1308.8. Schmidt D, Herrmann C, Jürgens H, Harms D. Malignant peripheral neuroectodermal tumor and its necessary distinction from Ewing's sarcoma. A report from the Kiel Pediatric Tumor Registry. Cancer. 1991. 68:2251–2259.9. Lefkowitz IB, Packer RJ, Ryan SG, Shah N, Alavi J, Rorke LB, et al. Late recurrence of primitive neuroectodermal tumor/medulloblastoma. Cancer. 1988. 62:826–830.