J Korean Ophthalmol Soc.
2008 Apr;49(4):681-684. 10.3341/jkos.2008.49.4.681.
A Case of Green Laser Pointer Injury to the Macula
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul Artificial Eye Center, Clinical Research Institute, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Seoul National University Hospital Health Care System Gangnam Center, Healthcare Reaserch Institute, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Ophthalmology, Seoul National University Boramae Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2211503
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/jkos.2008.49.4.681
Abstract
-
PURPOSE: We report a case of macular injury by accidental exposure to a green laser pointer.
CASE SUMMARY
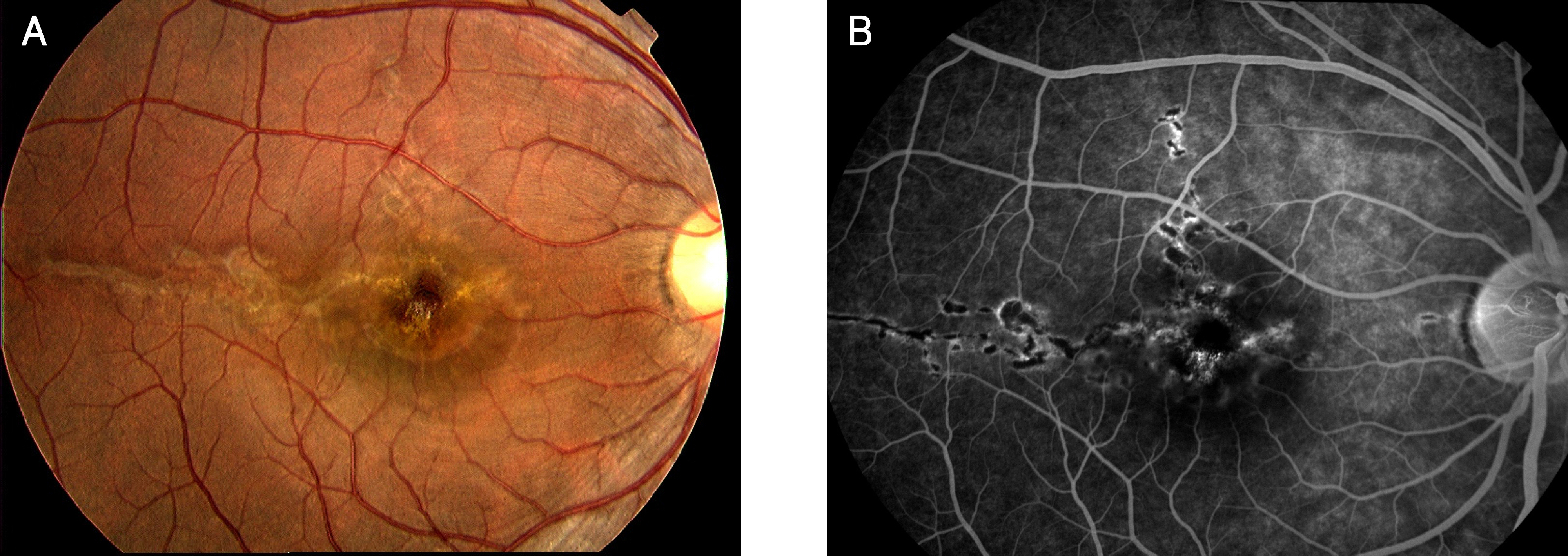
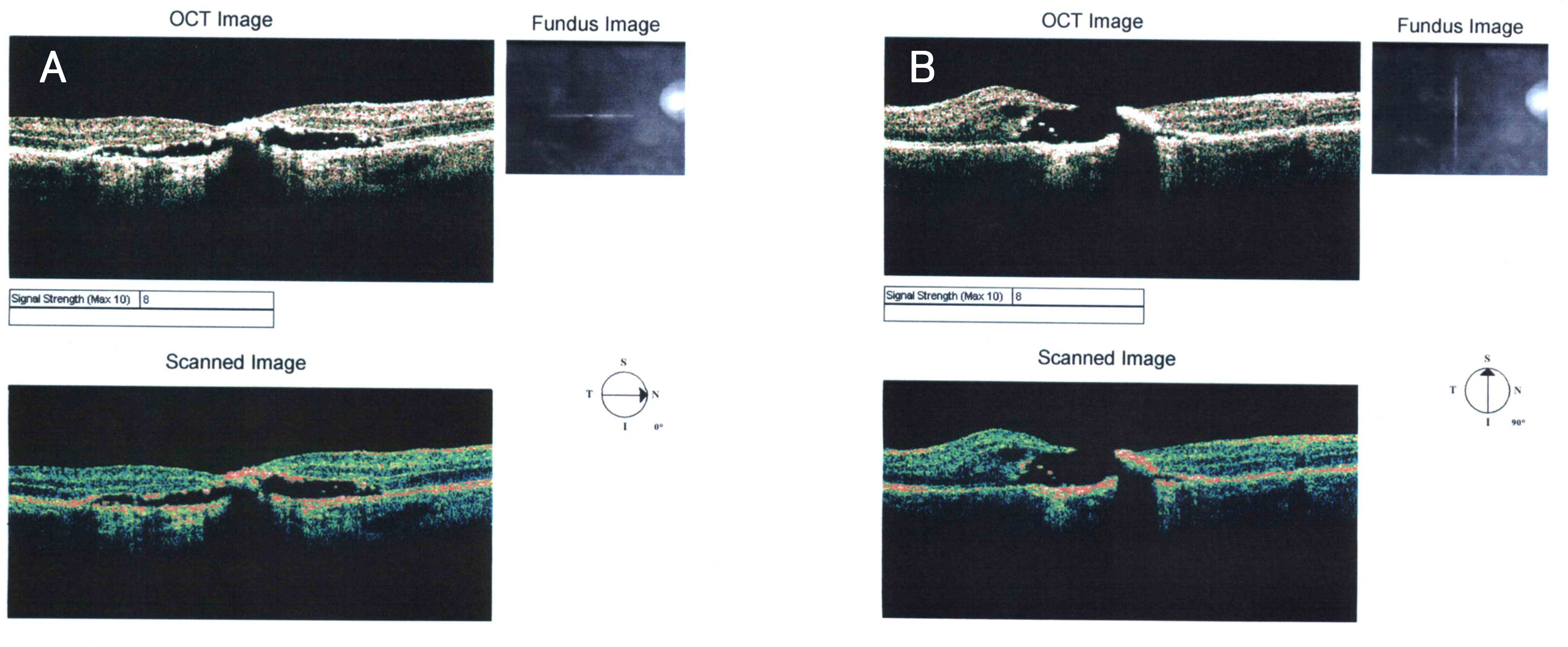
A 25-year-old man had an acute reduction of visual acuity in his right eye two years ago after accidental exposure to a green laser pointer for a few seconds. The patient's best corrected visual acuity was counting fingers in his right eye. Fundus examination and optical coherence tomography showed a macular hole and a linear retinal scar in his right eye.
CONCLUSIONS
Green laser pointers may cause macular damage after exposure of just a few seconds, which can lead to irreversible reduction of visual acuity.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
A Case of Retinal Injury During a Laser Show
Jun Woo Chun, Young Jun Jang, Seung Woo Lee
J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2011;52(11):1377-1380. doi: 10.3341/jkos.2011.52.11.1377.A Case of Maculopathy from Handheld Green Laser Pointer
Young Jun Kim, In Young Chung, Seong Jae Kim, Jong Moon Park, Yong Seop Han
J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2015;56(3):447-451. doi: 10.3341/jkos.2015.56.3.447.
Reference
-
References
1. Mainster MA. Blinded by the light‐ not! Arch Ophthalmol. 1999; 117:1547–8.2. Yolton RL, Citek K, Schmeisser E, et al. Laser pointers: toys, nuisances, or significant eye hazards? J Am Optom Assoc. 1999; 70:285–9.3. Abbasi K. UK bans powerful laser pointers. BMJ. 1997; 315:1253.
Article4. Robertson DM, McLaren JW, Salomao DR, Link TP. Retinopathy from a green laser pointer: a clinicopathologic study. Arch Ophthalmol. 2005; 123:629–33.5. Namgung M, Park JS, Choi YI. A Case of Nd:YAG laser injury to the macula. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2004; 45:1756–60.6. Sell CH, Bryan JS. Maculopathy from handheld diode laser pointer. Arch Ophthalmol. 1999; 117:1557–8.
Article7. Zamir E, Kaiserman I, Chowers I. Laser pointer maculopathy. Am J Ophthalmol. 1999; 127:728–9.
Article8. Robertson DM, Lim TH, Salomao DR, et al. Laser pointers and the human eye: a clinicopathologic study. Arch Ophthalmol. 2000; 118:1686–91.9. Mainster MA. Wavelength selection in macular photocoagulation. Tissue optics, thermal effects, and laser systems. Ophthalmology. 1986; 93:952–8.10. Alhalel A, Glovinsky Y, Treister G, et al. Long‐ term follow up of accidental parafoveal laser burns. Retina. 1993; 13:152–4.11. Mainster MA, Timberlake GT, Warren KA, et al. Pointers on laser pointers. Ophthalmology. 1997; 104:1213–4.
Article12. Ham WT Jr, Geeraets WJ, Mueller HA, et al. Retinal burn thresholds for the helium‐ neon laser in the rhesus monkey. Arch Ophthalmol. 1970; 84:797–809.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Maculopathy from Handheld Green Laser Pointer
- Maculopathy from Red Laser Pointer
- A Case of Green Laser Pointer-induced Atypical Impending Macular Hole Treated with Vitrectomy in a Pediatric Patient
- Novel Adjuvant Method to Assist Localisation of a Cyclodialysis Cleft
- A Case of Nd: YAG Laser Injury to the Macula