J Korean Soc Spine Surg.
2001 Sep;8(3):248-252. 10.4184/jkss.2001.8.3.248.
Posterior Epidural Migration of Herniated Lumbar Intervertebral Disc: Two Cases Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Ulsan University Hospital, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Ulsan, Korea. yscho@uuh.ulsan.kr
- KMID: 2209742
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4184/jkss.2001.8.3.248
Abstract
-
STUDY DESIGN: case report and review of the literature
OBJECTIVES
to report two cases of posterior epidural migration of herniated lumbar intervertebral disc and review the literature Summary of Background Data : Posterior epidural migration of herniated lumbar intervertebral disc is extremely rare. The large size of the fragment eventually exceeded the limits of the anterior epidural space and the fragment subsequently settled posterior the thecal sac because of spatial and size constraints.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Two cases of herniation of intervertebral disc which were caused by posteriorly migrated disc material were treated surgically with open discectomy. The magnetic resonance images, surgical treatment and related literature are reviewed.
RESULTS
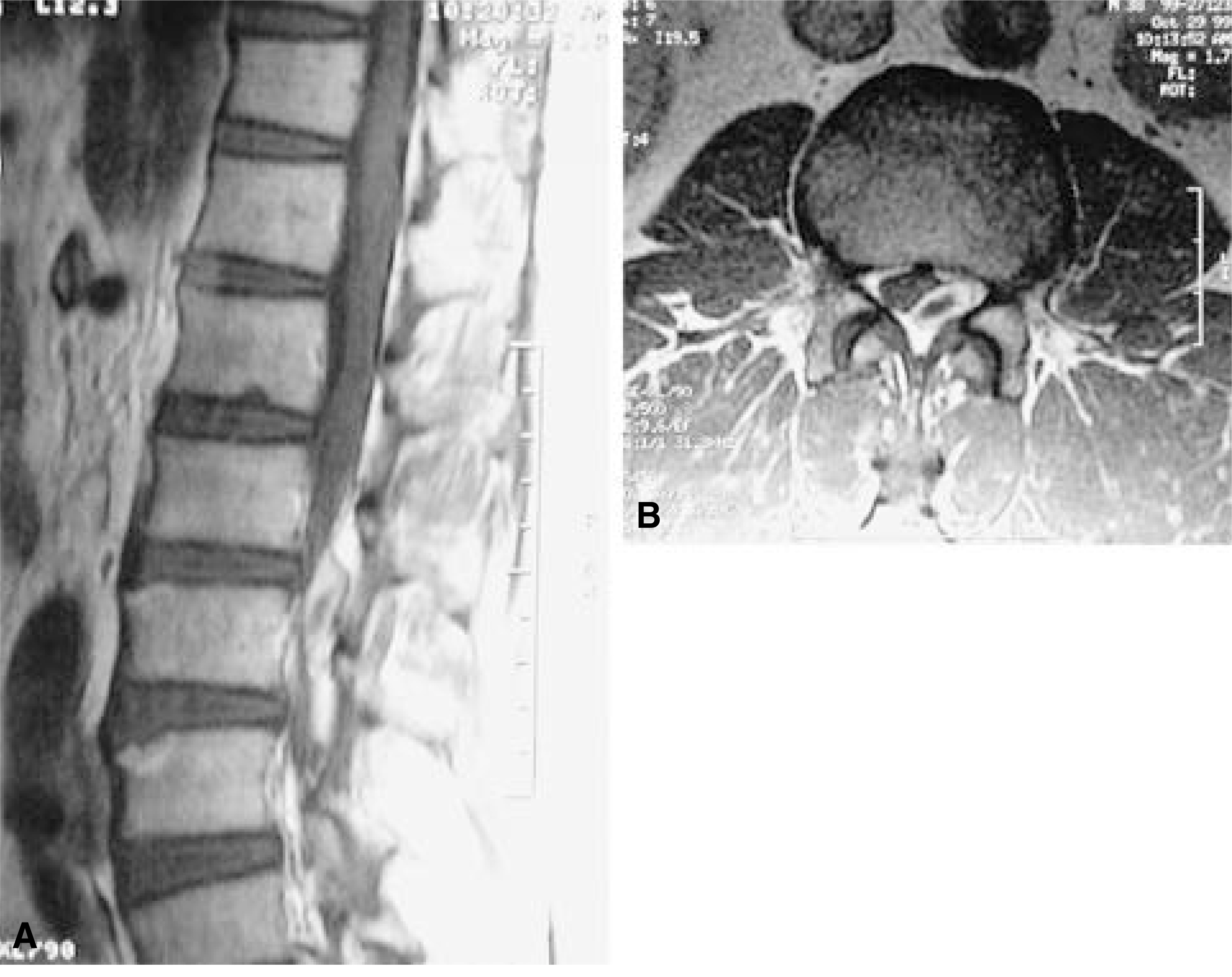
Preoperative magnetic resonance images of the posterior epidural migration of herniated lumbar intervertebral disc showed a large epidural mass. The mass was of intermediate signal intensity on T1-weighted images, was of low signal intensity on T2-weighted images and was enhanced marginally with gadolinium-DTPA on T1-weighted images. Immediately after operation, a significant reduction of symptoms were achieved. The patients recovered fully at two year follow-up.
CONCLUSIONS
Lumbar disc herniation by posterior epidural migration of sequestered fragment can be diagnosed with clinical findings and MRI including Gadolinium-DTPA enhancement. It should be differentiated from epidural mass and could be managed surgically with good results.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1). Bonaroti EA, Welch WC. Posterior epidural migration of an extruded lumbar disc fragment causing cauda equina syndrome. Spine. 23:378–381. 1998.
Article2). Cho JL, Park YS, Han JH. Posterior epidural migration of a sequestrated intervertebral lumbar disc. A Case report. The J of Korean Orthop Assoc. 34:985–8. 1999.
Article3). Dillon WP, Kaseff LG, Knackstedt VE, Osborn AG. Computed tomogragphy and differential diagnosis of the extruded lumbar disc. Journal of Computer Assisted Tomography. 7(6):969–975. 1983.4). Ebeling U, Reulen HJ. Are there typical localizations of lumbar disc herniations? A prospective study. Acta Neu -rochir(Wien). 117:143–8. 1992.5). Fries JW, Abodeely DA, Vijungco JG, Yaeger VL, Gaffey WR. Computed tomography of herniated and extruded nucleus pulposus. Journal of Computer Assisted Tomography. 6:874–887. 1982.
Article6). Lutz JD, Smith RR, Jones HM. CT myelography of a fragment of a lumbar disc sequestrated posterior to the thecal sac. Am J Neuroradioigy. 11:610–11. 1990.7). Manabe S, Tateishi A. Epidural migration of extruded cervical disc and its surgical treatment. Spine. 11:873–8. 1986.
Article8). Masaryk TJ, Ross JS, Mondic MT, Boumphery F, Bohlman H, Wilber G. High-resolution imaging of sequestered lumbar intervertebral discs. Am J Neuroradioigy. 7:709–711. 1986.9). Modic MT, Feiglin DH, Pirano DW. Vertebral osteo-myelitis: assessment using MR. Radiology. 157:157–166. 1985.
Article10). Schellinger D, Manz HJ, Vidic B. Disk fragment migration. Radiology. 175:831–6. 1990.
Article11). Wiltse LL, Fonseca AS, Amster J, Dimartino P, Ravessoud FA. Relationship of the dura, Hofmann's ligaments, Baston's plexus and a fibrovascular membrane lying on the posterior surface of the vertebral bodies and attaching to the deep layer of the posterior longitudinal ligament: An anatomical, radiologic, and clinical study. Spine. 18:1030–43. 1993.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Posterior Epidural Migration of Lumbar Ruptured Disc: Report of Two Cases
- Posterior Epidural Migration of a Sequestrated Intervertebral Lumbar Disc: A Case Report
- Posterior Epidural Migration of a Sequestrated Intervertebral lumbar Disc with Cauda Equina Syndrome: Two Cases Report
- Dorsal Epidural Migration of Lumbar Sequestered Disc Fragment: Report of Three Cases
- Delayed-Onset Leg Weakness Caused by Posterior Migration of a Herniated Disc to the Thecal Sac Mimicking Epidural Hematoma in a Flexion-Distraction Injury of the Lumbar Spine: A Case Report