J Korean Soc Spine Surg.
2006 Sep;13(3):177-183. 10.4184/jkss.2006.13.3.177.
Factors affecting Reduction of Slippage in Posterolateral Fusion for Spondylolytic Spondylolisthesis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Inha University College of Medicine, Inchon, Korea. srp2002@inha.com
- KMID: 2209639
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4184/jkss.2006.13.3.177
Abstract
-
STUDY DESIGN: A retrospective study.
OBJECTIVES
The purpose of this study was to analyze the reduction of spondylolisthesis after postural reduction and pedicle screw instrumentation for low-grade spondylolytic spondylolisthesis, and to determine the factors affecting reduction.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
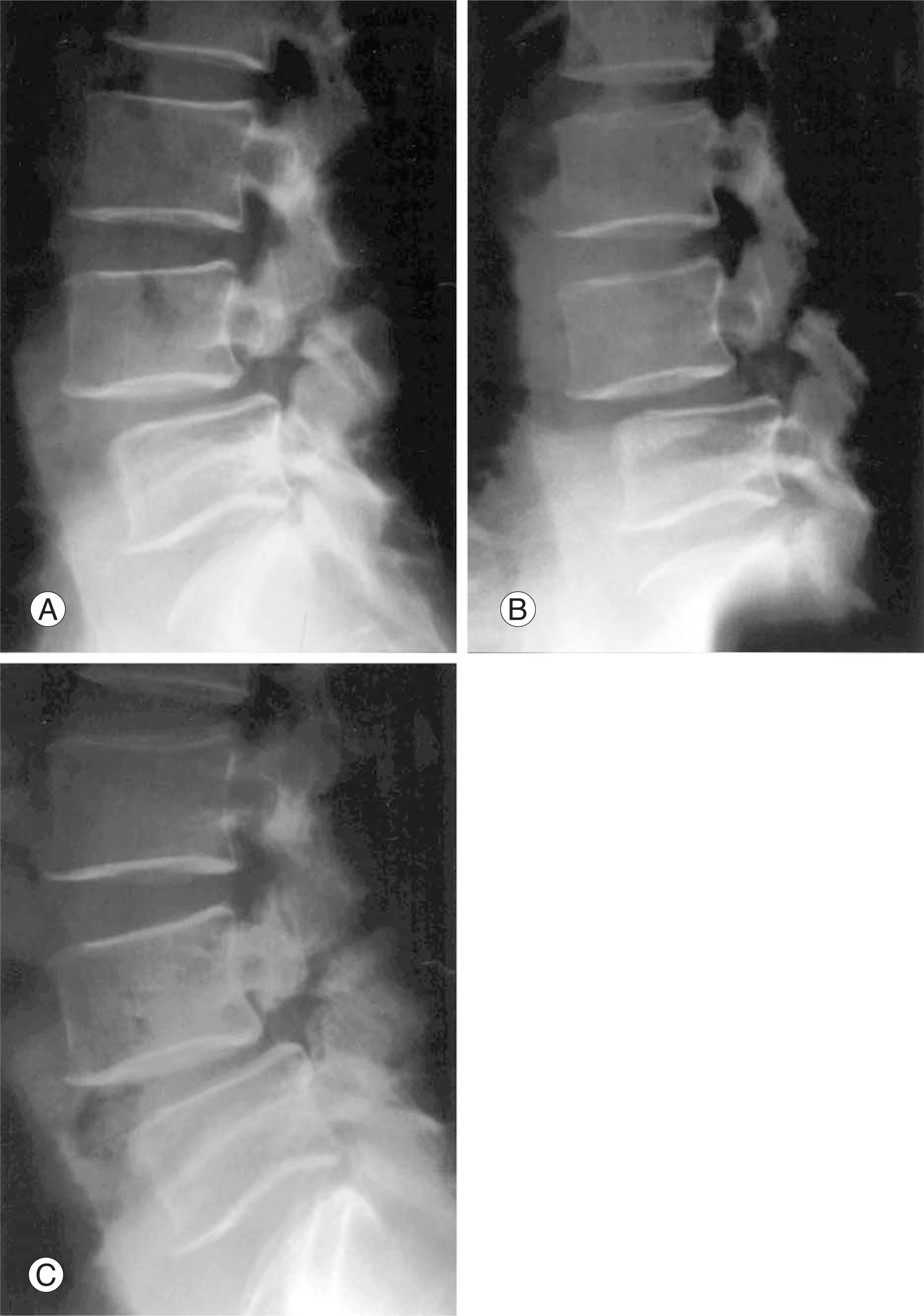
Twenty patients (mean age 52.5 years old; range, 30-71 years old), who underwent pedicle screw instrumentation and posterolateral fusion after wide laminectomy and facetectomy, were reviewed. The minimum follow-up period was 2 years. The percentage of slippage was measured on lateral radiographs by the Taillard method. We measured the slip angle, sacral inclination, lumbar lordosis, disc height, and angulation and translation on flexion-extension stress views. These radiological parameters were analyzed statistically for correlation with the reduction of slippage.
RESULTS
In these passive reduction surgeries, no forceful reduction was attempted. The average percentage of slippage was 20.6% preoperatively, 13.0% after instrumentation, and 19.5% at the last visit. The reduction of slippage had a correlation with hypermobile angulation on flexion-extension radiographs (p=0.02). There were no significant correlations between the amount of reduction and translation on flexion-extension radiographs (P=0.99), slip angle (P=0.79), disc space height (P=0.6), lumbar lordosis (P=0.68), and sacral inclination (P=0.35).
CONCLUSION
Loss of reduction that was achieved by postural reduction with pedicle screw instrumentation for spondylolytic spondylolisthesis occurred at the final follow-up. There was a negative correlation between the reduction of slippage and hypermobile angulation on flexion-extension dynamic radiographs.
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Minimally Invasive Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion in Patients with Low Grade Spondylolisthesis - Comparison of the Unilateral and Bilateral Approaches -
Sang-Hyuk Min, Dae-Hee Lee
J Korean Orthop Assoc. 2009;44(4):429-435. doi: 10.4055/jkoa.2009.44.4.429.
Reference
-
01). Edwards CC., Bradford DS. Controversies: Instru-mented reduction of spondylolisthesis. Spine. 1994. 19:1535–1537.02). Bradford DS., Boachie-Adjei O. Treatment of severe spondylolisthesis by anterior and posterior reduction and stabilization. A long-term follow-up study. J Bone Joint Surg. 1990. 72A:1060–1066.
Article03). Laursen M., Thomsen K., Eiskjaer SP., Hansen ES., Bunger CE. Functional outcome after partial reduction and 360 degree fusion in grade III-V spondylolisthesis in adolescent and adult patients. J Spinal Disord. 1999. 12:300–306.04). Mulholland RC. Comment on topographic relations of neural and ligamentous structures of the lumbosacral junction: in vitro investigation. Spondylolisthesis-no reduction. partial reduction or total reduction? Eur Spine J. 2001. 10:133–134.05). Molinari MR., Bridwell KH., Lenke LG., Baldus C. Anterior column support in surgery for high-grade, isthmic spondylolisthesis. Clin Orthop. 2002. 394:109–120.
Article06). Spruit M., Pavlov PW., Leitao J., De Kleuver M., Ander-son PG., Den Boer F. Posterior reduction and anterior lumbar interbody fusion in symptomatic low-grade adult isthmic spondylolisthesis: short-term radiological and functional outcome. Eur Spine J. 2002. 11:428–433.07). Madan S., Boeree NR. Outcome of posterior lumbar interbody fusion versus posterolateral fusion for spondylolytic spondylolisthesis. Spine. 2002. 27:1536–1542.
Article08). Fabris DA., Costantini S., Nena U. Surgical treatment of severe L5-S1 spondylolisthesis in childeren and adoles-cents: Results of intraoperative reduction, posterior interbody fusion, and segmental pedicle fixation. Spine. 1996. 21:728–733.09). Wiltse LL., Winter RB. Terminology and measurement of spondylolisthesis. J Bone Joint Surg. 1983. 65:768–772.
Article10). Roca J., Ubierna MT., Caceres E., Iborra M. One-stage decompression and posterolateral and interbody fusion for severe spondylolisthesis. An analysis of 14 patients. Spine. 1999. 24:709–714.11). Montgomery DM. Fischgrund JS. Passive reduction of spondylolisthesis on the operating room table: a prospective study. J Spinal Disord. 1994. 7:167–172.12). Suk SI., Lee CK., Kim WJ., Lee JH., Cho KJ., Kim HG. Adding posterior lumbar interbody fusion to pedicle screw fixation and posterolateral fusion after decompression in spondylotic spondylolisthesis. Spine. 1997. 22:210–219.13). Naderi SN., Manisali M., Acar F., Ozaksoy D., Mertol T., Arda MN. Factors affecting reduction in low-grade lum-bosacral spondylolisthesis. J Neurosurg. 2003. 99:151–156.
Article14). O' Brien MF. Low-grade isthmic/lytic spondylolisthesis in adults. Inst Course Lect. 2003. 52:511–524.15). Floman Y. Progression of lumbosacral isthmic spondylolisthesis in adults. Spine. 2000. 25:342–347.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Adding Posterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion to Pedicle Screw Fixatin and Posterolateral Fusion after Decompression in Spondylolytic Spondylolisthesis
- Comparison between Posterolateral Fusion with Pedicle Screw Fixation and Anterior Interbody Fusion with Pedicle Screw Fixation in Spondylolytic Spondylolisthesis of the Lumbar Spine
- Comparison between Posterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion with Pedicle Screw Fixation and Posterolateral Fusion with Pedicle Screw Fixation in Spondylolytic Spondylolisthesis in Adults
- Results of the Posterolateral Fusion Using a Pedicle Screw for the Spondylolisthesis
- Comparison between Posterolateral Fusion with Pedicle Screw Fixation and Anterior Interbody Fusion with Pedicle Screw Fixation in Adult Spondylolytic Spondylolisthesis