J Korean Soc Spine Surg.
2006 Sep;13(3):153-162. 10.4184/jkss.2006.13.3.153.
Ossification of Posterior Longitudinal Ligament
- Affiliations
-
- 1Spine Center, Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Sun General Hospital, Daejeon, Korea. chspine@korea.com
- KMID: 2209636
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4184/jkss.2006.13.3.153
Abstract
- No abstract available.
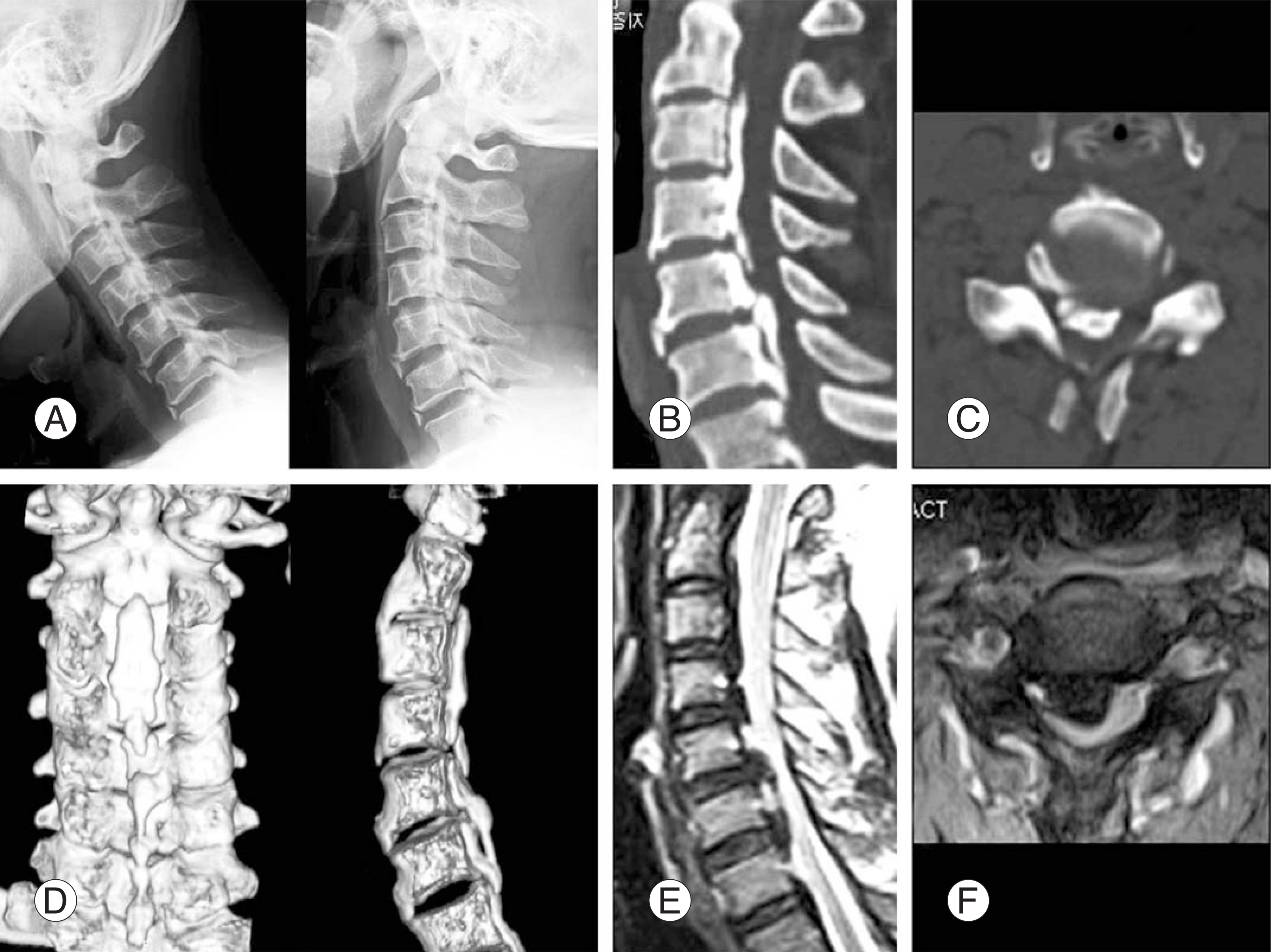
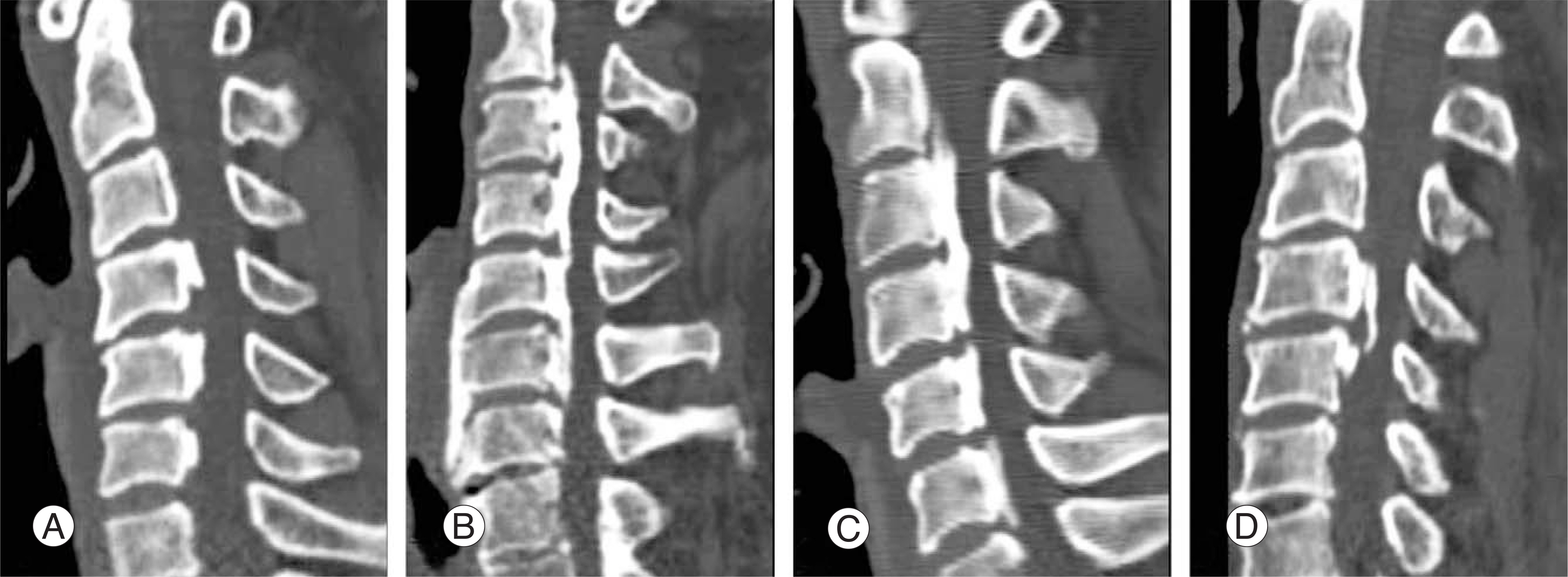
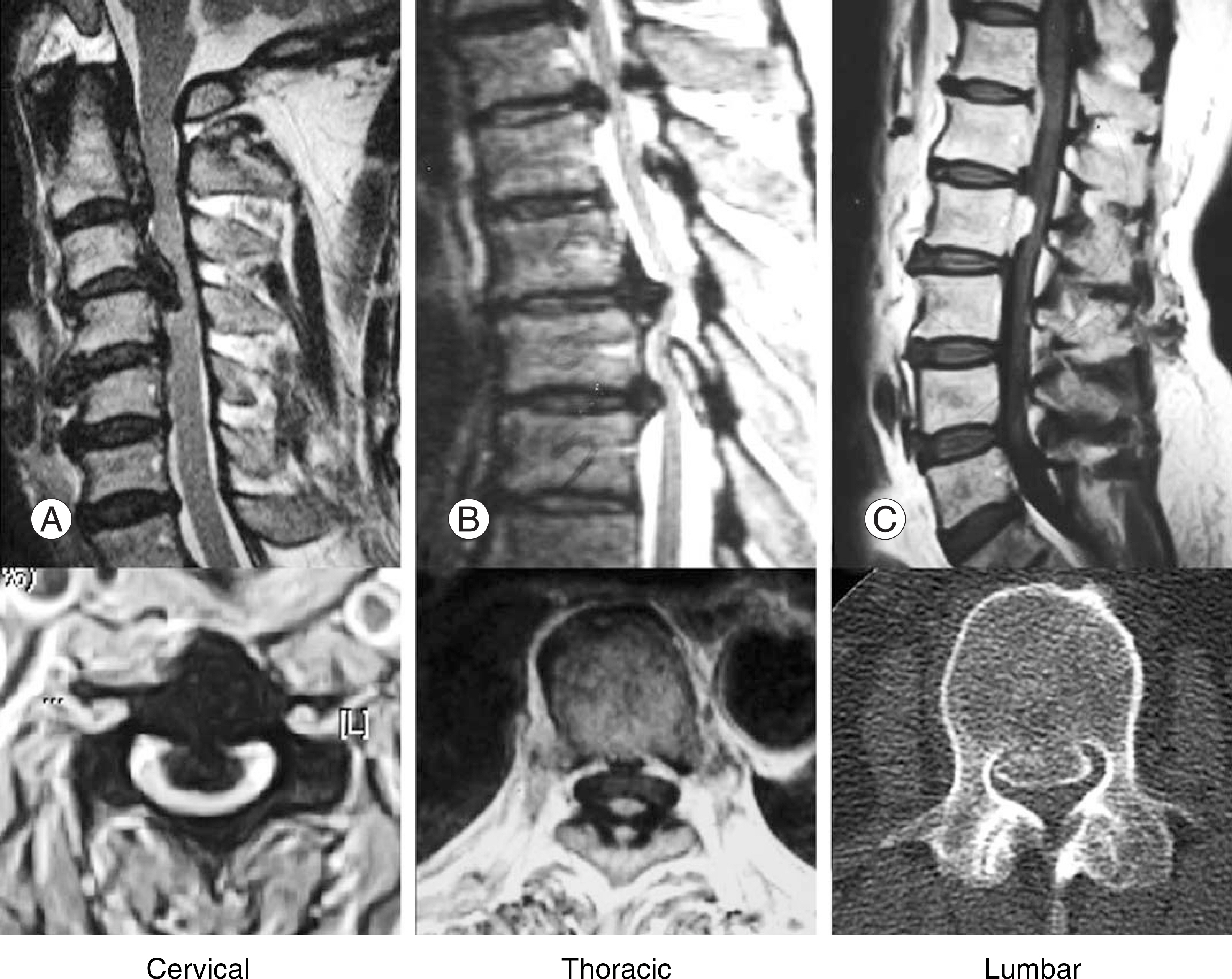
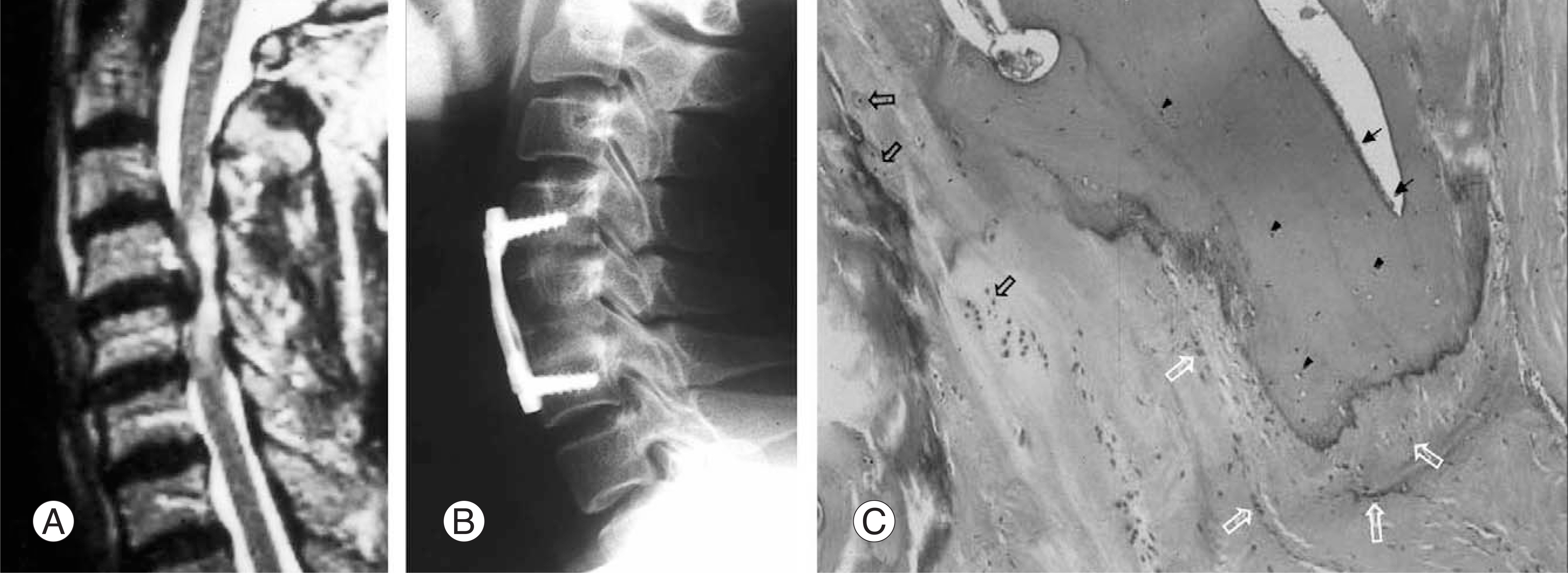
Figure
Reference
-
01). Inaba H., Nakae K., Kurokawa T. Statistical analysis for the national survey of ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligaments (in Japanese). In: Investigation committee 1976 report on the ossification of the spinal ligaments of the Japanese ministry of Public Health and Welfare, Tokyo. 1977. 29–39.02). Tsuyama N. Ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament of the spine. Clin Orthop. 1984. 184:71–84.
Article03). Key CA. Paraplegia depending on disease of the ligaments of the spine. Guy' s Hosp Rep. 1938. 3:17–34.04). Tsukimoto H. A case report: autopsy of syndrome of compression of spinal cord owing to ossification within spinal canal of cervical spine(in Japanese). Nippon Geka Hokan. 1960. 29:1003–1007.05). Yamaura I., Isobe Y., Kamikozuru M, et al. Evaluation of surgical treatment of the posterior longitudinal ligament in the cervical spine; anterior decompression (in Japanese). Seikeigeka. 1976. 27:87–95.06). Yamaura I. Anterior approach (anterior floating method) and its surgical results for cervical myelopathy caused by ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament (OPLL). J West Pac Orthop Assoc. 1990. 17:47–55.07). Hirabayashi K. Expansive open-door laminoplasty for cervical spondylotic myelopathy (in Japanese). Geka (surgery). 1978. 32:1159–1163.08). Hirabayashi K., Miyakawa J., Satomi K., Maruyama T., Wakano K. Operative results and postoperative progression of ossification among patients with ossification of cervical posterior longitudinal ligament. Spine. 1981. 6:354–364.
Article09). Hirabayashi K., Satomi K. Operative procedure and results of expansive open-door laminoplasty. Spine. 1988. 13:870–876.
Article10). Kurokawa T. Enlargement of spinal canal by the sagittal splitting of spinous processes (in Japanese). Bessatsu Seikeigeka. 1982. 2:234–240.11). Itoh T., Tsuji H. Technical improvements and results of laminoplasty for compressive myelopathy in the cervical spine. Spine. 1985. 10:729–736.
Article12). Kawai S., Sunago K., Doi K., Sakai M., Toguchi T. Cervical laminoplasty (Hattori' s method). Spine. 1988. 13:1245–1250.13). Tomita K., Nomura S., Umeda S., Baba K. Cervical laminoplasty to enlarge the spinal canal in multilevel ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament in myelopathy. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 1988. 107:148–153.14). Matsunaga S., Sakou T., Taketomi , et al. Effects of strain distribution in the intervertebral discs on the progression of ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligaments. Spine. 1996. 21:184–189.
Article15). Matsunaga S., Kukita M., Hayashi K, et al. Pathogenesis of myelopathy in patients with ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament. J Neurosurg Spine. 2002. 2:168–172.
Article16). Taketomi E. Progression of the posterior longitudinal ligament in the cervical spine. J Jpn Spine Res Soc. 1997. 8:359–366.17). Chiba K., Yamamoto I., Hirabayashi H, et al. Multicen-ter study investigating the postoperative progression of ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament in the cervical spine; a new computer-assisted measurement. J Neurosurg Spine. 2005. 3:17–23.
Article18). Epstein N. Ossification of the posterior longitudinal liga-ment; Diagnosis and surgical management. Neurosurg Q. 1992. 2:223–241.19). Chang H., Bahk WJ., An JG., Choi KH. Pre and postoperative evaluation of cervical myelopathy using MR imaging. J Korean Soc Spine Surg. 1994. 1:326–336.20). Matsunaga S., Sakou T., Taketomi , et al. The natural course of myelopathy caused by ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligaments in the cervical spine. Clin Orthop. 1994. 305:168–177.21). Masunaga S., Sakou T., Hayashi K., Ishidou Y., Hirotsu M., Komiya S. Trauma-induced myelopathy in patients with ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament. J Neurosurg Spine. 2002. 2:172–175.22). Ogawa Y., Chiba K., Matsumoto M, et al. Long term results after expansive open-door laminoplasty for the segmental-type of ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament of the cervical spine: a comparison with non-seg-mental type lesion. J Neurosurg Spine. 2005. 3:198–204.23). Mizuno J., Nakagawa H., Matsno N., Song J. Dural ossi-fication associated with cervical ossification of posterior longitudinal ligament: frequency of dural ossification and compression of neuroimaging modalities in ability to iden-tify the disease. J Neurosurg Spine. 2005. 2:425–430.24). Epstein N. Circumferential cervical surgery for ossification of posterior longitudinal ligament, A multianalytic outcome study. Spine. 2004. 29:1340–1345.25). Kawai S., Sunago K., Doi K., Sakai M., Taguchi T. Cervical laminoplasty (Hattori' s method). Spine. 1988. 13:1245–1250.26). Iwasaki M., Kawaguchi Y., Kimmura T., Yonenobu K. Long term result of expansive laminoplasty for ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament of the cervical spine: more than 10 years follow up. J Neurosurg Spine. 2002. 2:180–189.27). Yonenobu K., Okada K., Fuji T, et al. Causes of neuro-logic deterioration following surgical treatment of cervical myelopathy. Spine. 1991. 11:818–823.
Article28). Tsuzuki N., Abe R., Saiki K, et al. Paralysis of the arm after posterior decompression of the spinal cord II; Analy-ses of Clinical Findings. Eur Spine J. 1993. 2:197–202.29). Tsuzuki N., Abe R., Saiki K, et al. Extradural tethering effect as one mechanism of radiculopathy complicating posterior decompression of the cervical spinal cord. spine. 1996. 21:203–211.
Article30). Dai L., Ni B., Yuan W, et al. Radiculopathy after laminoplasty for cervical compressive myelopathy. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1998. 80:846–849.31). Chiba K., Toyama Y., Matsumotor M, et al. Segmental motor paralysis after expansive open door laminoplasty. Spine. 2002. 27:2108–2115.32). Sakura H., Hosomo N., Mukai Y., Ishii T., Yoshikawa H. C5 palsy after decompression surgery for cervical myelopa-thy, Review of the literature. Spine. 2003. 28:2447–2451.33). Seiki A., Takeshita K., Kawaguchi ., Nakajima S., Akune T., Nakamura K. Postoperative expansion of intramedullary high intensity areas on T2-weighted magnetic resonance imaging after cervical laminoplasty. Spine. 2004. 29:1478–1482.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Ossification of the Posterior Longitudinal Ligament: 2 cases report
- Ossification of posterior longitudinal ligament of the cervical spine in Korean
- Does Ossification of the Posterior Longitudinal Ligament Progress after Fusion?
- Anterior Decompression and Interbody Fusion for Ossification of the Posterior Longitudinal Ligament of the Cervical Spine: Case Report
- Genetics of Ossification of the Posterior Longitudinal Ligament of the Spine: A Mini Review