J Korean Soc Radiol.
2010 Feb;62(2):179-183. 10.3348/jksr.2010.62.2.179.
MDCT Findings of Bilateral Renal Cortical Necrosis: Unilateral Complete and Contralateral Limited Renal Cortical Necrosis: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Inje University, Seoul Paik Hospital, Korea. captsong@naver.com
- KMID: 2208966
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2010.62.2.179
Abstract
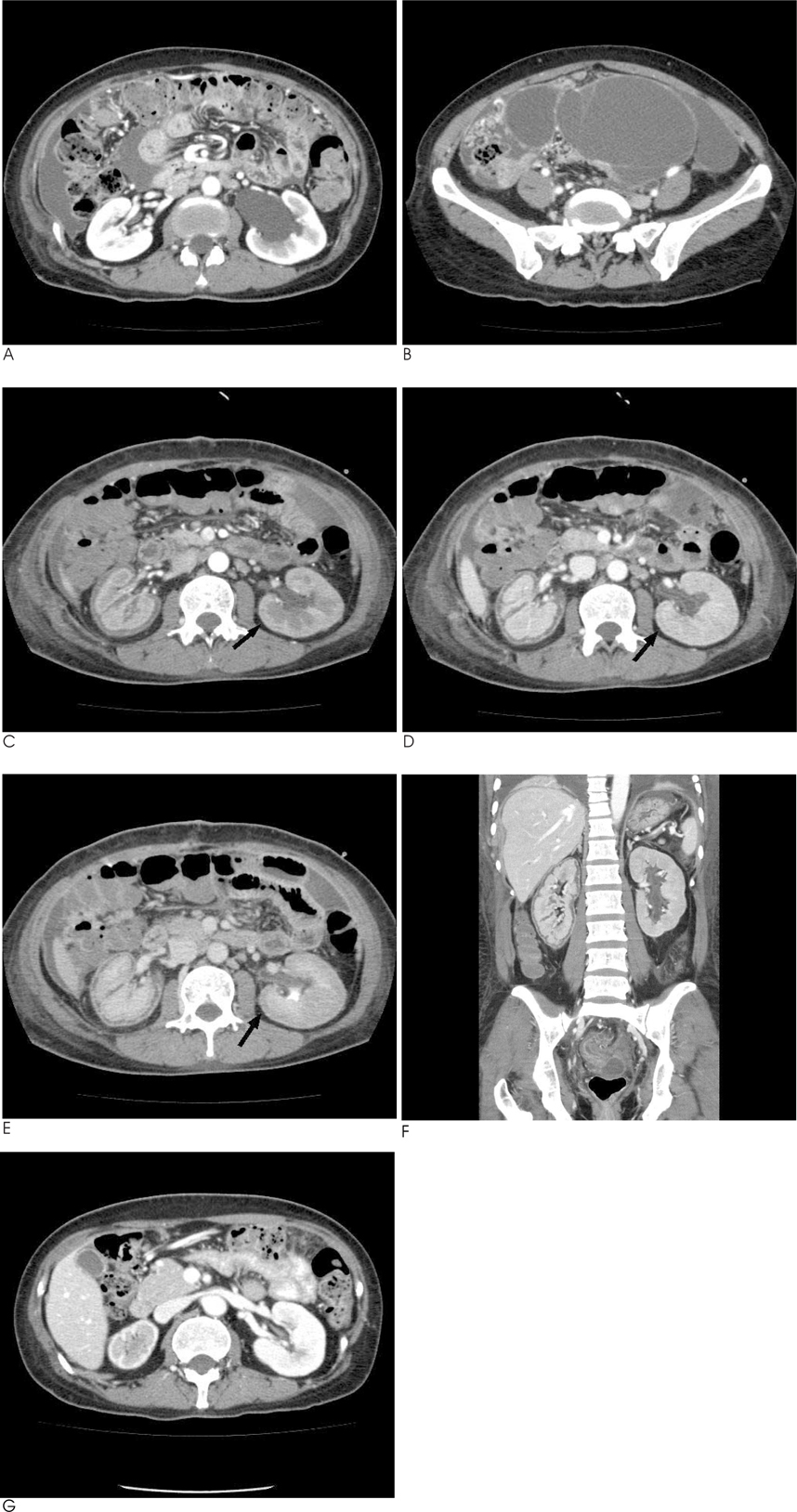
- Acute renal cortical necrosis (RCN) is a rare condition of partial or complete necrosis of the renal cortex, and this usually spares a thin tissue rim under the capsule and usually a thicker layer adjacent to the corticomedullary junction. We found bilateral RCN, including limited RCN in a hydronephrotic kidney, on three phase multi-detector row CT. This disparity of RCN between the two kidneys is a very rare condition. So here we report the MDCT findings of bilateral RCN, including limited RCN in a hydronephrotic kidney.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Piero R, Arrigo S, Tullio B, Giuseppe R. Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura, hemolytic uremic syndrome, and acute cortical necrosis. In : Robert WS, editor. Diseases of the Kidney and Urinary Tract. 7th Ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins;2001. p. 1900–1903.2. Goergen TG, Lindstrom RR, Tan H, Lilley J. CT appearance of acute renal cortical necrosis. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1981; 137:176–177.3. Chugh KS, Singhal PC, Kher VK, Gupta VK, Malik GH, Narayan G, et al. Spectrum of acute cortical necrosis in Indian patients. Am J Med Sci. 1983; 286:10–20.4. Deutsch V, Frankl O, Drory Y, Eliahou H, Braf ZF. Bilateral renal cortical necrosis with survival through the acute phase with a note on the value of selective nephroangiography. Am J Med. 1971; 50:828–834.5. Blute ML, Templeton AC. Unilateral renal cortical necrosis. Br J Urol. 1985; 57:243–244.6. Ljungqvist A. Structure of the arteriole-glomerular units in the different zones of the kidney. Micro-angiographic and histologic evidence of an extraglomerular medullary circulation. Nephron. 1964; 1:329–337.7. Steinhardt GF, Liapis H, Philips B, Vogler G, Nag M, Yoon KW. Insulin-like growth factor improves renal architecture of fetal kidneys with complete ureteral obstruction. J Urol. 1995; 154:690–693.8. Kühl PG, Schonig G, Schweer H, Seyberth HW. Increased renal biosynthesis of prostaglandin E2 and thromboxane B2 in human congenital obstructive uropathy. Pediatr Res. 1990; 27:103–107.9. Tang L, Loutzenhiser K, Loutzenhiser R. Biphasic actions of prostaglandin E(2) on the renal afferent arteriole: role of EP(3) and EP(4) receptors. Circ Res. 2000; 86:663–670.10. Daghini E, Primak AN, Chade AR, Krier JD, Zhu XY, Litman EL, et al. Assessment of renal hemodynamics and function in pigs with 64-Section multidetector CT: comparison with electron-beam CT. Radiology. 2007; 243:405–412.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Diagnostic Value of Contrast-Enhanced CT in Acute Bilateral Renal Cortical Necrosis: A Case Report
- A Case of Acute Renal Failure due to Acute Bilateral Renal Cortical Necrosis
- A Case of Bilateral Renal Cortical Necrosis Associated with Acute Pancreatitis
- Complete Recovery of Renal Function in Bilateral Renal Cortical Necrosis: A Case Report
- A Case of Diffuse Cortical Necrosis after Glue Sniffing