J Korean Soc Radiol.
2010 Feb;62(2):163-165. 10.3348/jksr.2010.62.2.163.
Multidetector-Row CT Findings of an Internal Supravesical Hernia: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Cheonan Hospital, Soonchunhyang University, Korea. hcshin@schca.ac.kr
- 2Department of Surgery, Cheonan Hospital, Soonchunhyang University, Korea.
- KMID: 2208962
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2010.62.2.163
Abstract
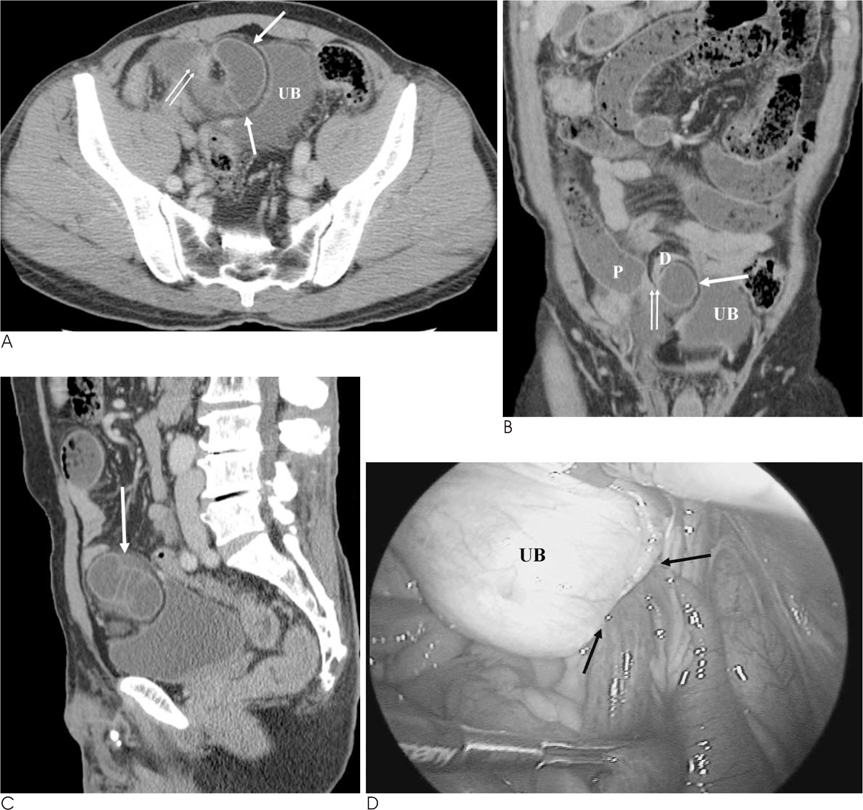
- A supravesical hernia occurs in the supravesical fossa and is either classified as an external or internal supravesical hernia. Most patients with internal supravesical hernias present with small bowel obstruction. Internal supravesical hernias are less common than external supravesical hernia. To date, there are few reports describing the radiological findings of supravesical hernias. To our knowledge, this is the first reported multidetector row CT (MDCT) depiction of this type of hernia. We report here on the MDCT findings of a patient with an internal supravesical hernia presenting with small bowel obstruction.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Takeyama N, Gokan T, Ohgiya Y, Satoh S, Hashizume T, Hataya K, et al. CT of internal hernias. Radiographics. 2005; 25:997–1015.2. Sasaya T, Yamaguchi A, Isogai M, Harada T, Kaneoka Y, Suzuki M. Supravesical hernia: CT diagnosis. Abdom Imaging. 2001; 26:89–91.3. Jan YT, Jeng KS, Liu YP, Yang FS. Internal supravesical hernia. Am J Surg. 2008; 196:e27–e28.4. Mehran A, Szomstein S, Soto F, Rosenthal R. Laparoscopic repair of an internal strangulated supravesical hernia. Surg Endosc. 2004; 18:554–556.5. Auh YH, Rubenstein WA, Schneider M, Reckler JM, Whalen JP, Kazam E. Extraperitoneal paravesical spaces: CT delineation with US correlation. Radiology. 1986; 159:319–328.6. Saravanan B, Paramu MK, Ranganathan E. Supravesical hernia - a rare cause of intestinal obstruction. Int J Surg. 2008; 6:471–472.7. Sozen I, Nobel J. Inguinal mass due to an external supravesical hernia and acute abdomen due to an internal supravesical hernia: a case report and review of the literature. Hernia. 2004; 8:389–392.8. Kusama M, Kimura K, Koyanagi Y, Ito S, Kaise H, Tamura K. A case of external supravesical hernia. Nippon Geka Gakkai Zasshi. 1993; 94:526–529.9. Tretbar LL, Gustafson GE. Internal supravesical hernia: a rare hernia causing small bowel obstruction. Am J Surg. 1968; 116:907–908.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Sacroiliitis in Ankylosing Spondylitis: Comparison with Multidetector Row CT and Plain Radiography
- Multidetector Row CT Findings of a Sternal Variation
- CT Findings of Congenital Transmesenteric Hernia: Case Report
- Multidetector-Row CT Findings of Gastric Cystic Lymphangioma: A Case Report
- A case of coronary artery-pulmonary artery fistula communicated with aorto-pulmonary fistula via common channel detected by Multidetector row CT (MDCT) and coronary angiography