J Korean Soc Radiol.
2013 Sep;69(3):243-250. 10.3348/jksr.2013.69.3.243.
Cumulative Radiation Exposures during Diagnosis and Treatments with Diagnostic Radiology Tools: In Patient with Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Chonnam National University Hospital, Gwangju, Korea. kjkrad@jnu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Radiology, Chonnam National University Hwasun Hospital, Hwasun, Korea.
- KMID: 2208808
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2013.69.3.243
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To evaluate the cumulative radiation dose for diagnosis and treatment with diagnostic radiology tools for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Cumulative radiation dose of 98 patients with hepatocellular carcinoma were examined by diagnostic CT, CT for follow-up, once or repeated transarterial chemoembolization (TACE), and X-ray examinations. Thus, we calculated the total cumulative effective doses per patient.
RESULTS
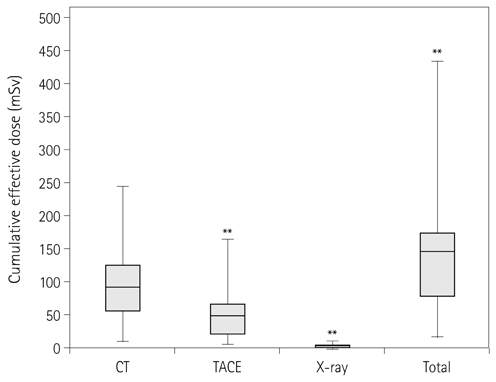
The mean follow-up periods were 85 (51-102) weeks. A total of 565 CT scans, 262 TACEs, and 1679 X-ray examinations were enrolled. Cumulative effective dose values per person of 91.4 +/- 50.6 (8.4-244.7) mSv, 49.2 +/- 44.7 (5.3-247.6) mSv, and 3.6 +/- 4.7 (0.02-22.04) mSv were measured for CT, TACE, and X-ray examinations. Total cumulative effective dose values per person were measured as 144.2 +/- 87.4 (15.4-513.5) mSv.
CONCLUSION
The patient who underwent TACE are exposed to pretty high dose radiations, thus, significant efforts to reduce the radiation dose are necessary.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Lee W. Current status of medical radiation exposure and regulation efforts. J Korean Med Assoc. 2011; 54:1248–1252.2. Lee SY, Lim HS, Han MS. The Evaluation of patients' radiation dose during TACE of interventional radiology. J Radiol Sci Technol. 2011; 34:209–214.3. Health Insurance Review & Assessment Service. 2005 National health insurance statistical yearbook. Seoul: Health Insurance Review & Assessment Service;2006.4. ICRP. 1990 Recommendations of the International Commission on Radiological Protection. ICRP publication 60. Stockholm, Sweden: ICRP;1991.5. ICRP. The 2007 recommendations of the International Commission on Radiological Protection. ICRP publication 103. Stockholm, Sweden: ICRP;2007.6. Valentin J. Avoidance of radiation injuries from medical interventional procedures. Ann ICRP. 2000; 30:7–67.7. Miller DL, Kwon D, Bonavia GH. Reference levels for patient radiation doses in interventional radiology: proposed initial values for U.S. practice. Radiology. 2009; 253:753–764.8. Chung JW. Korea Food & Drug Administration. Evaluation of patient dose in interventional radiology. Seoul: Korea Food & Drug Administration;2007.9. Llovet JM, Bruix J. Systematic review of randomized trials for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: chemoembolization improves survival. Hepatology. 2003; 37:429–442.10. Jessen KA, Shrimpton PC, Geleijns J, Panzer W, Tosi G. Dosimetry for optimisation of patient protection in computed tomography. Appl Radiat Isot. 1999; 50:165–172.11. Compagnone G, Giampalma E, Domenichelli S, Renzulli M, Golfieri R. Calculation of conversion factors for effective dose for various interventional radiology procedures. Med Phys. 2012; 39:2491–2498.12. Wall BF, Hart D. National Radiological Protection Board. Revised radiation doses for typical X-ray examinations. Report on a recent review of doses to patients from medical X-ray examinations in the UK by NRPB. Br J Radiol. 1997; 70:437–439.13. National Research Council (US). Committee to Assess Health Risks from Exposure to Low Levels of Ionizing Radiation. Health risks from exposure to low levels of ionizing radiation: BEIR VII phase 2. Washington DC: National Academies Press;2006.14. Preston DL, Ron E, Tokuoka S, Funamoto S, Nishi N, Soda M, et al. Solid cancer incidence in atomic bomb survivors: 1958-1998. Radiat Res. 2007; 168:1–64.15. International Agency for Research on Cancer. IARC monographs on the evaluation of carcinogenic risks to humans. Ionizing radiation: part 1. X- and gamma-radiation and neutrons. Lyon: International Agency for Research on Cancer;2000.16. Pierce DA, Preston DL. Radiation-related cancer risks at low doses among atomic bomb survivors. Radiat Res. 2000; 154:178–186.17. Brenner D, Elliston C, Hall E, Berdon W. Estimated risks of radiation-induced fatal cancer from pediatric CT. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2001; 176:289–296.18. United Nations Scientific Committee on the Effects of Atomic Radiation. Effect of ionizing radiation: UNSCEAR 2006 report to the general assembly with scientific annexes. Vienna: United Nations;2006.19. Valentin J. Low-dose extrapolation of radiation-related cancer risk. Ann ICRP. 2005; 35:1–140.20. Smith-Bindman R, Lipson J, Marcus R, Kim KP, Mahesh M, Gould R, et al. Radiation dose associated with common computed tomography examinations and the associated lifetime attributable risk of cancer. Arch Intern Med. 2009; 169:2078–2086.21. Jung SE. Korea Food & Drug Administration. Evaluation study of patient radiation dose in CT. Seoul: Korea Food & Drug Administration;2008.22. Park MY, Jung SE. CT radiation dose and radiation reduction strategies. J Korean Med Assoc. 2011; 54:1262–1268.23. Hidajat N, Mäurer J, Schröder RJ, Nunnemann A, Wolf M, Pauli K, et al. Relationships between physical dose quantities and patient dose in CT. Br J Radiol. 1999; 72:556–561.24. Kalender WA, Polacin A. Physical performance characteristics of spiral CT scanning. Med Phys. 1991; 18:910–915.25. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Safety Investigation of CT Brain Perfusion Scans. update 2010 Sep 11. accessed 2012 Sep 28. Available from: http://www.fda.gov/medicaldevices/safety/alertsandnotices/ucm185898.htm.26. Kang SJ. National Institute of Food and Drug Safety Evaluation. Guideline for optimization and justification of CT. Cheongwon: Korea Food & Drug Administration;2012.27. Mettler FA Jr, Huda W, Yoshizumi TT, Mahesh M. Effective doses in radiology and diagnostic nuclear medicine: a catalog. Radiology. 2008; 248:254–263.28. Jeong WK. Radiation exposure and its reduction in the fluoroscopic examination and fluoroscopy-guided interventional radiology. J Korean Med Assoc. 2011; 54:1269–1276.29. Balter S, Hopewell JW, Miller DL, Wagner LK, Zelefsky MJ. Fluoroscopically guided interventional procedures: a review of radiation effects on patients' skin and hair. Radiology. 2010; 254:326–341.30. Koenig TR, Wolff D, Mettler FA, Wagner LK. Skin injuries from fluoroscopically guided procedures: part 1, characteristics of radiation injury. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2001; 177:3–11.31. Griffey RT, Sodickson A. Cumulative radiation exposure and cancer risk estimates in emergency department patients undergoing repeat or multiple CT. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2009; 192:887–892.32. Sodickson A, Baeyens PF, Andriole KP, Prevedello LM, Nawfel RD, Hanson R, et al. Recurrent CT, cumulative radiation exposure, and associated radiation-induced cancer risks from CT of adults. Radiology. 2009; 251:175–184.33. Cardis E, Vrijheid M, Blettner M, Gilbert E, Hakama M, Hill C, et al. Risk of cancer after low doses of ionising radiation: retrospective cohort study in 15 countries. BMJ. 2005; 331:77.34. Bor D, Sancak T, Olgar T, Elcim Y, Adanali A, Sanlidilek U, et al. Comparison of effective doses obtained from dose-area product and air kerma measurements in interventional radiology. Br J Radiol. 2004; 77:315–322.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Imaging Diagnosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- Noninvasive diagnostic criteria for hepatocellular carcinoma
- Radiologic Diagnosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- Diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma: Which MRI contrast agent? Which diagnostic criteria?
- A Concise Review of Autoantibodies to Tumor-Associated Antigens for Diagnosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma