J Korean Soc Radiol.
2013 Sep;69(3):239-242. 10.3348/jksr.2013.69.3.239.
Cervical Spinal Monostotic Fibrous Dysplasia: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Haeundae Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea. okkimmd@hanafos.com
- KMID: 2208807
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2013.69.3.239
Abstract
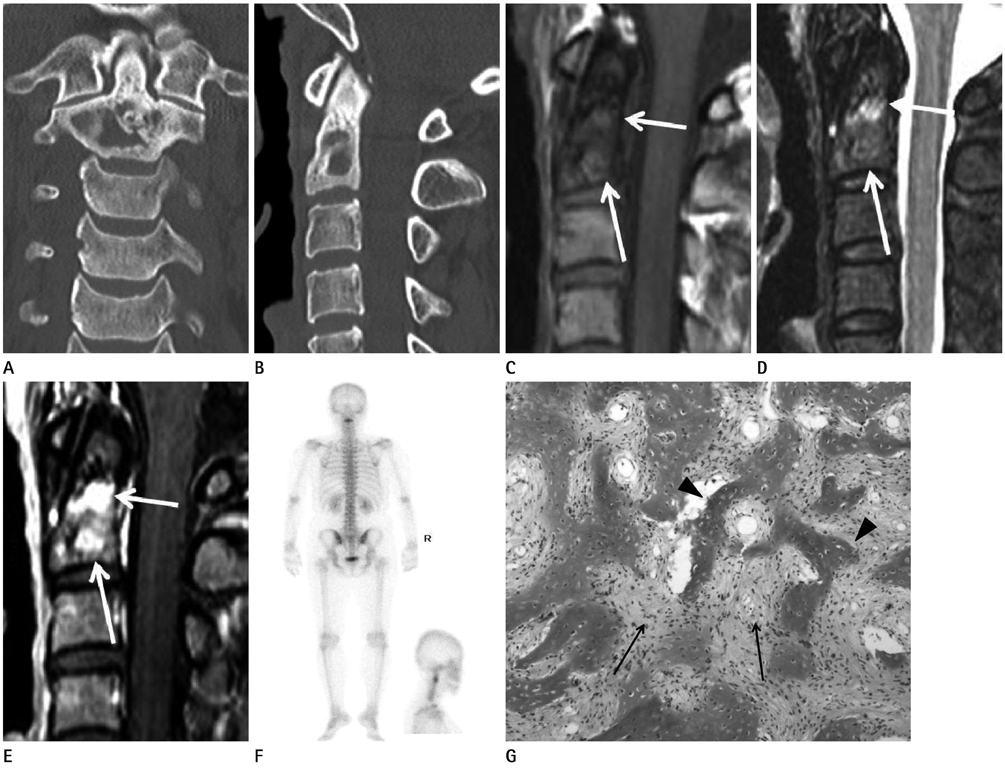
- Monostotic fibrous dysplasia of the cervical vertebra is quite unusual. The author reports a case of monostotic fibrous dysplasia affecting the second cervical vertebra with descriptions from the CT, MR and bone scanning findings.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Arantes M, Vaz AR, Honavar M, Resende M, Pereira JR. Fibrous dysplasia of the first cervical vertebra. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2008; 33:E933–E935.2. Proschek D, Orler R, Stauffer E, Heini P. Monostotic fibrous dysplasia of the spine: report of a case involving a cervical vertebra. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2007; 127:75–79.3. Schoenfeld AJ, Koplin SA, Garcia R, Hornicek FJ, Mankin HJ, Raskin KA, et al. Monostotic fibrous dysplasia of the spine: a report of seven cases. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2010; 92:984–988.4. Gogia N, Marwaha V, Atri S, Gulati M, Gupta R. Fibrous dysplasia localized to spine: a diagnostic dilemma. Skeletal Radiol. 2007; 36:Suppl 1. S19–S23.5. Mauras N, Blizzard RM. The McCune-Albright syndrome. Acta Endocrinol Suppl (Copenh). 1986; 279:207–217.6. Dreizin D, Glen C, Jose J. Mazabraud syndrome. Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ). 2012; 41:332–335.7. Kransdorf MJ, Moser RP Jr, Gilkey FW. Fibrous dysplasia. Radiographics. 1990; 10:519–537.8. Park SK, Lee IS, Choi JY, Cho KH, Suh KJ, Lee JW, et al. CT and MRI of fibrous dysplasia of the spine. Br J Radiol. 2012; 85:996–1001.9. Asazuma T, Sato M, Masuoka K, Yasuoka H, Tsuji T, Aida S. Monostotic fibrous dysplasia of the lumbar spine: case report and review of the literature. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2005; 18:535–538.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Monostotic Fibrous Dysplasia of the Cervical Spine: A Case Report
- Pathologic Fracture in Cervical Spine with Monostotic Fibrous Dysplasia: Case Report
- Monostotic Fibrous Dysplasia in the Metacarpal Bone: A Case Report
- Osteosarcoma Arising in Monostotic Fibrous Dysplasia of the Femur: A Case Report
- Monostotic Fibrous Dysplasia of Inferior Turbinate