J Korean Soc Radiol.
2016 Apr;74(4):245-253. 10.3348/jksr.2016.74.4.245.
Change of Apparent Diffusion Coefficient Immediately after Recanalization through Intra-Arterial Revascularization Therapy in Acute Ischemic Stroke
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Pusan National University Yangsan Hospital, Yangsan, Korea. skbaik9@gmail.com
- 2Department of Neurosurgery, Pusan National University Yangsan Hospital, Yangsan, Korea.
- 3Department of Neurology, Pusan National University Yangsan Hospital, Yangsan, Korea.
- KMID: 2208782
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2016.74.4.245
Abstract
- PURPOSE
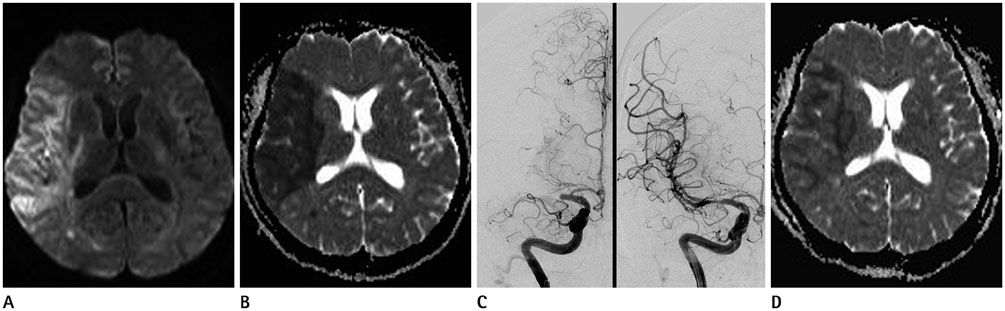
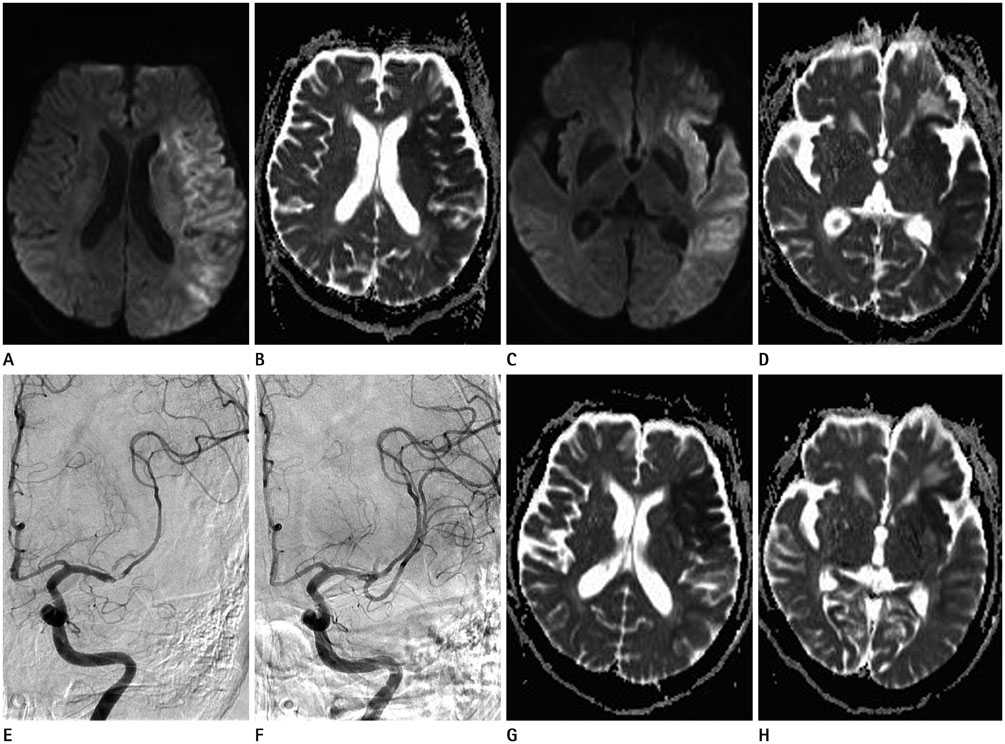
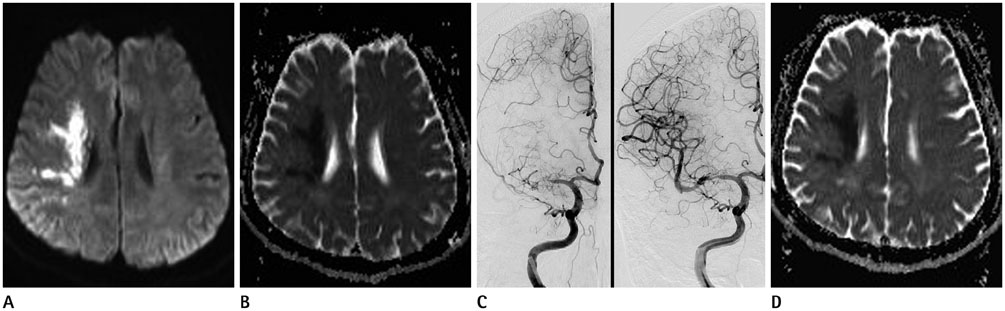
Intra-arterial revascularization therapy (IART) for acute ischemic stroke has become increasingly popular recently. However, early change in apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) values after full recanalization in human stroke has not received much attention. The aim of this study was to evaluate ADC changes immediately after interventional full-recanalization in patients with acute ischemic stroke.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
ADC values of 25 lesions from 18 acute ischemic stroke patients were recorded with both pre- and post-recanalization ADC maps. Measurement was done by placing region of interests over the representative images of the lesion. For analysis, lesions were divided into territorial infarction (TI) and watershed infarction (WI).
RESULTS
Mean ADC values of the overall 25 lesions before IART were 415.12 × 10(-6) mm2/sec, and increased to 619.08 × 10(-6) mm2/sec after the IART. Average relative ADC (rADC) value for 22 TI increased from 0.59 to 0.92 (p < 0.000), whereas, average rADC value for 3 WI did not change significantly.
CONCLUSION
There was a conspicuous increase of ADC values immediately after full-recanalization in TI lesions. On the other hand, WI lesions did not show significant change in ADC values after recanalization.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Schlaug G, Siewert B, Benfield A, Edelman RR, Warach S. Time course of the apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) abnormality in human stroke. Neurology. 1997; 49:113–119.2. An H, Ford AL, Vo K, Powers WJ, Lee JM, Lin W. Signal evolution and infarction risk for apparent diffusion coefficient lesions in acute ischemic stroke are both time- and perfusion-dependent. Stroke. 2011; 42:1276–1281.3. Schwamm LH, Koroshetz WJ, Sorensen AG, Wang B, Copen WA, Budzik R, et al. Time course of lesion development in patients with acute stroke: serial diffusion- and hemodynamic-weighted magnetic resonance imaging. Stroke. 1998; 29:2268–2276.4. Lansberg MG, Thijs VN, O'Brien MW, Ali JO, de Crespigny AJ, Tong DC, et al. Evolution of apparent diffusion coefficient, diffusion-weighted, and T2-weighted signal intensity of acute stroke. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2001; 22:637–644.5. Burdette JH, Ricci PE, Petitti N, Elster AD. Cerebral infarction: time course of signal intensity changes on diffusion-weighted MR images. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1998; 171:791–795.6. Chen F, Suzuki Y, Nagai N, Jin L, Yu J, Wang H, et al. Rodent stroke induced by photochemical occlusion of proximal middle cerebral artery: evolution monitored with MR imaging and histopathology. Eur J Radiol. 2007; 63:68–75.7. Jiang Q, Zhang RL, Zhang ZG, Ewing JR, Divine GW, Chopp M. Diffusion-, T2-, and perfusion-weighted nuclear magnetic resonance imaging of middle cerebral artery embolic stroke and recombinant tissue plasminogen activator intervention in the rat. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1998; 18:758–767.8. Minematsu K, Li L, Sotak CH, Davis MA, Fisher M. Reversible focal ischemic injury demonstrated by diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging in rats. Stroke. 1992; 23:1304–1310. discussion 1310-13119. Neumann-Haefelin T, Kastrup A, de Crespigny A, Yenari MA, Ringer T, Sun GH, et al. Serial MRI after transient focal cerebral ischemia in rats: dynamics of tissue injury, blood-brain barrier damage, and edema formation. Stroke. 2000; 31:1965–1972. discussion 1972-197310. Shen Q, Fisher M, Sotak CH, Duong TQ. Effects of reperfusion on ADC and CBF pixel-by-pixel dynamics in stroke: characterizing tissue fates using quantitative diffusion and perfusion imaging. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2004; 24:280–290.11. Taheri S, Candelario-Jalil E, Estrada EY, Rosenberg GA. Spatiotemporal correlations between blood-brain barrier permeability and apparent diffusion coefficient in a rat model of ischemic stroke. PLoS One. 2009; 4:e6597.12. Liebeskind DS. Reperfusion for acute ischemic stroke: arterial revascularization and collateral therapeutics. Curr Opin Neurol. 2010; 23:36–45.13. Kidwell CS, Saver JL, Mattiello J, Starkman S, Vinuela F, Duckwiler G, et al. Thrombolytic reversal of acute human cerebral ischemic injury shown by diffusion/perfusion magnetic resonance imaging. Ann Neurol. 2000; 47:462–469.14. Inoue M, Mlynash M, Christensen S, Wheeler HM, Straka M, Tipirneni A, et al. Early diffusion-weighted imaging reversal after endovascular reperfusion is typically transient in patients imaged 3 to 6 hours after onset. Stroke. 2014; 45:1024–1028.15. Higashida RT, Furlan AJ, Roberts H, Tomsick T, Connors B, Barr J, et al. Trial design and reporting standards for intra-arterial cerebral thrombolysis for acute ischemic stroke. Stroke. 2003; 34:e109–e137.16. Li F, Liu KF, Silva MD, Omae T, Sotak CH, Fenstermacher JD, et al. Transient and permanent resolution of ischemic lesions on diffusion-weighted imaging after brief periods of focal ischemia in rats: correlation with histopathology. Stroke. 2000; 31:946–954.17. Carmichael ST. Rodent models of focal stroke: size, mechanism, and purpose. NeuroRx. 2005; 2:396–409.18. Tagaya M, Liu KF, Copeland B, Seiffert D, Engler R, Garcia JH, et al. DNA scission after focal brain ischemia. Temporal differences in two species. Stroke. 1997; 28:1245–1254.19. Ringer TM, Neumann-Haefelin T, Sobel RA, Moseley ME, Yenari MA. Reversal of early diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging abnormalities does not necessarily reflect tissue salvage in experimental cerebral ischemia. Stroke. 2001; 32:2362–2369.20. Henninger N, Sicard KM, Fisher M. Spectacular shrinking deficit: insights from multimodal magnetic resonance imaging after embolic middle cerebral artery occlusion in Sprague-Dawley rats. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2007; 27:1756–1763.21. Marks MP, Tong DC, Beaulieu C, Albers GW, de Crespigny A, Moseley ME. Evaluation of early reperfusion and i.v. tPA therapy using diffusion- and perfusion-weighted MRI. Neurology. 1999; 52:1792–1798.22. Marchal G, Young AR, Baron JC. Early postischemic hyperperfusion: pathophysiologic insights from positron emission tomography. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1999; 19:467–482.23. Macfarlane R, Moskowitz MA, Sakas DE, Tasdemiroglu E, Wei EP, Kontos HA. The role of neuroeffector mechanisms in cerebral hyperperfusion syndromes. J Neurosurg. 1991; 75:845–855.24. Lee SK, Kim DI, Kim SY, Kim DJ, Lee JE, Kim JH. Reperfusion cellular injury in an animal model of transient ischemia. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2004; 25:1342–1347.25. Huang IJ, Chen CY, Chung HW, Chang DC, Lee CC, Chin SC, et al. Time course of cerebral infarction in the middle cerebral arterial territory: deep watershed versus territorial subtypes on diffusion-weighted MR images. Radiology. 2001; 221:35–42.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Reversal of a Large Ischemic Lesion with Low Apparent Diffusion Coefficient Value by Rapid Spontaneous Recanalization
- Superselective Intra-arterial Fibrinolysis for Acute Cerebral Ischemic Infarct: Usefulness of Diffusion Weighted MR Imaging1
- Evolution of Endovascular Therapy in Acute Stroke: Implications of Device Development
- Intra-arterial Thrombolytic Therapy in Acute Ischemic Stroke a Preliminary Study
- Percutaneous Transluminal Angioplasty of Intracranial Artery for the Treatment of Acute Ischemic Stroke