J Korean Rheum Assoc.
2010 Mar;17(1):66-70. 10.4078/jkra.2010.17.1.66.
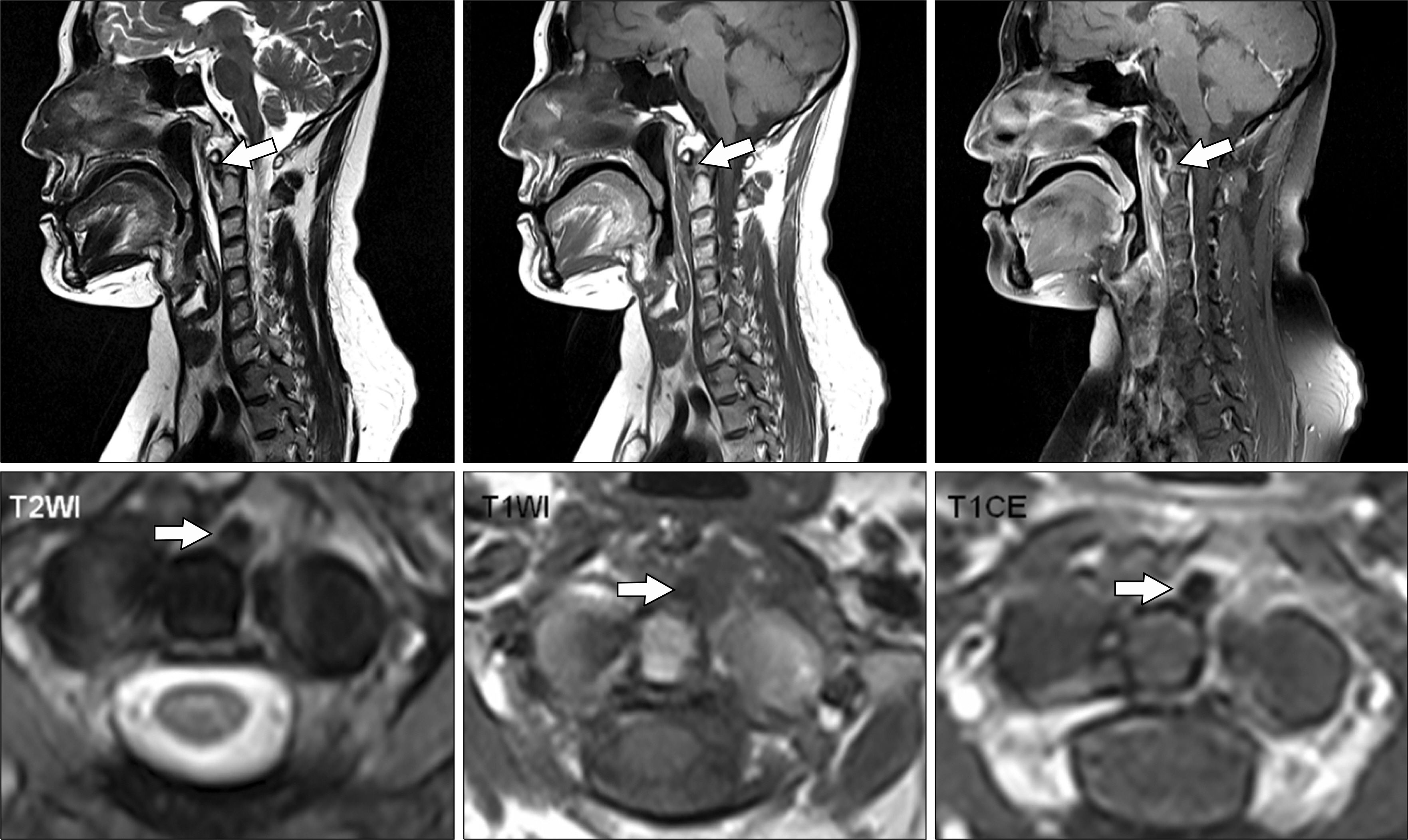
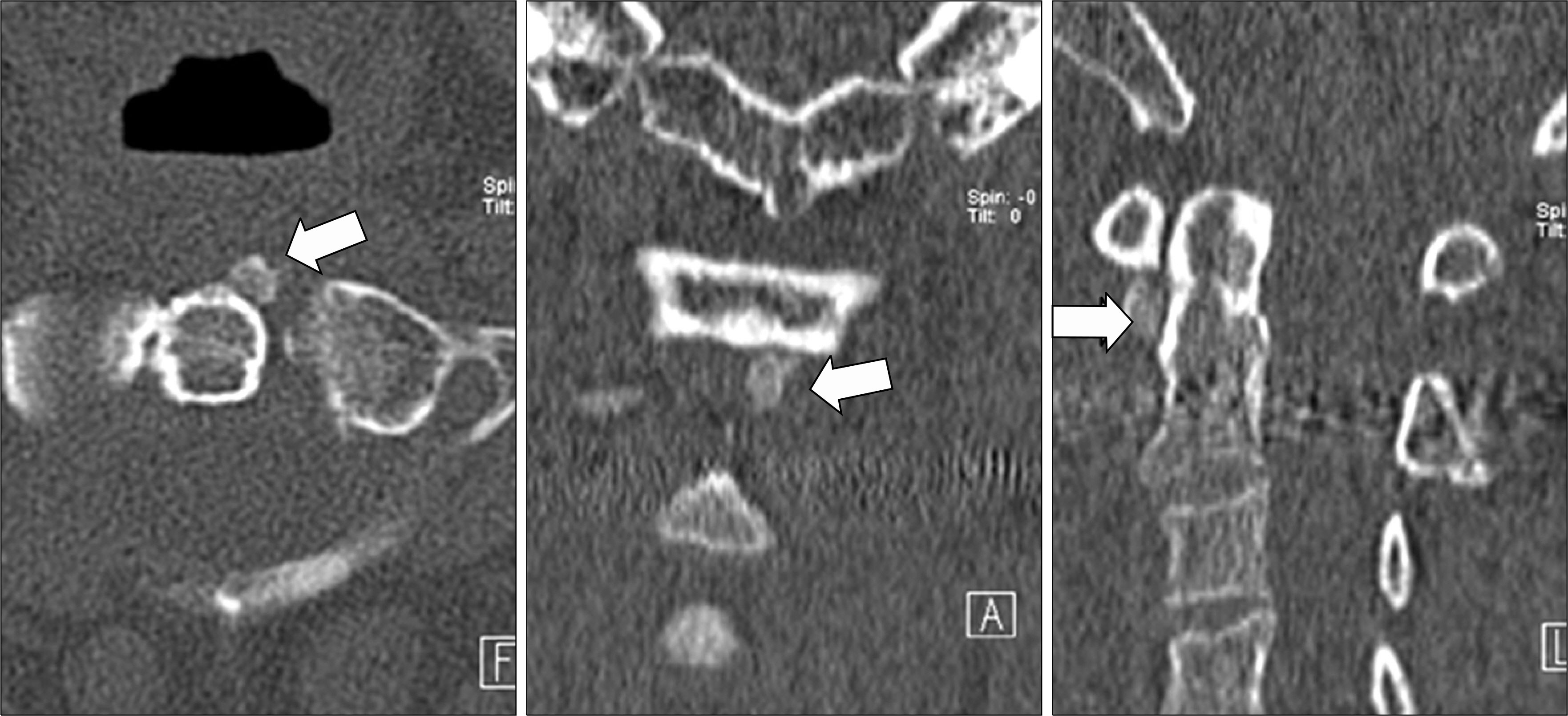
Calcific Tendinitis of the Longus Colli Muscle in a Patient with Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, College of Medicine, Jeju National University, Jeju, Korea. slera@cheju.ac.kr
- 2Department of Radiology, College of Medicine, Jeju National University, Jeju, Korea.
- KMID: 2201995
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4078/jkra.2010.17.1.66
Abstract
- No abstract available.
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
A Case of Retropharyngeal Calcific Tendinitis in a Patient with Ankylosing Spondylitis
Hyae Jin Yoon, Changnam Son, Seunghun Lee, Kungbin Joo, Tae Hwan Kim
J Rheum Dis. 2013;20(6):385-388. doi: 10.4078/jrd.2013.20.6.385.
Reference
-
1). Haun CL. Retropharyngeal tendinitis. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1978. 130:1137–40.
Article2). Hartley J. Acute cervical pain associated with retropharyngeal calcium deposit. A case report. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1964. 46:1753–4.3). Kaplan MJ., Eavey RD. Calcific tendinitis of the longus colli muscle. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1984. 93:215–9.
Article4). De Maeseneer M., Vreugde S., Laureys S., Sartoris DJ., De Ridder F., Osteaux MM. Calcific tendinitis of the longus colli muscle. Head Neck. 1977. 19:545–8.5). Artenian DJ., Lipman JK., Scidmore GK., Brant-Zawadzki M. Acute neck pain due to tendonitis of the longus colli: CT and MRI findings. Neuroradiology. 1989. 31:166–9.
Article6). Fahlgren H. Retropharyngeal tendinitis: three probable cases with an unusually low epicentre. Cephalalgia. 1988. 8:105–10.
Article7). Diaw AM., De Maeseneer M., Shahabpour M., Machiels F., Osteaux M. Calcium hydroxyapatite deposition disease of the neck: finding in three patients. J Belge Radiol. 1998. 81:73–4.8). Keats TE. The inferior accessory ossicle of the anterior arch of the atlas. Am J Roentgenol Radium Ther Nucl Med. 1967. 101:834–6.
Article9). Ekbom K., Torhall J., Annell K., Traff J. Magnetic resonance imaging in retropharyngeal tendinitis. Cephalalgia. 1994. 14:266–9.
Article10). Mihmanli I., Karaarslan EK. Kanberoglu K. Inflammation of vertebral bone associated with acute calcific tendinitis of the longus colli muscle. Neuroradiology. 2001. 43:1098–101.11). Constantin A., Marin F., Bon E., Fedele M., Lagarrigue B., Bouteiller G. Calcification of the transverse ligament of the atlas in chondrocalcinosis: computed tomography study. Ann Rheum Dis. 1996. 55:137–9.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Acute Retropharyngeal Calcific Tendinitis in an Unusual Location: a Case Report in a Patient with Rheumatoid Arthritis and Atlantoaxial Subluxation
- Acute Calcific Prevertebral Tendinitis without Differentiated by Simple X-ray
- Acute Longus Colli Tendinitis without Calcification
- Acute Calcific Tendinitis of the Longus Colli Muscle in the Cervical Spine
- The Acute Calcific Prevertebral Tendinitis: Report of Two Cases