J Korean Rheum Assoc.
2010 Dec;17(4):360-367. 10.4078/jkra.2010.17.4.360.
Associations between TBX21 Gene Polymorphisms and Korean Patients with Behcet's Disease
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Chungnam National University School of Medicine, Daejeon, Korea. kangsw@cnuh.co.kr
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea.
- 3Department of Internal Medicine, Hallym University College of Medicine, Kangdong Sacred Heart Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Internal Medicine, Gil Medical Center, Gachon University of Medicine and Science, Incheon, Korea.
- KMID: 2201893
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4078/jkra.2010.17.4.360
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
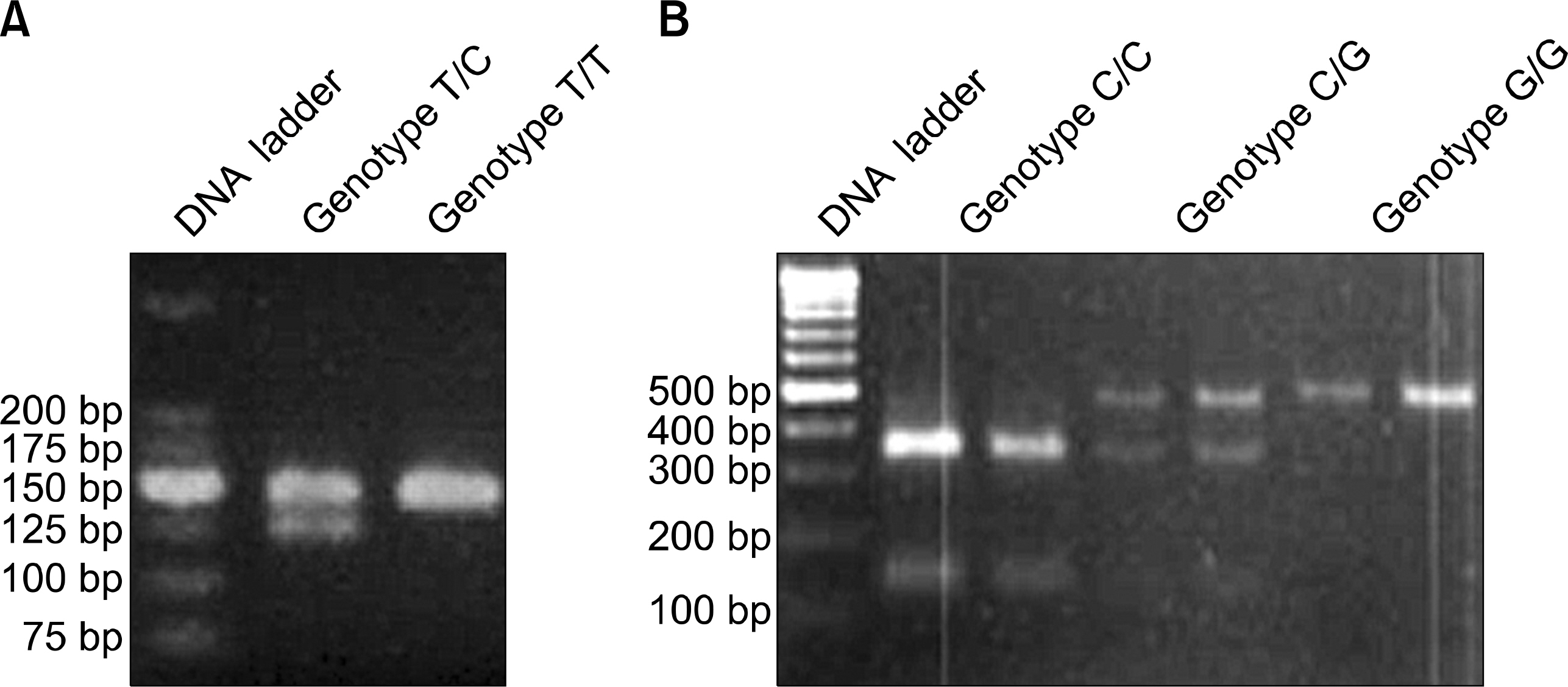
Behcet's disease (BD) is a chronic systemic inflammatory disease with unknown etiology. A number of clinical and laboratory findings suggest a strongly polarized Th1 immune response in BD. T-bet is a newly identified Th1 specific T-box transcription factor selectively expressed in Th1 cells. However, it is not yet clear whether the T-bet protein is involved in the proposed Th1-mediated pathogenesis of BD at the transcriptional level. Therefore, this study investigated the potential associations of two single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) at positions -99 (C/G) and -1993 (T/C) in the exon and promoter regions of the TBX21 gene with susceptibility to BD in the Korean population.
METHODS
105 patients with BD and 105 healthy controls were studied. All subjects were genotyped using restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis. The genotypes of the two groups were compared with the chi-square or Fisher's exact tests.
RESULTS
The genotypic and allelic distributions of the two SNPs did not differ significantly between the two groups. Furthermore, no associations between the polymorphisms and clinical manifestations were found, except a central nervous system manifestation and arthritis. Furthermore, no associations between the polymorphisms and severity were identified.
CONCLUSION
TBX21 gene polymorphisms were not associated with susceptibility, clinical manifestations, or severity of BD in the Korean population.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1). Sakane T., Takeno M., Suzuki N., Inaba G. Behcet's disease. N Engl J Med. 1999. 341:1284–91.2). Jang WC., Park SB., Nam YH., Lee SS. Interleukin-18 gene polymorphisms in Korean patients with Behcet's disease. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2005. ;23 (4 Suppl 38): S59-63.3). Chang HK., Kim JW. The clinical features of Behcet's disease in Yongdong districts: analysis of a cohort followed from 1997 to 2001. J Korean Med Sci. 2002. 17:784–9.
Article4). Chang HK., Kim JU. The study of HLA antigens in a familial Behcet's disease. J Korean Rheum Assoc. 2000. 7:20–5.5). Bang D., Yoon KH., Chung HG., Choi EH., Lee ES., Lee S. Epidemiological and clinical features of Behcet's disease in Korea. Yonsei Med J. 1997. 38:428–36.6). Kaklamani VG., Vaiopoulos G., Kaklamanis PG. Behcet's Disease. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 1998. 27:197–217.7). Gul A. Behcet's disease: an update on the pathogenesis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2001. ;19 (5 Suppl 24): S6-12.8). Direskeneli H. Behcet's disease: infectious aetiology, new auto antigens and HLA-B51. Ann Rheum Dis. 2001. 60:996–1002.9). Li B., Yang P., Zhou H., Zhang Z., Xie C., Lin X, et al. T-bet expression is up regulated in active Behcet's disease. Br J Ophthalmol. 2003. 87:1264–67.10). Akahoshi M., Obara K., Hirota T., Matsuda A., Takahashi N. Functional promotor polymorphism in the TBX21 gene associated with aspirin-induced asthma. Hum Genet. 2005. 117:16–26.11). Sasaki Y., Ihara K., Kuromaru R., Kusuhara K., Hara T. Identification of a novel type 1 diabetes susceptibility gene, T-bet. Hum Genet. 2004. 115:177–84.
Article12). Wang J., Fathman JW., Lugo-Villarino G. Transcription factor T-bet regulates inflammatory arthritis through its function in dendritic cells. J Clin Invest. 2006. 116:414–21.
Article13). Frohman EM., Racke MK., Raine CS. Multiple sclerosis-the plaque and its pathogenesis. N Engl J Med. 2006. 354:942–55.14). International study group for Behcet's disease. Criteria for diagnosis of Behcet's disease. Lancet. 1990. 335:1078–80.15). GuUl A., Uyar A., Inanc M., OUcal L., Tugal-Tutkun I., Aral O, et al. Lack of association of HLA-B51 with a severe disease course in BehcLet's disese. Rheumatology. 2001. 40:668–72.16). Fortune F., Walker J., Lehner T. The expression of gamma delta T cell receptor and the prevalence of primed, activated and IgA-bound T cells in Behcet's syndrome. Clin Exp Immunol. 1990. 82:326–32.17). Suzuki Y., Hoshi K., Matsuda T., Mizushima Y. Increased peripheral blood gamma delta+ T cells and natural killer cells in Behcet's disease. J Rheumatol. 1992. 19:588–92.18). Hamzaoui K., Hamzaoui A., Hentati F., Kahan A., Ayed K., Chabbou A, et al. Phenotype and functional profile of T cells expressing gamma delta receptor from patients with active Behcet's disease. J Rheumatol. 1994. 21:2301–6.19). Bank I., Duvdevani M., Livneh A. Expansion of gammadelta T-cells in Behcet's disease: role of disease activity and microbial flora in oral ulcers. J Lab Clin Med. 2003. 141:33–40.20). Freysdottir J., Lau S., Fortune F. Gammadelta T cells in Behcet's disease (BD) and recurrent aphthous stomatitis (RAS). Clin Exp Immunol. 1999. 118:451–7.21). Szabo SJ., Kim ST., Costa GL., Zhang X., Fathman CG., Glimcher LH. A novel transcription factor, T-bet, direct Th1 lineage commitment. Cell. 2000. 100:655.22). Grogan JL., Mohrs M., Harmon B. Early transcription and silencing of cytokine genes underlie polarization of T helper cell subsets. Immunity. 2001. 14:205–15.
Article23). Mullen AC., High FA., Hutchins AS. Role of T-bet in commitment of TH1 cells before IL-12-dependent selection. Science. 2001. 292:1907–10.24). Frassanito MA., Dammacco R., Cafforio P., Dammacco F. Th1 polarization of the immune response in Behcet's disease, a putative pathogenetic role of interleukin-12. Arthritis Rheum. 1999. 42:1967–74.25). Sugi-Ikai N., Nakazawa M., Nakamura S., Ohno S., Minami M. Increased frequencies of interleukin-2 and interferon-gamma-producing T cells in patients with active Behcet's disease. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1998. 39:996–1004.26). Frassanito MA., Dammacco R., Cafforio P., Dammacco F. Th1 polarization of the immune response in Behcet's disease: a putative pathogenetic role of inter-leukin-12. Arthritis Rheum. 1999. 42:1967–74.27). Chang HK., Lee SS., Kim JW., Jee YK., Kim JU., Lee YW, et al. The prevalence of atopy and atopic diseases in Behcet's disease. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2003. ;21 (4 Suppl 30): S31-4.28). Hajeer AH., Hutchinson IV. Influence of TNF alpha gene polymorphisms on TNF alpha production and disease. Hum Immunol. 2001. 62:1191–9.29). Evereklioglu C., Er H., Turkoz Y., Cekmen M. Serum levels of TNF-alpha, sIL-2R, IL-6 and IL-8 are increased and associated with elevated lipid peroxidation in patients with Behcet's disease. Mediators Inflamm. 2002. 11:87–93.30). Turan B., Gallati H., Erdi H., Gurler A., Michel BA., Villiger PM. Systemic levels of the T cell regulatory cytokines IL-10 and IL-12 in Bechcet's disease; soluble TNFR-75 as a biological marker of disease activity. J Rheumatol. 1997. 24:128–32.31). Yamashita N., Kaneoka H., Kaneko S., Takeno M., Oneda K., Koizumi H, et al. Role of gammadelta T lymphocytes in the development of Behcet's disease. Clin Exp Immunol. 1997. 107:241–7.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Association of TBX21 polymorphisms in a Korean population with rheumatoid arthritis
- Polymorphisms of TNF-alpha Gene and TNF Receptor Gene in Behcet's Disease
- Circulating VEGF levels and genetic polymorphisms in Behçet’s disease: a meta-analysis
- Genetic Associations of Mitochondrial DNA Polymorphisms with Behcet's Disease in a Korean Population: A Pilot Study
- A Case of Behcet's Disease Associated with Pyoderma Gangrenosum