J Korean Neurotraumatol Soc.
2010 Jun;6(1):43-47. 10.13004/jknts.2010.6.1.43.
Relationship between the Level of Fibrinogen and the Signal Density on Brain Computed Tomography in the Chronic Subdural Hematoma
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, College of Medicine, Kyungpook National University, Kyungpook National University Hospital, Daegu, Korea. nsdoctor@naver.com
- KMID: 2192363
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.13004/jknts.2010.6.1.43
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the relationship between fibrinogen levels and computed tomography (CT) findings in patients who had chronic subdural hematomas (CSDHs).
METHODS
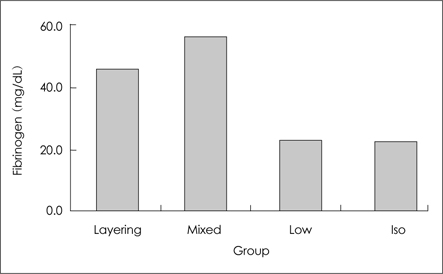
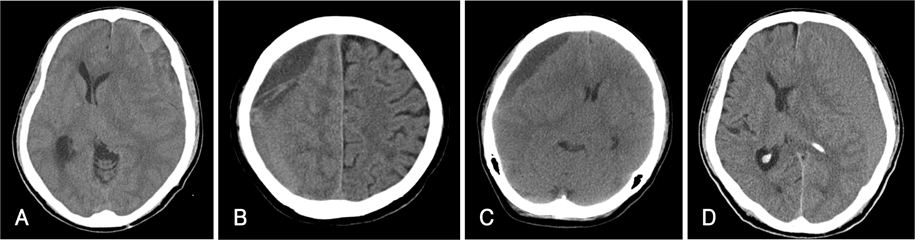
The study group was composed of 12 consecutive patients who had CSDH between January and December 2006. Patients with CSDH were divided on the basis of CT findings into group A (layering, mixed type) and group B (low, iso type). We performed surgery and obtained a sample from the subdural hematoma for measurement of the concentration of fibrinogen.
RESULTS
The mean level of fibrinogen was 57.3 mg/dL in group A, and in <25 mg/dL group B. The concentration of fibrinogen was significantly higher in the layering and mixed type group than in the low and iso type group (p=0.003).
CONCLUSION
The layering, mixed type of CSDH demonstrated higher concentrations of fibrinogen in subdural hematomas than in low, iso type patients.
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Factors Affecting Postoperative Recurrence of Chronic Subdural Hematoma
Woo-Keun Kong, Byong-Chul Kim, Keun-Tae Cho, Seung-Koan Hong
Korean J Neurotrauma. 2012;8(2):122-127. doi: 10.13004/kjnt.2012.08.0.122.A Clinical Analysis in Risk Factors of Chronic Subdural Hematoma: Focusing on the Age
Yang-Won Sim, Kyung-Soo Min, Mou-Seop Lee, Young-Gyu Kim, Dong-Ho Kim
Korean J Neurotrauma. 2012;8(2):115-121. doi: 10.13004/kjnt.2021.8.0.115.
Reference
-
1. Elms MJ, Bunce IH, Bundesen PG, Rylatt DB, Webber AJ, Masci PP, et al. Rapid detection of cross-linked fibrin degradation products in plasma using monoclonal antibody-coated latex particles. Am J Clin Pathol. 1986; 85:360–364.
Article2. Frati A, Salvati M, Mainero F, Ippoliti F, Rocchi G, Raco A, et al. Inflammation markers and risk factors for recurrence in 35patients with a posttraumatic chronic subdural hematoma: a prospective study. J Neurosurg. 2004; 100:24–32.3. Fujisawa H, Ito H, Saito K, Ikeda K, Nitta H, Yamashita J. Immunohistochemical localization of tissue-type plasminogen activator in the lining wall of chronic subdural hematoma. Surg Neurol. 1991; 35:441–445.
Article4. Ito H, Komai T, Yamamoto S. Fibrinolytic enzyme in the lining walls of chronic subdural hematoma. J Neurosurg. 1978; 48:197–200.
Article5. Ito H, Saito K, Yamamoto S, Hasegawa T. Tissue-type plasminogen activator in the chronic subdural hematoma. Surg Neurol. 1988; 30:175–179.
Article6. Kao MC. Sedimentation level in chronic subdural hematoma visible of computerized tomography. J Neurosurg. 1983; 58:246–251.7. Katano H, Kamiya K, Mase M, Tanikawa M, Yamada K. Tissue plasminogen activator in chronic subdural hematomas as a predictor of recurrence. J Neurosurg. 2006; 104:79–84.
Article8. Kawakami Y, Chikama M, Tamiya T, Shimamura Y. Coagulation and fibrinolysis in chronic subdural hematoma. Neurosurgery. 1989; 25:25–29.
Article9. Ko BS, Lee JK, Seo BR, Moon SJ, Kim JH, Kim SH. Clinical analysis of risk factors related to recurrent chronic subdural hematoma. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2008; 43:11–15.
Article10. Lim DJ, Chung YG, Park YK, Song JH, Lee HK, Lee KC, et al. Relationship between tissue plasminogen activator inhibitor and CT image in chronic subdural hematoma. J Korean Med Sci. 1995; 10:373–378.11. Markwalder TM. Chronic subdural hematomas: a review. J Neurosurg. 1981; 54:637–645.
Article12. Matsumoto M, Sakata Y, Yamazaki T, Endo G, Ohishi H, Takasu N. Local coagulofibrinolysis in the postsurgical recovery of patients with chronic subdural hematoma. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 1999; 141:177–181.13. Mosesson MW. Fibrinogen and fibrin structure and functions. J Thromb Haemost. 2005; 3:1894–1904.
Article14. Murakami H, Hirose Y, Sagoh M, Shimizu K, Kojima M, Gotoh K, et al. Why do chronic subdural hematomas continue to grow slowly and not coagulate? Role of thrombomodulin in the mechanism. J Neurosurg. 2002; 96:877–884.
Article15. Nakaguchi H, Tanishima , Yoshimasu N. Factors in the natural history of chronic subdural hematomas that influences their postoperative recurrences. J Neurosurg. 2001; 95:256–262.16. Nomura S, Kashiwagi S, Fujisawa H, Ito H, Nakamura K. Characterization of local hyperfibrinolysis in chronic subdural hematoma by SDS-PAGE and immunoblot. J Neurosurg. 1994; 81:910–913.17. Park SH, Lee SH, Park J, Hwang JH, Hamn IS. Chronic subdural hematoma preceded by traumatic subdural hygroma. J Clin Neurosci. 2008; 15:868–872.
Article18. Saito K, Ito H, Hasegawa T, Yamamoto S. Plasmin-alpha 2-plasmin inhibitor complex and alpha 2-plasmin inhibitor in chronic subdural hematoma. J Neurosurg. 1989; 70:68–72.19. Suzuki M, Endo S, Inada K, Kudo A, Kitakami A, Kuroda K, et al. Inflammatory cytokines locally elevated in chronic subdural hematoma. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 1998; 140:51–55.20. Suzuki M, Kudo A, Kitakami A, Doi M, Kubo N, Kuroda K, et al. Local hypercoagulative activity precedes hyperfibrinolytic activity in the subdural space during development of chronic subdural hematoma from subdural effusion. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 1998; 140:261–265. discussion 265-266.21. Weir B, Gordon P. Factors affection coagulation: fibrinolysis in chronic subdural fluid collections. J Neurosurg. 1983; 58:242–245.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Relationship of Fibrinogen Degradation Products to Clinical Findings in Chronic Subdural Hematoma
- Evolution of Chronic Subdural Hematoma based on Brain CT findings and Appropriate Treatment Methods
- Acute-on-chronic subdural hematoma by spinal anesthesia in a patient with undiagnosed chronic subdural hematoma: A case report
- Chronic Subdural Hematoma Superimposed on Posttraumatic Subdural Hygroma: A Report of Three Cases
- A Case of Infected Subdural Hematoma