J Korean Neurosurg Soc.
2015 Nov;58(5):491-493. 10.3340/jkns.2015.58.5.491.
Neuralgic Amyotrophy Manifesting as Mimicking Posterior Interosseous Nerve Palsy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Chuncheon Sacred Heart Hospital, College of Medicine, Hallym University, Chuncheon, Korea. nssur771@hallym.or.kr
- 2Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Chuncheon Sacred Heart Hospital, College of Medicine, Hallym University, Chuncheon, Korea.
- KMID: 2191419
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2015.58.5.491
Abstract
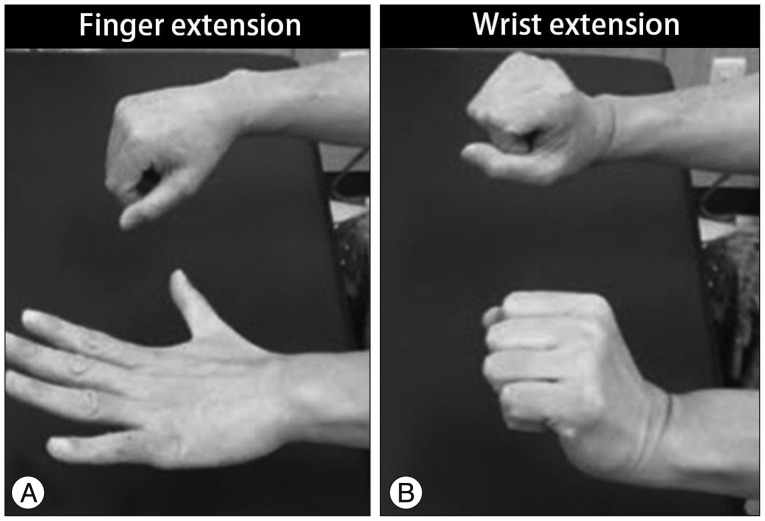
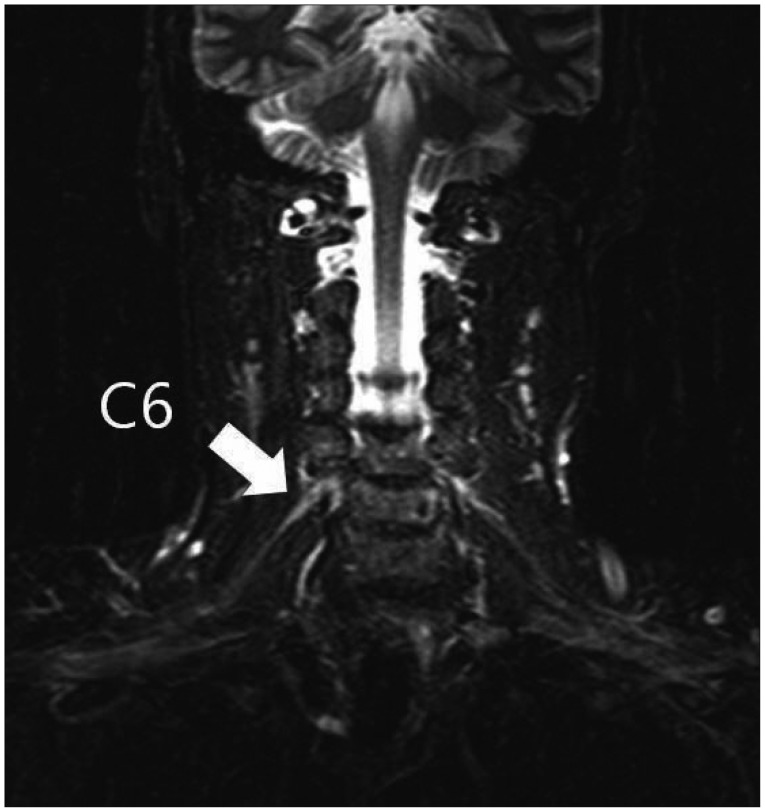
- The upper trunk of the brachial plexus is the most common area affected by neuralgic amyotrophy (NA), and paresis of the shoulder girdle muscle is the most prevalent manifestation. Posterior interosseous nerve palsy is a rare presentation in patients with NA. It results in dropped finger on the affected side and may be misdiagnosed as entrapment syndrome or compressive neuropathy. We report an unusual case of NA manifested as PIN palsy and suggest that knowledge of clinical NA phenotypes is crucial for early diagnosis of peripheral nerve palsies.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Avram R, Hynes NM. Posterior interosseous nerve compression secondary to a parosteal lipoma : case report and literature review. Can J Plast Surg. 2004; 12:69–72. PMID: 24115878.2. Derkash RS, Niebauer JJ. Entrapment of the posterior interosseous nerve by a fibrous band in the dorsal edge of the supinator muscle and erosion of a groove in the proximal radius. J Hand Surg Am. 1981; 6:524–526. PMID: 7276485.
Article3. Duman I, Guvenc I, Kalyon TA. Neuralgic amyotrophy, diagnosed with magnetic resonance neurography in acute stage : a case report and review of the literature. Neurologist. 2007; 13:219–221. PMID: 17622915.
Article4. Hashizume H, Nishida K, Nanba Y, Shigeyama Y, Inoue H, Morito Y. Non-traumatic paralysis of the posterior interosseous nerve. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1996; 78:771–776. PMID: 8836068.
Article5. Jou IM, Wang HN, Wang PH, Yong IS, Su WR. Compression of the radial nerve at the elbow by a ganglion : two case reports. J Med Case Rep. 2009; 3:7258. PMID: 19830153.
Article6. Rosenbaum R. Disputed radial tunnel syndrome. Muscle Nerve. 1999; 22:960–967. PMID: 10398221.
Article7. Tjoumakaris FP, Anakwenze OA, Kancherla V, Pulos N. Neuralgic amyotrophy (Parsonage-Turner syndrome). J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2012; 20:443–449. PMID: 22751163.
Article8. Tsairis P, Dyck PJ, Mulder DW. Natural history of brachial plexus neuropathy. Report on 99 patients. Arch Neurol. 1972; 27:109–117. PMID: 4339239.9. van Alfen N. Clinical and pathophysiological concepts of neuralgic amyotrophy. Nat Rev Neurol. 2011; 7:315–322. PMID: 21556032.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Current Concepts of Anterior Interosseous Nerve Syndrome
- Delayed palsy of Posterior Interosseous Nerve due to compression of the Arcade of Frohse and old anterior dislocation of the radial head
- Posterior Interosseous Nerve Syndrome: Case of Report
- Successful recovery of anterior interosseous nerve palsy caused by blunt trauma at the forearm level: a case report
- Incomplete Anterior Interosseous Nerve Palsy That Accompanied a Monteggia Fracture