J Korean Neurosurg Soc.
2014 Jun;55(6):365-369. 10.3340/jkns.2014.55.6.365.
Spinal Epidural Lipomatosis in Korean
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Cheju Halla Hospital, Jeju, Korea. sangpyung@yahoo.co.kr
- KMID: 2191119
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2014.55.6.365
Abstract
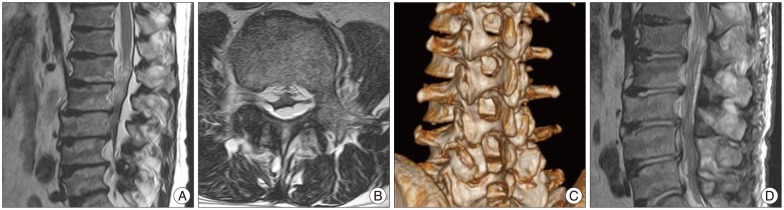
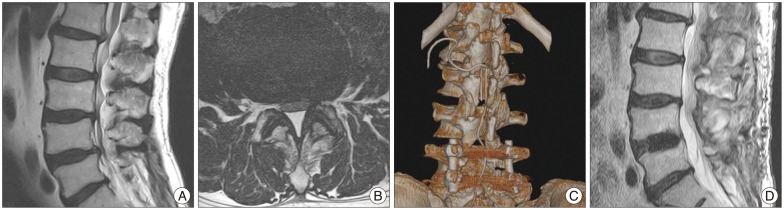
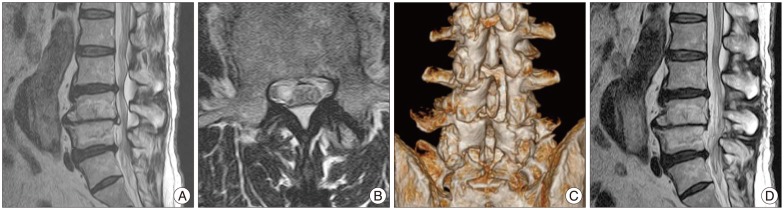
- Spinal epidural lipomatosis (SEL) is a rare disorder, regarded in literature as a consequence of administration of exogenous steroids, associated with a variety of systemic diseases, endocrinopathies and the Cushing's syndrome. Occasionally, SEL may occur in patients not exposed to steroids or suffering from endocrinopathies, namely, idiopathic SEL. Thus far, case studies of SEL among Korean have been published rather sporadically. We reviewed the clinical features of SEL cases, among Koreans with journal review, including this report of three operated cases. According to this study, there were some differences between Korean and western cases. Koreans had higher incidences of idiopathic SEL, predominant involvement in the lumbar segments, very few thoracic involvement and lower MBI, as opposed to westerners.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Al-Khawaja D, Seex K, Eslick GD. Spinal epidural lipomatosis--a brief review. J Clin Neurosci. 2008; 15:1323–1326. PMID: 18954986.2. Badami JP, Hinck VC. Symptomatic deposition of epidural fat in a morbidly obese woman. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1982; 3:664–665. PMID: 6816044.3. Chang H, Bahk WJ, Lim KH. Lumbar epidural lipomatosis. J Korean Soc Spine Surg. 1996; 3:256–251.4. Choi KC, Kang BU, Lee CD, Lee SH. Rapid progression of spinal epidural lipomatosis. Eur Spine J. 2012; 21(Suppl 4):S408–S412. PMID: 21667131.
Article5. Choi SM, Choi G, Lee SH. Cauda equina syndrome due to spinal epidural lipomatosis. Korea J Spine. 2005; 2:65–67.6. Choy WS, Kim HJ, Kim KH, Ong SS, Park JH. Lumbar epidural lipomatosis. J Korean Soc Spine Surg. 1998; 5:136–142.7. Doo TH, Kim HJ, Shin DA. Lumbosacral epidural lipomatosis with compressive neuropathy. New Med J. 2006; 49:43–47.8. Fan CY, Wang ST, Liu CL, Chang MC, Chen TH. Idiopathic spinal epidural lipomatosis. J Chin Med Assoc. 2004; 67:258–261. PMID: 15357116.9. Fogel GR, Cunningham PY 3rd, Esses SI. Spinal epidural lipomatosis : case reports, literature review and meta-analysis. Spine J. 2005; 5:202–211. PMID: 15795966.
Article10. Haddad SF, Hitchon PW, Godersky JC. Idiopathic and glucocorticoid-induced spinal epidural lipomatosis. J Neurosurg. 1991; 74:38–42. PMID: 1984504.
Article11. Han YM, Ahn MS. Idiopathic spinal epidural lipomatosis. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2001; 30:795–799.12. Ju WI, Ahn JG, Ji C, Park SC, Cho KS, Park CK, et al. Spinal epidural lipomatosis. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 1999; 28:110–113.13. Kawai M, Udaka F, Nishioka K, Houshimaru M, Koyama T, Kameyama M. A case of idiopathic spinal epidural lipomatosis presented with radicular pain caused by compression with enlarged veins surrounding nerve roots. Acta Neurol Scand. 2002; 105:322–325. PMID: 11939947.
Article14. Kim DY, Kim JW, Jeong JH, Choi JH. Symptomatic spinal epidural lipomatosis secondary to obesity. Kosin Med J. 2008; 23:111–113.15. Kim HS, Han IH, Lee JH, Choi BK. Symptomatic spinal epidural lipomatosis induced by repeated epidural steroid injections. Korean J Spine. 2009; 6:218–220.16. Kim IW, Koo CH, Park JS, Baek SU, Lee SD, Lee KH, et al. Adrenal cortical adenoma associated with spinal epidural lipomatosis and paraplegia. J Korean Pediatr Soc. 1986; 29:86–92.17. Kim NG, Choi NC, Kwon OY, Jeon SC, Lim BH. A case of spinal epidural lipomatosis associated with phenytoin induced hypothyroidism and obesity. J Korean Neurol Assoc. 1997; 15:670–676.18. Kim SY. Spinal epidural lipomatosis : a case report. Korean J Pain. 2009; 22:249–252.19. Kim TW, Huh YS, Chi MP, Kim JO, Kim JC. Spinal epidural lipomatosis : report of four cases. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2000; 29:1527–1532.20. Lee M, Lekias J, Gubbay SS, Hurst PE. Spinal cord compression by extradural fat after renal transplantation. Med J Aust. 1975; 1:201–203. PMID: 1092979.
Article21. Lee SB, Park HK, Chang JC, Jin SY. Idiopathic thoracic epidural lipomatosis with chest pain. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2011; 50:130–133. PMID: 22053234.
Article22. Lee SS, Ha GH, Yon JH, Son JY, Hong KH, Shin DY. Epidural lipomatosis discovered during managing of lower back pain : a case report. Korean J Anesthesiol. 1998; 35:381–384.
Article23. Min WK, Oh CW, Jeon IH, Kim SY, Park BC. Decompression of idiopathic symptomatic epidural lipomatosis of the lumbar spine. Joint Bone Spine. 2007; 74:488–490. PMID: 17681857.24. Park GY, Cho JH, Lee SY. Lumbar spinal stenosis induced by epidural lipomatosis : a case report. J Korean Acad Rehabil Med. 2004; 28:618–621.25. Park SH, Rho SW, Sung KH. Idiopathic spinal epidural lipomatosis. Korean J Spine. 2006; 3:99–101.26. Robertson SC, Traynelis VC, Follett KA, Menezes AH. Idiopathic spinal epidural lipomatosis. Neurosurgery. 1997; 41:68–74. discussion 74-75. PMID: 9218297.
Article27. Seong BY, Park CJ, Park SJ, Kim SW, Lee TG. Lumbar spinal epidural lipomatosis : two cases report. J Korean Soc Spine Surg. 1998; 5:333–341.28. Yim YB, Jo YJ, Kim DS, Jeong DS, Park KH, Song GS, et al. Idiopathic spinal epidural lipomatosis in a non-obese healthy man. J Korean Neurol Assoc. 1998; 16:402–407.