J Korean Neurosurg Soc.
2014 Mar;55(3):178-180. 10.3340/jkns.2014.55.3.178.
Management of Otogenic Brain Abscess Using the Transmastoid Approach
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Otorhinolaryngology-Head & Neck Surgery, Korea University Ansan Hospital, Ansan, Korea.
- 2Department of Neurosurgery, Korea University Ansan Hospital, Ansan, Korea. neuron19@korea.ac.kr
- KMID: 2191088
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2014.55.3.178
Abstract
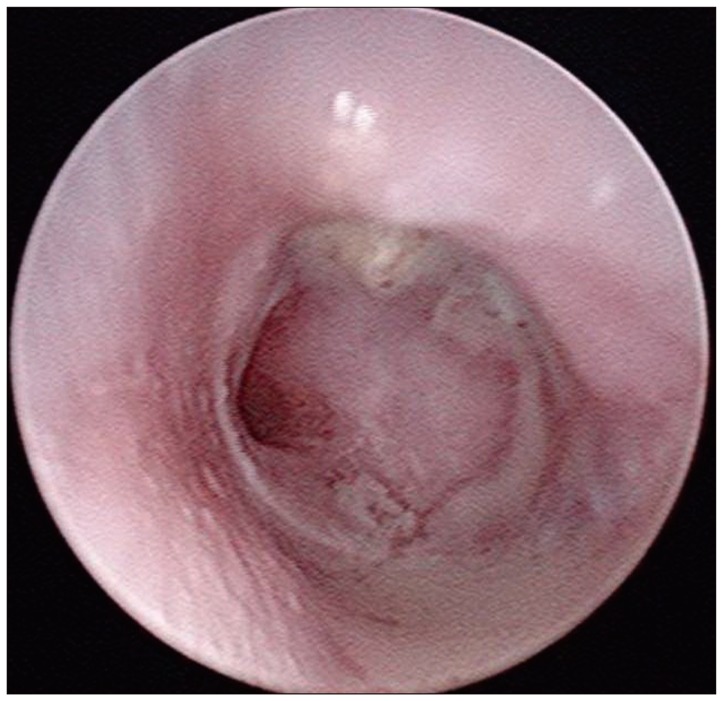
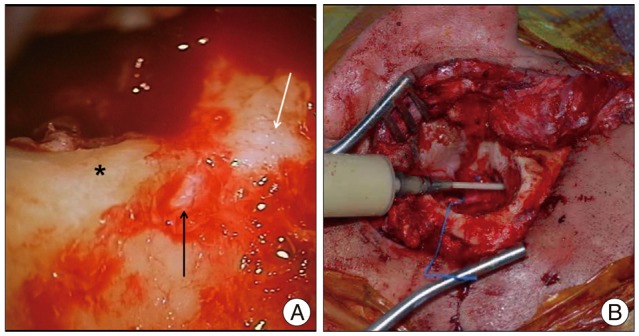
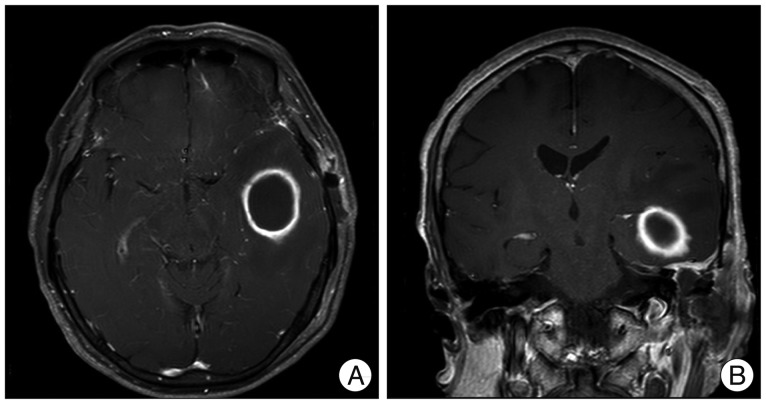
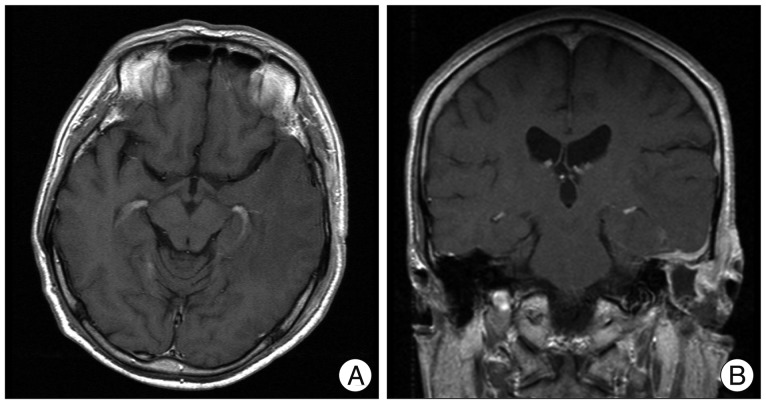
- Despite significant advances in the treatment of all forms of chronic otitis media (COM), complications still can and do occur, with intracranial complications representing the most life-threatening cases, often requiring immediate therapeutic intervention. Herein, we present a rare case of rapidly progressing facial paralysis with concomitant severe headache and ipsilateral hearing loss secondary to an otogenic brain abscess, treated with the transmastoid approach, drainage, and facial nerve decompression.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Aebi C, Kaufmann F, Schaad UB. Brain abscess in childhood--long-term experiences. Eur J Pediatr. 1991; 150:282–286. PMID: 2029923.
Article2. Basit AS, Ravi B, Banerji AK, Tandon PN. Multiple pyogenic brain abscesses : an analysis of 21 patients. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1989; 52:591–594. PMID: 2732727.3. Bernardini GL. Diagnosis and management of brain abscess and subdural empyema. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2004; 4:448–456. PMID: 15509445.
Article4. Hippargekar PM, Shinde AD. Trans-mastoid needle aspiration for otogenic brain abscesses. J Laryngol Otol. 2003; 117:422–423. PMID: 12803800.
Article5. Kangsanarak J, Fooanant S, Ruckphaopunt K, Navacharoen N, Teotrakul S. Extracranial and intracranial complications of suppurative otitis media. Report of 102 cases. J Laryngol Otol. 1993; 107:999–1004. PMID: 8288994.
Article6. Kurien M, Job A, Mathew J, Chandy M. Otogenic intracranial abscess : concurrent craniotomy and mastoidectomy--changing trends in a developing country. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1998; 124:1353–1356. PMID: 9865758.7. Lu CH, Chang WN, Lui CC. Strategies for the management of bacterial brain abscess. J Clin Neurosci. 2006; 13:979–985. PMID: 17056261.
Article8. Ludman H. Complications of suppurative otitis media. In : Scott-Brown WG, Kerr AG, Groves J, editors. Scott-Brown's otolaryngology. ed 5. London: Butterworths;1987. p. 264–291.9. Moorthy RK, Rajshekhar V. Management of brain abscess : an overview. Neurosurg Focus. 2008; 24:e3. PMID: 18518748.10. Morwani KP, Jayashankar N. Single stage, transmastoid approach for otogenic intracranial abscess. J Laryngol Otol. 2009; 123:1216–1220. PMID: 19607739.
Article11. Nalbone VP, Kuruvilla A, Gacek RR. Otogenic brain abscess : the Syracuse experience. Ear Nose Throat J. 1992; 71:238–242. PMID: 1505373.12. Osma U, Cureoglu S, Hosoglu S. The complications of chronic otitis media : report of 93 cases. J Laryngol Otol. 2000; 114:97–100. PMID: 10748823.13. Penido Nde O, Borin A, Iha LC, Suguri VM, Onishi E, Fukuda Y, et al. Intracranial complications of otitis media : 15 years of experience in 33 patients. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2005; 132:37–42. PMID: 15632907.
Article14. Sennaroglu L, Sozeri B. Otogenic brain abscess : review of 41 cases. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2000; 123:751–755. PMID: 11112974.15. Sharma BS, Gupta SK, Khosla VK. Current concepts in the management of pyogenic brain abscess. Neurol India. 2000; 48:105–111. PMID: 10878771.16. Stapleton SR, Bell BA, Uttley D. Stereotactic aspiration of brain abscesses : is this the treatment of choice? Acta Neurochir (Wien). 1993; 121:15–19. PMID: 8475802.
Article17. Strowitzki M, Schwerdtfeger K, Steudel WI. Ultrasound-guided aspiration of brain abscesses through a single burr hole. Minim Invasive Neurosurg. 2001; 44:135–140. PMID: 11696881.
Article18. Syal R, Singh H, Duggal KK. Otogenic brain abscess : management by otologist. J Laryngol Otol. 2006; 120:837–841. PMID: 16824235.