J Korean Neurosurg Soc.
2014 Feb;55(2):92-95. 10.3340/jkns.2014.55.2.92.
Spontaneous Carotid-Cavernous Fistula in the Type IV Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. hsk4428@yahoo.com
- KMID: 2191052
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2014.55.2.92
Abstract
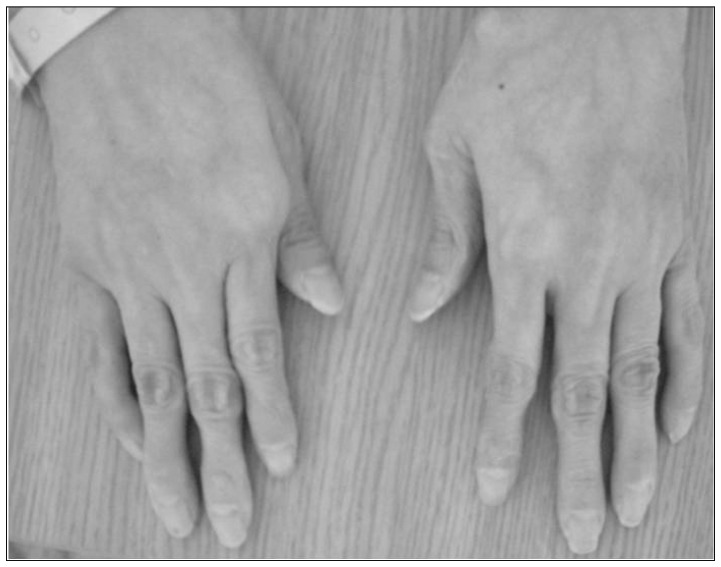
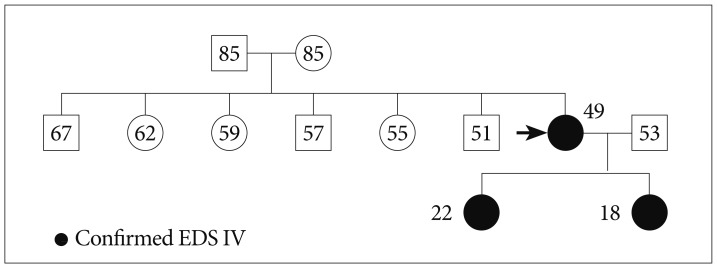
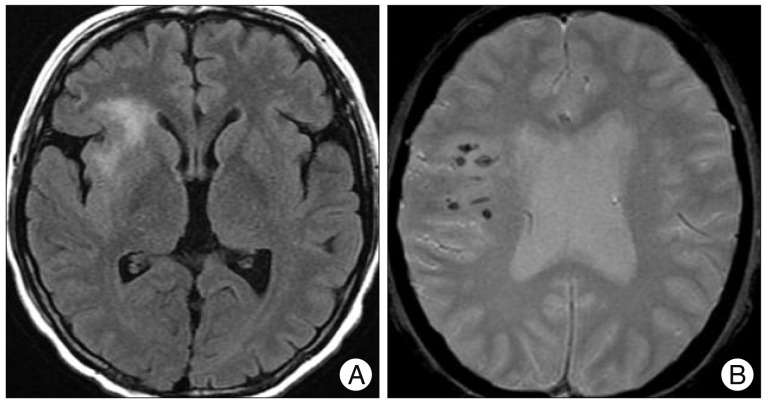
- Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (EDS) is a rare inherited connective disease. Among several subgroups, type IV EDS is frequently associated with spontaneous catastrophic bleeding from a vascular fragility. We report on a case of carotid-cavernous fistula (CCF) in a patient with type IV EDS. A 46-year-old female presented with an ophthalmoplegia and chemosis in the right eye. Subsequently, seizure and cerebral infarction with micro-bleeds occurred. CCF was completely occluded with transvenous coil embolization without complications. Thereafter, the patient was completely recovered. Transvenous coil embolization can be a good treatment of choice for spontaneous CCF with type IV EDS. However, every caution should be kept during invasive procedure.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Complete Reversal of Diffusion Restriction after Treatment of Traumatic Carotid-Cavernous Fistula
Jeong Hyun Shim, Inbo Han
Korean J Neurotrauma. 2017;13(2):171-175. doi: 10.13004/kjnt.2017.13.2.171.
Reference
-
1. Barrow DL, Spector RH, Braun IF, Landman JA, Tindall SC, Tindall GT. Classification and treatment of spontaneous carotid-cavernous sinus fistulas. J Neurosurg. 1985; 62:248–256. PMID: 3968564.
Article2. Bashir Q, Thornton J, Alp S, Debrun GM, Aletich VA, Charbel F, et al. Carotid-cavernous fistula associated with Ehlers-Danlos syndrome type IV. A case report and review of literature. Interv Neuroradiol. 1999; 5:313–320. PMID: 20670529.
Article3. Beighton P, de Paepe A, Danks D, Finidori G, Gedde-Dahl T, Goodman R, et al. International Nosology of Heritable Disorders of Connective Tissue, Berlin, 1986. Am J Med Genet. 1988; 29:581–594. PMID: 3287925.
Article4. Beighton P, De Paepe A, Steinmann B, Tsipouras P, Wenstrup RJ. Ehlers-Danlos National Foundation (USA) and Ehlers-Danlos Support Group (UK). Ehlers-Danlos syndromes : revised nosology, Villefranche, 1997. Am J Med Genet. 1998; 77:31–37. PMID: 9557891.5. Burrows NP. The molecular genetics of the Ehlers-Danlos syndrome. Clin Exp Dermatol. 1999; 24:99–106. PMID: 10233664.
Article6. Debrun GM, Aletich VA, Miller NR, DeKeiser RJ. Three cases of spontaneous direct carotid cavernous fistulas associated with Ehlers-Danlos syndrome type IV. Surg Neurol. 1996; 46:247–252. PMID: 8781594.
Article7. Farley MK, Clark RD, Fallor MK, Geggel HS, Heckenlively JR. Spontaneous carotid-cavernous fistula and the Ehlers-Danlos syndromes. Ophthalmology. 1983; 90:1337–1342. PMID: 6664673.
Article8. Forlodou P, de Kersaint-Gilly A, Pizzanelli J, Viarouge MP, Auffray-Calvier E. Ehlers-Danlos syndrome with a spontaneous caroticocavernous fistula occluded by detachable balloon : case report and review of literature. Neuroradiology. 1996; 38:595–597. PMID: 8880727.
Article9. Halbach VV, Higashida RT, Dowd CF, Barnwell SL, Hieshima GB. Treatment of carotid-cavernous fistulas associated with Ehlers-Danlos syndrome. Neurosurgery. 1990; 26:1021–1027. PMID: 2362658.
Article10. Horowitz MB, Purdy PD, Valentine RJ, Morrill K. Remote vascular catastrophes after neurovascular interventional therapy for type 4 Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2000; 21:974–976. PMID: 10815681.11. Julien I, De Boucaud D. [Spontaneous carotid-cavernous fistula and Ehlers-Danlos diseases]. Presse Med. 1971; 79:1241–1242. PMID: 5556792.12. Kanner AA, Maimon S, Rappaport ZH. Treatment of spontaneous carotid-cavernous fistula in Ehlers-Danlos syndrome by transvenous occlusion with Guglielmi detachable coils. Case report and review of the literature. J Neurosurg. 2000; 93:689–692. PMID: 11014550.
Article13. Kashiwagi S, Tsuchida E, Goto K, Shiroyama Y, Yamashita T, Takahasi M, et al. Balloon occlusion of a spontaneous carotid-cavernous fistula in Ehlers-Danlos syndrome type IV. Surg Neurol. 1993; 39:187–190. PMID: 8456380.
Article14. Lach B, Nair SG, Russell NA, Benoit BG. Spontaneous carotid-cavernous fistula and multiple arterial dissections in type IV Ehlers-Danlos syndrome. Case report. J Neurosurg. 1987; 66:462–467. PMID: 3819843.
Article15. North KN, Whiteman DA, Pepin MG, Byers PH. Cerebrovascular complications in Ehlers-Danlos syndrome type IV. Ann Neurol. 1995; 38:960–964. PMID: 8526472.
Article16. Pepin M, Schwarze U, Superti-Furga A, Byers PH. Clinical and genetic features of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome type IV, the vascular type. N Engl J Med. 2000; 342:673–680. PMID: 10706896.
Article17. Pope FM, Martin GR, Lichtenstein JR, Penttinen R, Gerson B, Rowe DW, et al. Patients with Ehlers-Danlos syndrome type IV lack type III collagen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975; 72:1314–1316. PMID: 1055406.
Article18. Pope FM, Nicholls AC, Narcisi P, Temple A, Chia Y, Fryer P, et al. Type III collagen mutations in Ehlers Danlos syndrome type IV and other related disorders. Clin Exp Dermatol. 1988; 13:285–302. PMID: 3076851.
Article19. Povey S, Falk CT. Report of the committee on the genetic constitution of chromosome 2. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1989; 51:91–105. PMID: 2676388.
Article20. Schievink WI, Michels VV, Piepgras DG. Neurovascular manifestations of heritable connective tissue disorders. A review. Stroke. 1994; 25:889–903. PMID: 8160237.
Article21. Schievink WI, Piepgras DG, Earnest F 4th, Gordon H. Spontaneous carotid-cavernous fistulae in Ehlers-Danlos syndrome Type IV. Case report. J Neurosurg. 1991; 74:991–998. PMID: 2033461.22. Schoolman A, Kepes JJ. Bilateral spontaneous carotid-cavernous fistulae in Ehlers-Danlos syndrome. Case report. J Neurosurg. 1967; 26:82–86. PMID: 6018786.
Article23. Schwarze U, Goldstein JA, Byers PH. Splicing defects in the COL3A1 gene : marked preference for 5' (donor) spice-site mutations in patients with exon-skipping mutations and Ehlers-Danlos syndrome type IV. Am J Hum Genet. 1997; 61:1276–1286. PMID: 9399899.
Article24. Serbinenko FA. Occlusion of the cavernous portion of the carotid artery with a balloon as a method of treating carotid-cavernous anastomosis. Vopr Neirokhir. 1971; 35:3–9. PMID: 5147941.25. The Human Gene Mutation Database. accessed on January 14, 2013. Available at : http://www.hgmd.cf.ac.uk/ac/gene.php?gene=COL3A1.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Spontaneous Hemothorax in a Patient with Type IV Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome: A case report
- Surgical Treatment of Acute Type A Aortic Dissection in Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome
- Classical Type Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome: Report of a Case and Review of Literature
- A case of type VI Ehlers-Danlos syndrome
- Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome: 2 Cases Report