J Korean Neurosurg Soc.
2014 Jan;55(1):64-65. 10.3340/jkns.2014.55.1.64.
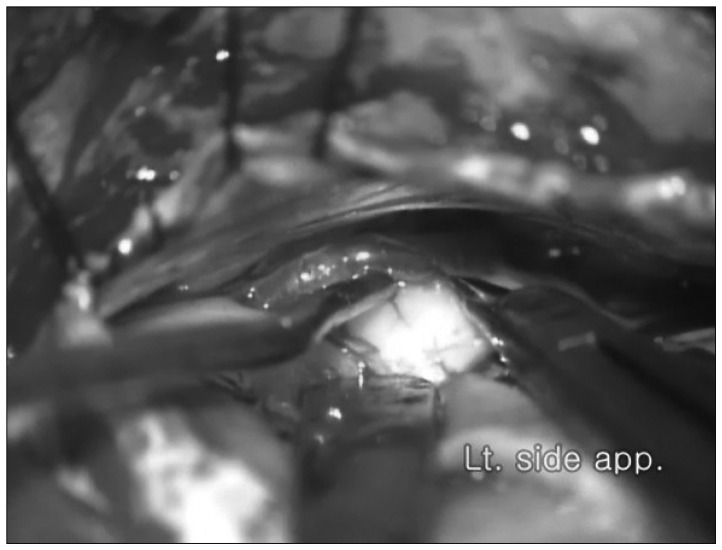
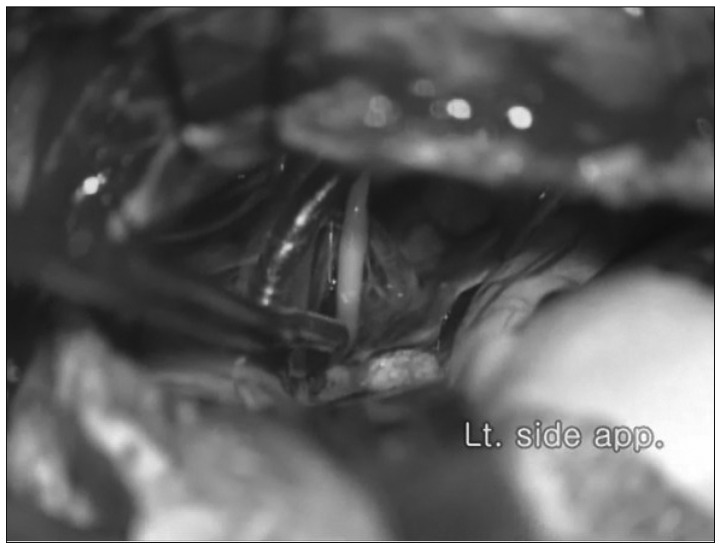
Significance of Arachnoid Dissection to Obtain Optimal Exposure of Lower Cranial Nerves and the Facial Nerve Root Exit Zone during Microvascular Decompression Surgery
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Soonchunhyang University Bucheon Hospital, Soonchunhyang University School of Medicine, Bucheon, Korea. bumtkim@gmail.com
- KMID: 2191046
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2014.55.1.64
Abstract
- No abstract available.
Figure
Reference
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Cerebellar Cortical Artery Dissection Technique for the Preservation of Operative Fields during Microvascular Decompression for Hemifacial Spasm: Technical Note
- Microvascular Decompression of the Fifth and Seventh Cranial Nerves
- A Case of Hemifacial Spasm Caused by an Artery Passing Through the Facial Nerve
- Para-condylar Foraminal Approach in Microvascular Decompression for Hemifacial Spasm
- Intraoperative Neurophysiological Monitoring during Microvascular Decompression Surgery for Hemifacial Spasm