J Korean Neurosurg Soc.
2013 Jul;54(1):58-60. 10.3340/jkns.2013.54.1.58.
Spinal Subarachnoid Hematoma as a Complication of an Intramuscular Stimulation : Case Report and a Review of Literatures
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Konkuk University School of Medicine, Chungju, Korea.
- 2Department of Neurosurgery, Konkuk University School of Medicine, Chungju, Korea. cysns@kku.ac.kr
- KMID: 2190861
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2013.54.1.58
Abstract
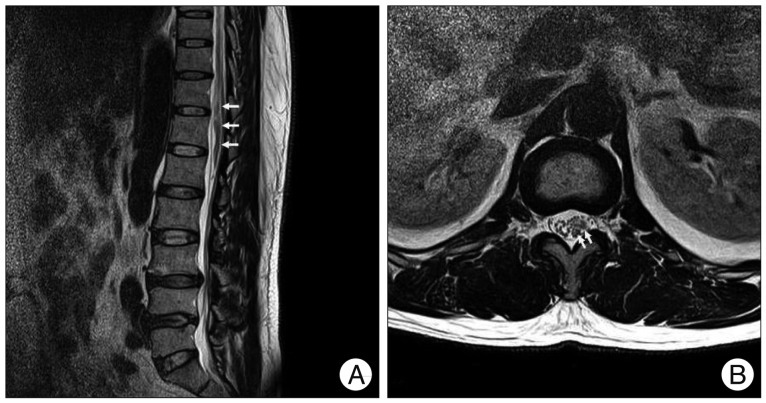
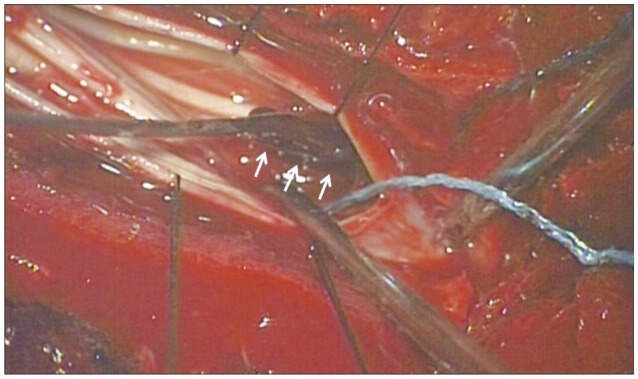
- Intramuscular stimulation (IMS) is widely used to treat myofascial pain syndrome. IMS is a safe procedure but several complications have been described. To our knowledge, spinal subarachnoid hematoma has never been reported as a complication of an IMS. The authors have experienced a case of spinal subarachnoid hematoma occurring after an IMS, which was tentatively diagnosed as intracranial subarachnoid hemorrhage because of severe headache. Patient was successfully treated with surgery. Here, we report our case with a review of literature.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Chee YL, Crawford JC, Watson HG, Greaves M. Guidelines on the assessment of bleeding risk prior to surgery or invasive procedures. British Committee for Standards in Haematology. Br J Haematol. 2008; 140:496–504. PMID: 18275427.
Article2. Domenicucci M, Ramieri A, Paolini S, Russo N, Occhiogrosso G, Di Biasi C, et al. Spinal subarachnoid hematomas : our experience and literature review. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2005; 147:741–750. discussion 750. PMID: 15711890.
Article3. Knowles PR, Randall NP, Lockhart AS. Vascular trauma associated with routine spinal anaesthesia. Anaesthesia. 1999; 54:647–650. PMID: 10417455.
Article4. Kreppel D, Antoniadis G, Seeling W. Spinal hematoma : a literature survey with meta-analysis of 613 patients. Neurosurg Rev. 2003; 26:1–49. PMID: 12520314.
Article5. Lee YJ, Ahn K, Lee SC. The deep dry needling techniques, and interventional muscle & nerve stimulation (IMS) for the treatment of chronic pain. Korean J Pain. 2006; 19:1–7.
Article6. Liu WH, Lin JH, Lin JC, Ma HI. Severe intracranial and intraspinal subarachnoid hemorrhage after lumbar puncture : a rare case report. Am J Emerg Med. 2008; 26:633.e1–633.e3. PMID: 18534309.7. Nam KH, Choi CH, Yang MS, Kang DW. Spinal epidural hematoma after pain control procedure. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2010; 48:281–284. PMID: 21082060.
Article8. Nam SG, Jeon IS, Heo HM, Hwang KH, Park W. Assessment of intramuscular stimulation in patients with myofascial pain syndrome using thermography. J Korean Pain Soc. 2003; 16:54–59.9. Seet RC, Lim EC, Wilder-Smith EP, Ong BK. Spontaneous epidural haematoma presenting as cord compression in a patient receiving clopidogrel. Eur J Neurol. 2005; 12:811–812. PMID: 16190921.
Article10. Song JY, Chen YH, Hung KC, Chang TS. Traumatic subdural hematoma in the lumbar spine. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2011; 27:473–476. PMID: 21943822.
Article11. Srbely JZ, Dickey JP, Lee D, Lowerison M. Dry needle stimulation of myofascial trigger points evokes segmental anti-nociceptive effects. J Rehabil Med. 2010; 42:463–468. PMID: 20544158.
Article12. Sung JH, Hong JT, Son BC, Lee SW. Clopidogrel-induced spontaneous spinal epidural hematoma. J Korean Med Sci. 2007; 22:577–579. PMID: 17596676.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Subarachnoid hematoma after spinal anesthesia: A case report
- Spontaneous Spinal Subdural and Subarachnoid Hemorrhage with Concomitant Intracerebral Hemorrhage: A Case Report
- Traumatic Acute Spinal Subarachnoid Hematoma: A Case Report
- Is intramuscular stimulation a safe procedure in unpracticed hands?: a case of cervical epidural hematoma resulting in hemiparesis: A case report
- Angiographically Occult Vascular Malformation of the Cauda Equina Presenting Massive Spinal Subdural and Subarachnoid Hematoma