J Korean Hip Soc.
2011 Mar;23(1):7-14. 10.5371/jkhs.2011.23.1.7.
Joint Preserving Operations for Femoral Head Osteonecrosis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Pohang St. Mary's Hospital, Pohang, Korea.
- 2Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea. khkoo@snu.ac.kr
- 3Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, College of Medicine, Chung-Ang University, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2190770
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5371/jkhs.2011.23.1.7
Abstract
- Osteonecrosis of the femoral head mainly occurs in young patients, and the hip joint with osteonecrosis of the femoral head can be preserved by adequate joint-preserving surgery. This review article includes the information, surgical technique, pitfalls and results of several types of joint preserving surgeries.
MeSH Terms
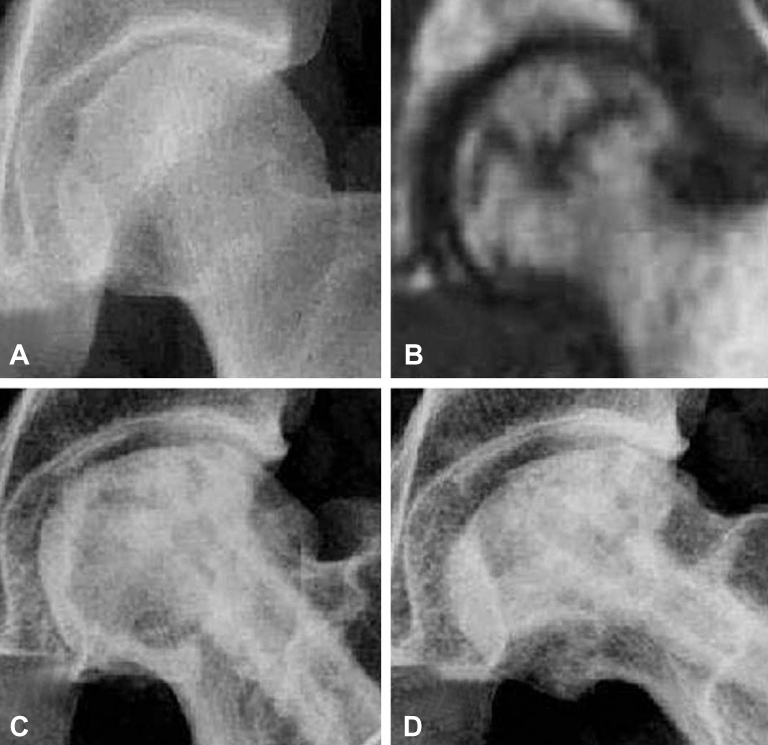
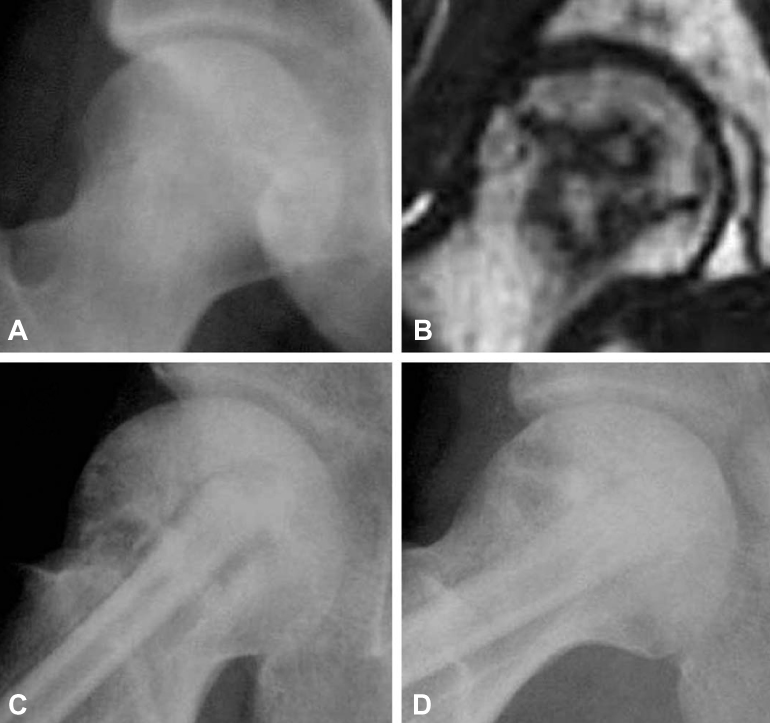
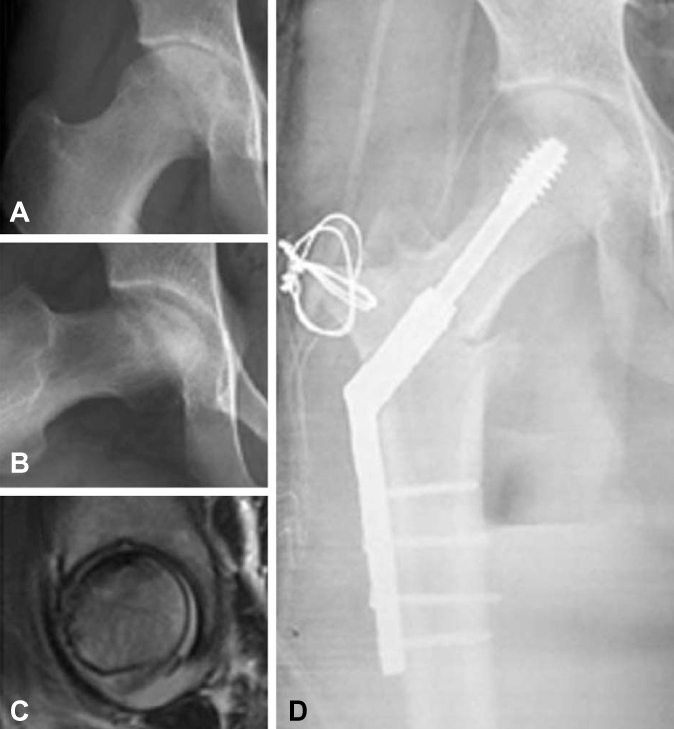
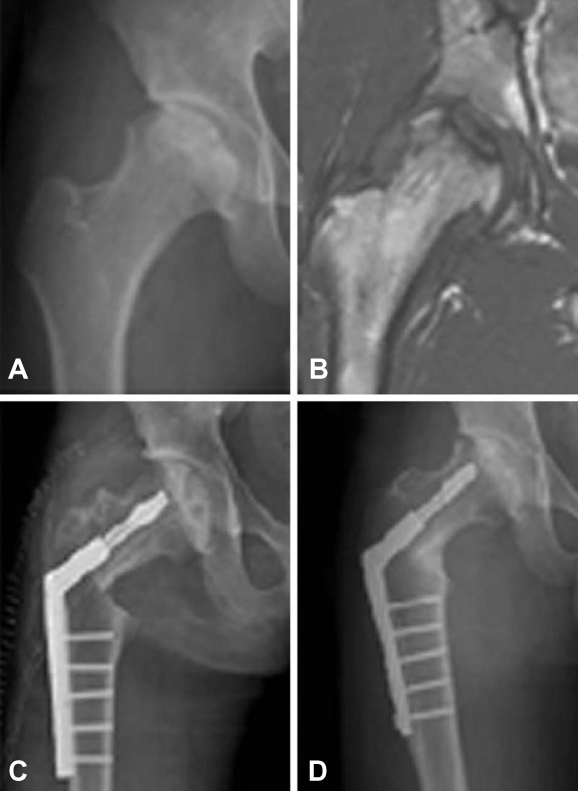
Figure
Reference
-
1. Koo KH, Kim R. Quantifying the extent of osteonecrosis of the femoral head. A new method using MRI. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1995. 77:875–880.
Article2. Koo KH, Song HR, Yang JW, Yang P, Kim JR, Kim YM. Trochanteric rotational osteotomy for osteonecrosis of the femoral head. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2001. 83:83–89.
Article3. Lafforgue P, Dahan E, Chagnaud C, Schiano A, Kasbarian M, Acquaviva PC. Early-stage avascular necrosis of the femoral head: MR imaging for prognosis in 31 cases with at least 2 years of follow-up. Radiology. 1993. 187:199–204.
Article4. Mont MA, Hungerford DS. Non-traumatic avascular necrosis of the femoral head. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1995. 77:459–474.
Article5. Ohzono K, Saito M, Takaoka K, et al. Natural history of nontraumatic avascular necrosis of the femoral head. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1991. 73:68–72.
Article6. Sugioka Y. Transtrochanteric anterior rotational osteotomy of the femoral head in the treatment of osteonecrosis affecting the hip: a new osteotomy operation. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1978. 130:191–201.7. Urbaniak JR, Coogan PG, Gunneson EB, Nunley JA. Treatment of osteonecrosis of the femoral head with free vascularized fibular grafting. A long-term follow-up study of one hundred and three hips. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1995. 77:681–694.
Article8. Israelite C, Nelson CL, Ziarani CF, Abboud JA, Landa J, Steinberg ME. Bilateral core decompression for osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2005. 441:285–290.
Article9. Lieberman JR, Conduah A, Urist MR. Treatment of osteonecrosis of the femoral head with core decompression and human bone morphogenetic protein. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2004. 429:139–145.
Article10. Steinberg ME, Larcom PG, Strafford B, et al. Core decompression with bone grafting for osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2001. 386:71–78.
Article11. Mont MA, Carbone JJ, Fairbank AC. Core decompression versus nonoperative management for osteonecrosis of the hip. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1996. 324:169–178.
Article12. Stulberg BN, Davis AW, Bauer TW, Levine M, Easley K. Osteonecrosis of the femoral head. A prospective randomized treatment protocol. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1991. 268:140–151.13. Koo KH, Kim R, Ko GH, Song HR, Jeong ST, Cho SH. Preventing collapse in early osteonecrosis of the femoral head. A randomised clinical trial of core decompression. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1995. 77:870–874.
Article14. Bozic KJ, Zurakowski D, Thornhill TS. Survivorship analysis of hips treated with core decompression for nontraumatic osteonecrosis of the femoral head. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1999. 81:200–209.
Article15. Fairbank AC, Bhatia D, Jinnah RH, Hungerford DS. Long-term results of core decompression for ischaemic necrosis of the femoral head. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1995. 77:42–49.
Article16. Powell ET, Lanzer WL, Mankey MG. Core decompression for early osteonecrosis of the hip in high risk patients. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1997. 335:181–189.
Article17. Steinberg ME, Bands RE, Parry S, Hoffman E, Chan T, Hartman KM. Does lesion size affect the outcome in avascular necrosis? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1999. 367:262–271.
Article18. Smith SW, Fehring TK, Griffin WL, Beaver WB. Core decompression of the osteonecrotic femoral head. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1995. 77:674–680.
Article19. Camp JF, Colwell CW Jr. Core decompression of the femoral head for osteonecrosis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1986. 68:1313–1319.
Article20. Hungerford DS. Response: the role of core decompression in the treatment of ischemic necrosis of the femoral head. Arthritis Rheum. 1989. 32:801–806.
Article21. Mont MA, Ragland PS, Etienne G. Core decompression of the femoral head for osteonecrosis using percutaneous multiple small-diameter drilling. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2004. 429:131–138.
Article22. Kim SY, Kim YG, Kim PT, Ihn JC, Cho BC, Koo KH. Vascularized compared with nonvascularized fibular grafts for large osteonecrotic lesions of the femoral head. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005. 87:2012–2018.
Article23. Yoo MC, Chung DW, Hahn CS. Free vascularized fibula grafting for the treatment of osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1992. 277:128–138.
Article24. Vail TP, Urbaniak JR. Donor-site morbidity with use of vascularized autogenous fibular grafts. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1996. 78:204–211.
Article25. Sugioka Y, Katsuki I, Hotokebuchi T. Transtrochanteric rotational osteotomy of the femoral head for the treatment of osteonecrosis. Follow-up statistics. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1982. 169:115–126.26. Atsumi T, Kajiwara T, Hiranuma Y, Tamaoki S, Asakura Y. Posterior rotational osteotomy for nontraumatic osteonecrosis with extensive collapsed lesions in young patients. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006. 88:Suppl 3. 42–47.
Article27. Sugioka Y, Hotokebuchi T, Tsutsui H. Transtrochanteric anterior rotational osteotomy for idiopathic and steroid-induced necrosis of the femoral head. Indications and long-term results. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1992. 277:111–120.28. Gardeniers JWM. Scoutens A, Arlet J, Gardeniers JWM, Hughes SPF, editors. The ARCO perspective for reaching one uniform staging system of osteonecrosis. 1993. New York: Plenum Press;375–380.29. Yoon TR, Abbas AA, Hur CI, Cho SG, Lee JH. Modified transtrochanteric rotational osteotomy for femoral head osteonecrosis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2008. 466:1110–1116.
Article30. Kerboul M, Thomine J, Postel M, Merle d'Aubigné R. The conservative surgical treatment of idiopathic aseptic necrosis of the femoral head. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1974. 56:291–296.
Article31. Merle D'Aubigné R, Postel M, Mazabraud A, Massias P, Gueguen J, France P. Idiopathic necrosis of the femoral head in adults. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1965. 47:612–633.32. Sakano S, Hasegawa Y, Torii Y, Kawasaki M, Ishiguro N. Curved intertrochanteric varus osteotomy for osteonecrosis of the femoral head. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2004. 86:359–365.
Article33. Yasunaga Y, Hisatome T, Tanaka R, Yamasaki T, Ochi M. Curved varus femoral osteotomy for minimal dysplastic hip in patients older than 45 years of age: comparison with rotational acetabular osteotomy. J Orthop Sci. 2005. 10:264–269.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Joint Preserving Non-surgical Treatment of Osteonecrosis of Femoral Head
- Osteonecrosis of Femoral Head after Pelvic Fracture: A Case Report
- Revitalization of Osteonecrosis of the Femoral head by Vascular Pedicled Iliac Bone Grafting: A Preliminary Report
- An Enlarged Iliopsoas Bursa Associated with Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head: A Case Report
- Posttraumatic Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head after Nine Years of Posterior Femoral Head Fracture Dislocation