J Korean Neurosurg Soc.
2012 Aug;52(2):152-155. 10.3340/jkns.2012.52.2.152.
A Case of Ectopic Rathke's Cleft Cyst in the Prepontine Cistern
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Keimyung University School of Medicine, Dongsan Medical Center, Daegu, Korea. bach1158@dsmc.or.kr
- KMID: 2190556
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2012.52.2.152
Abstract
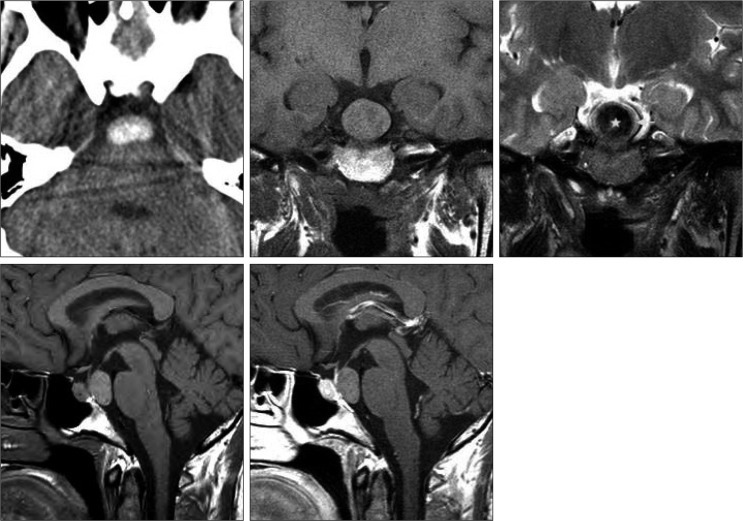
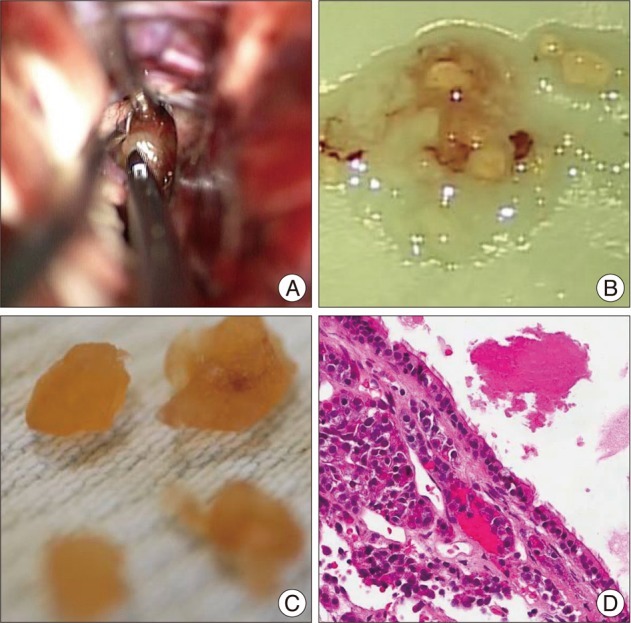
- A Rathke's cleft cyst (RCC) is a benign pituitary cyst derived from the remnant of Rathke's pouch, and usually presents as an intrasellar lesion with varying degrees of suprasellar extension. However, to date, a description of a primary prepontine RCC with no intrasellar component has not been reported. The author describes an exceptional case of a symptomatic RCC located behind the sella turcica in a 41-year-old woman who presented with severe headache. The author also provides an embryological hypothesis of the development of an ectopic RCC, with a special emphasis on radiologic characteristics.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Aho CJ, Liu C, Zelman V, Couldwell WT, Weiss MH. Surgical outcomes in 118 patients with Rathke cleft cysts. J Neurosurg. 2005; 102:189–193. PMID: 15739543.
Article2. Anand VK, Osborne CM, Harkey HL 3rd. Infiltrative clival pituitary adenoma of ectopic origin. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1993; 108:178–183. PMID: 8441545.
Article3. Barrow DL, Spector RH, Takei Y, Tindall GT. Symptomatic Rathke's cleft cysts located entirely in the suprasellar region : review of diagnosis, management, and pathogenesis. Neurosurgery. 1985; 16:766–772. PMID: 4010898.
Article4. Binning MJ, Gottfried ON, Osborn AG, Couldwell WT. Rathke cleft cyst intracystic nodule : a characteristic magnetic resonance imaging finding. J Neurosurg. 2005; 103:837–840. PMID: 16304987.
Article5. Chen CJ. Suprasellar and infrasellar craniopharyngioma with a persistent craniopharyngeal canal: case report and review of the literature. Neuroradiology. 2001; 43:760–762. PMID: 11594427.
Article6. Choi SH, Kwon BJ, Na DG, Kim JH, Han MH, Chang KH. Pituitary adenoma, craniopharyngioma, and Rathke cleft cyst involving both intrasellar and suprasellar regions : differentiation using MRI. Clin Radiol. 2007; 62:453–462. PMID: 17398271.
Article7. Chuang CC, Chen YL, Jung SM, Pai PC. A giant retroclival Rathke's cleft cyst. J Clin Neurosci. 2010; 17:1189–1191. PMID: 20627584.
Article8. Hanna E, Weissman J, Janecka IP. Sphenoclival Rathke's cleft cysts : embryology, clinical appearance and management. Ear Nose Throat J. 1998; 77:396–399. PMID: 9615520.
Article9. Kim JE, Kim JH, Kim OL, Paek SH, Kim DG, Chi JG, et al. Surgical treatment of symptomatic Rathke cleft cysts : clinical features and results with special attention to recurrence. J Neurosurg. 2004; 100:33–40. PMID: 14743909.
Article10. Kleinschmidt-DeMasters BK, Lillehei KO, Stears JC. The pathologic, surgical, and MR spectrum of Rathke cleft cysts. Surg Neurol. 1995; 44:19–26. discussion 26-27. PMID: 7482247.
Article11. Megdiche-Bazarbacha H, Ben Hammouda K, Aicha AB, Sebai R, Belghith L, Khaldi M, et al. Intrasphenoidal rathke cleft cyst. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2006; 27:1098–1100. PMID: 16687551.12. Nishioka H, Haraoka J, Izawa H, Ikeda Y. Magnetic resonance imaging, clinical manifestations, and management of Rathke's cleft cyst. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2006; 64:184–188. PMID: 16430718.
Article13. Osborn AG, Preece MT. Intracranial cysts : radiologic-pathologic correlation and imaging approach. Radiology. 2006; 239:650–664. PMID: 16714456.
Article14. Panagopoulos KP, Jolesz FA, el-Azouzi M, Black PM. Mucinous cysts of the pituitary stalk. Report of two cases. J Neurosurg. 1989; 71:276–278. PMID: 2746351.15. Ross DA, Norman D, Wilson CB. Radiologic characteristics and results of surgical management of Rathke's cysts in 43 patients. Neurosurgery. 1992; 30:173–178. discussion 178-179. PMID: 1545884.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Symptomatic Rathke's Cleft Cyst in the Interpeduncular Cistern: Case Report
- Suprasellar Rathke Cleft Cyst: A case report
- Rathke's Cleft Cyst: Case Report
- Large Ossified Rathke's Cleft Cyst: A Case Report and Review of the Literature
- Pituitary Tumors Composed of Adenohypophysial Adenoma and Rathke's Cleft Cyst Elements