J Korean Neurosurg Soc.
2012 Aug;52(2):133-137. 10.3340/jkns.2012.52.2.133.
Indications and Surgical Results of Twist-Drill Craniostomy at the Pre-Coronal Point for Symptomatic Chronic Subdural Hematoma Patients
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Soonchunhyang University College of Medicine, Bucheon Hospital, Bucheon, Korea. bumtkim@schmc.ac.kr
- KMID: 2190552
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2012.52.2.133
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
Twist-drill craniostomy (TDC) with closed-system drainage and burr-hole drainage (BHD) with a closed system are effective treatment options for chronic subdural hematoma (CSDH). The aim of this study was to analyze clinical data and surgical results from symptomatic CSDH patients who underwent TDC with closed-system drainage at the pre-coronal point (PCP).
METHODS
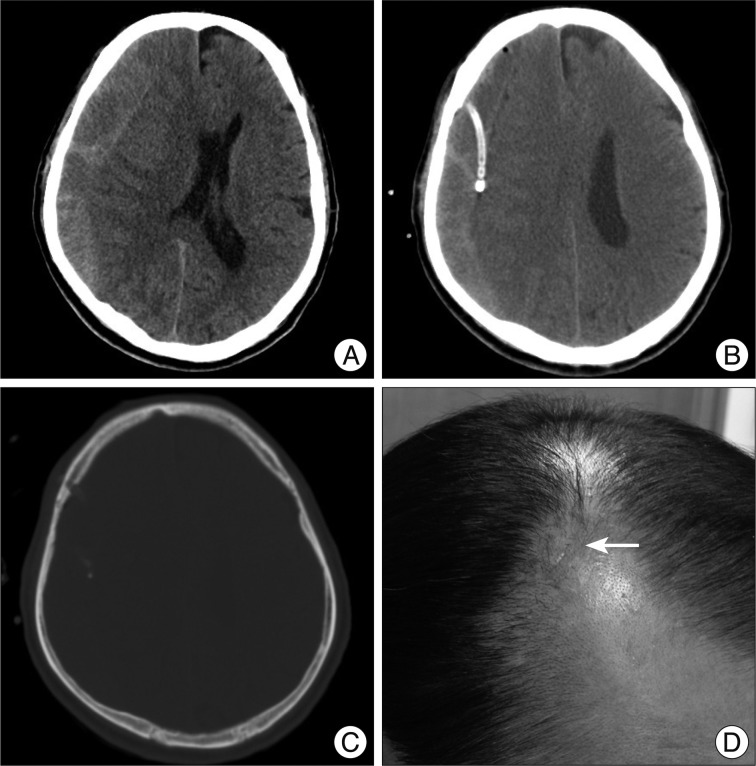
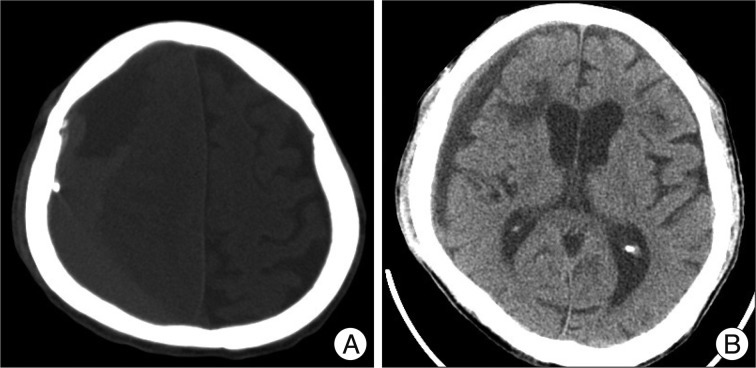
We analyzed data for 134 symptomatic CSDH patients who underwent TDC at the PCP with closed-system drainage. We defined the PCP for TDC to be 1 cm anterior to the coronal suture at the level of superior temporal line. TDC at the PCP with closed-system drainage was selected in patients with CSDH that extended beyond the coronal suture, confirmed by preoperative CT scans. Medical records, radiological findings, and clinical performance were reviewed retrospectively.
RESULTS
Of the 134 CSDH patients, 114 (85.1%) showed improved clinical performance and imaging findings after surgery. Catheter failures were seen in two cases (1.4%); the catheters were inserted in the epidural space. Recurrent cases were seen in eight patients (5.6%), and they were improved with a second BHD with a closed-system operation.
CONCLUSION
TDC at the PCP with closed-system drainage is safe and effective for patients with symptomatic CSDH whose hematomas extend beyond the coronal suture.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Twist-Drill or Burr Hole Craniostomy for Draining Chronic Subdural Hematomas: How to Choose It for Chronic Subdural Hematoma Drainage
Seong-Jong Lee, Sun-Chul Hwang, Soo Bin Im
Korean J Neurotrauma. 2016;12(2):107-111. doi: 10.13004/kjnt.2016.12.2.107.Comparison of the Indications and Treatment Results of Burr-Hole Drainage at the Maximal Thickness Area versus Twist-Drill Craniostomy at the Pre-Coronal Point for the Evacuation of Symptomatic Chronic Subdural Hematomas
Gi Hun Kim, Bum-Tae Kim, Soo-Bin Im, Sun-Chul Hwang, Je Hoon Jeong, Dong-Seong Shin
J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2014;56(3):243-247. doi: 10.3340/jkns.2014.56.3.243.
Reference
-
1. Camel M. Twist-drill craniostomy for the treatment of chronic subdural hematoma. Neurosurg Clin N Am. 2000; 11:515–518. PMID: 10918023.
Article2. Camel M, Grubb RL Jr. Treatment of chronic subdural hematoma by twist-drill craniotomy with continuous catheter drainage. J Neurosurg. 1986; 65:183–187. PMID: 3723175.
Article3. Carlton CK, Saunders RL. Twist drill craniostomy and closed system drainage of chronic and subacute subdural hematomas. Neurosurgery. 1983; 13:153–159. PMID: 6888695.
Article4. Horn EM, Feiz-Erfan I, Bristol RE, Spetzler RF, Harrington TR. Bedside twist drill craniostomy for chronic subdural hematoma : a comparative study. Surg Neurol. 2006; 65:150–153. discussion 153-154. PMID: 16427409.
Article5. Hwang SC, Im SB, Kim BT, Shin WH. Safe entry point for twist-drill craniostomy of a chronic subdural hematoma. J Neurosurg. 2009; 110:1265–1270. PMID: 19099378.
Article6. Kang HL, Shin HS, Kim TH, Hwang YS, Park SK. Clinical analysis of recurrent chronic subdural hematoma. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2006; 40:262–266.7. Kang MS, Koh HS, Kwon HJ, Choi SW, Kim SH, Youm JY. Factors influencing recurrent chronic subdural hematoma after surgery. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2007; 41:11–15.8. Ko BS, Lee JK, Seo BR, Moon SJ, Kim JH, Kim SH. Clinical analysis of risk factors related to recurrent chronic subdural hematoma. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2008; 43:11–15. PMID: 19096538.
Article9. Lega BC, Danish SF, Malhotra NR, Sonnad SS, Stein SC. Choosing the best operation for chronic subdural hematoma : a decision analysis. J Neurosurg. 2010; 113:615–621. PMID: 19877806.
Article10. Miranda LB, Braxton E, Hobbs J, Quigley MR. Chronic subdural hematoma in the elderly : not a benign disease. J Neurosurg. 2011; 114:72–76. PMID: 20868215.11. Muzii VF, Bistazzoni S, Zalaffi A, Carangelo B, Mariottini A, Palma L. Chronic subdural hematoma : comparison of two surgical techniques. Preliminary results of a prospective randomized study. J Neurosurg Sci. 2005; 49:41–46. discussion 46-47. PMID: 16247343.12. Oh HJ, Lee KS, Shim JJ, Yoon SM, Yun IG, Bae HG. Postoperative course and recurrence of chronic subdural hematoma. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2010; 48:518–523. PMID: 21430978.
Article13. Ramnarayan R, Arulmurugan B, Wilson PM, Nayar R. Twist drill craniostomy with closed drainage for chronic subdural haematoma in the elderly : an effective method. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2008; 110:774–778. PMID: 18538920.
Article14. Rand BO, Ward AA Jr, White LE Jr, White LE Jr. The use of the twist drill to evaluate head trauma. J Neurosurg. 1966; 25:410–415. PMID: 5925711.
Article15. Reinges MH, Hasselberg I, Rohde V, Küker W, Gilsbach JM. Prospective analysis of bedside percutaneous subdural tapping for the treatment of chronic subdural haematoma in adults. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2000; 69:40–47. PMID: 10864602.
Article16. Rychlicki F, Recchioni MA, Burchianti M, Marcolini P, Messori A, Papo I. Percutaneous twist-drill craniostomy for the treatment of chronic subdural haematoma. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 1991; 113:38–41. PMID: 1799141.
Article17. Sindou M, Ibrahim I, Maarrawi J. Chronic sub-dural hematomas : twist drill craniostomy with a closed system of drainage, for 48 hours only, is a valuable surgical treatment. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2010; 152:545–546. PMID: 19756354.
Article18. Smely C, Madlinger A, Scheremet R. Chronic subdural haematoma--a comparison of two different treatment modalities. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 1997; 139:818–825. discussion 825-826. PMID: 9351986.19. Stanisic M, Lund-Johansen M, Mahesparan R. Treatment of chronic subdural hematoma by burr-hole craniostomy in adults : influence of some factors on postoperative recurrence. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2005; 147:1249–1256. discussion 1256-1257. PMID: 16133770.
Article20. Sucu HK, Gökmen M, Ergin A, Bezircioğlu H, Gökmen A. Is there a way to avoid surgical complications of twist drill craniostomy for evacuation of a chronic subdural hematoma? Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2007; 149:597–599. PMID: 17486289.
Article21. Voelker JL, Sambasivan M. The role of craniotomy and trephination in the treatment of chronic subdural hematoma. Neurosurg Clin N Am. 2000; 11:535–540. PMID: 10918026.
Article22. Williams GR, Baskaya MK, Menendez J, Polin R, Willis B, Nanda A. Burr-hole versus twist-drill drainage for the evacuation of chronic subdural haematoma : a comparison of clinical results. J Clin Neurosci. 2001; 8:551–554. PMID: 11683603.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Comparison of the Indications and Treatment Results of Burr-Hole Drainage at the Maximal Thickness Area versus Twist-Drill Craniostomy at the Pre-Coronal Point for the Evacuation of Symptomatic Chronic Subdural Hematomas
- Twist-Drill or Burr Hole Craniostomy for Draining Chronic Subdural Hematomas: How to Choose It for Chronic Subdural Hematoma Drainage
- Erratum to "Comparison of the Indications and Treatment Results of Burr-Hole Drainage at the Maximal Thickness Area versus Twist-Drill Craniostomy at the Pre-Coronal Point for the Evacuation of Symptomatic Chronic Subdural Hematomas" by Kim GH, et al. (J Korean Neurosurg Soc 56 : 243-247, 2014)
- Treatment Results of Twist-drill Craniostomy with Closed-system Drainage for the Symptomatic Chronic Subdural Hematoma Patients
- How to Treat Chronic Subdural Hematoma? Past and Now