J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg.
2011 Feb;37(1):1-8. 10.5125/jkaoms.2011.37.1.1.
Clinical study of correlation between C-terminal cross-linking telopeptide of type I collagen and risk assessment, severity of disease, healing after early surgical intervention in patients with bisphophonate-related osteonecrosis of the jaws
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, School of Dentistry, Pusan National University, Yangsan, Korea. ssh8080@pusan.ac.kr
- KMID: 2189799
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5125/jkaoms.2011.37.1.1
Abstract
- INTRODUCTION
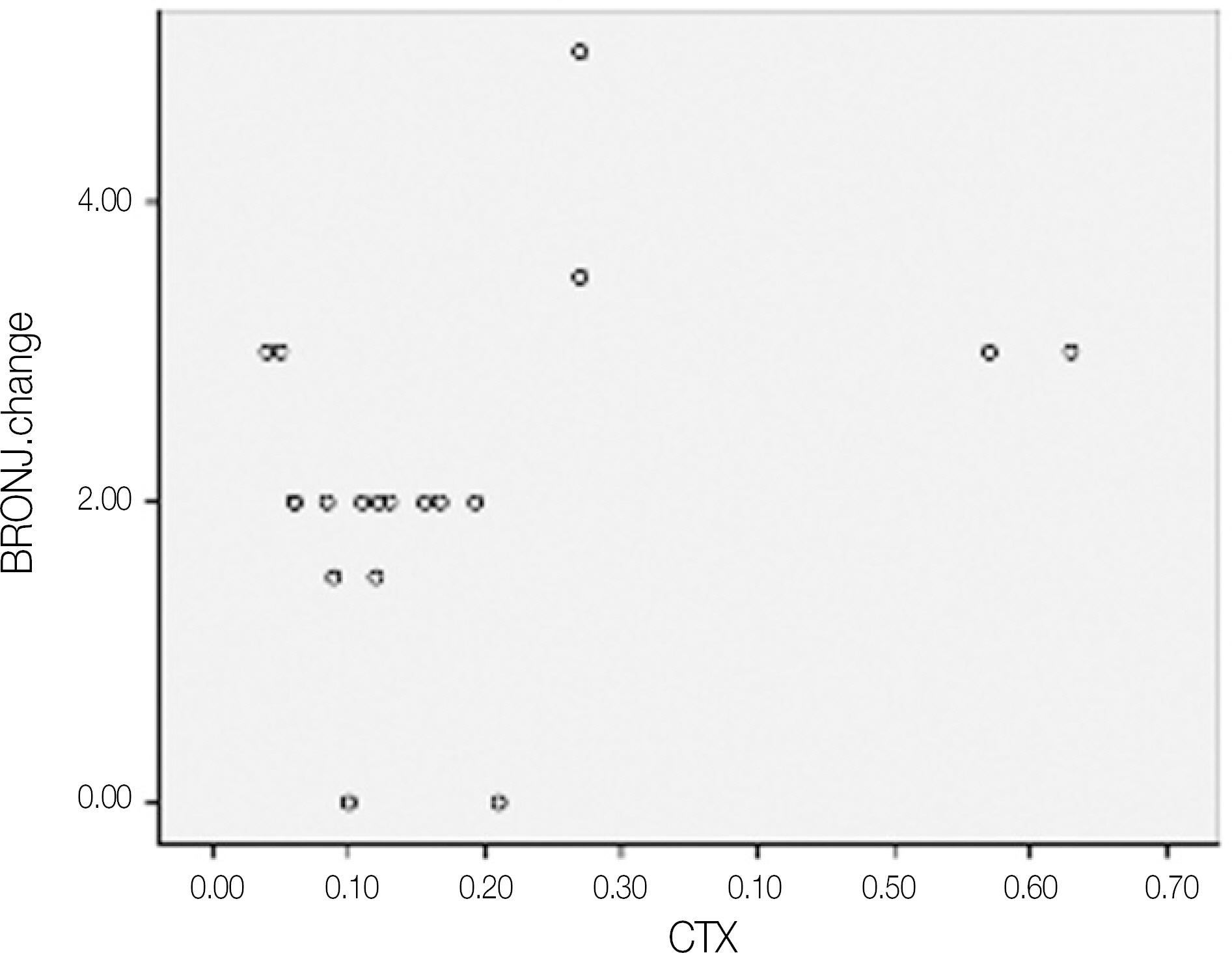
The utility of the C-terminal cross-linking telopeptide test (CTX) as a method for staging Bisphosphonate-related osteonecrosis of the jaws (BRONJ) and its healing process was examined.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
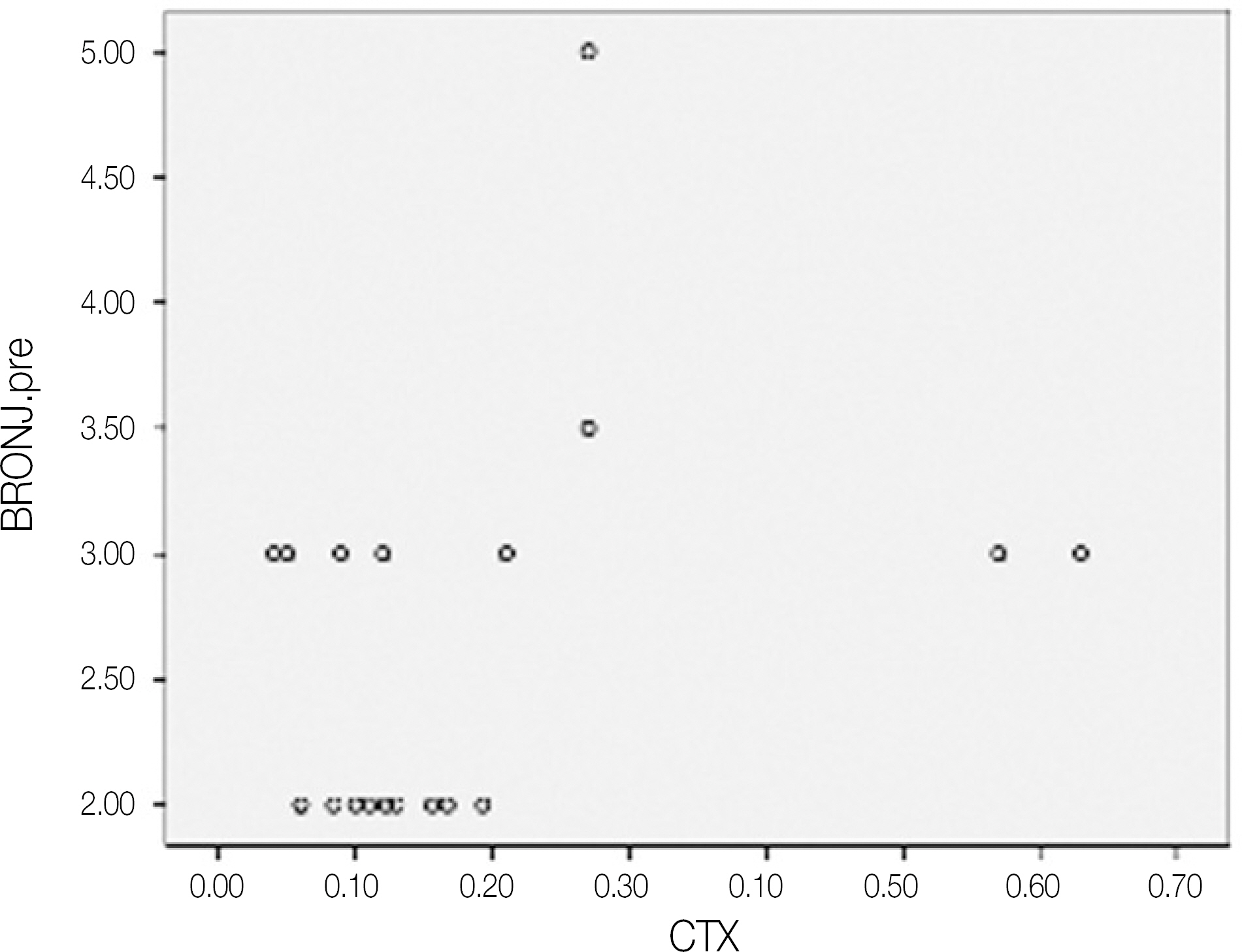
A total 19 patients who were diagnosed with BRONJ underwent a fasted morning CTX test, were enrolled in this study. The serum CTX values ranged from 50 to 630 pg/mL (mean 60). The risk assessment was rated according to the CTX values of the individual patient (minimal risk, > or =150 pg/mL, moderate, 100 to 150 pg/mL, high, < or =100 pg/mL). The BRONJ scores were then calculated according to the number of BRONJ lesions and their stage. The operation was done as soon as possible, regardless of BORNJ stage.
RESULTS
The mean duration of bisphosphonate therapy was 4.1 years. Of the 19 patients, 15, 2 ans 2 received alendronate, risedronate and zoledronate, respecively. Of the 19 patients who underwent a sequestrectomy, saucerization and smoothing, 15 healed after the initial surgery, 1 patient healed after one more surgical procedure, 3 patients did not heal completely but showed improvement in symptoms. Therefore, 17 out of the 19 patients healed completely with complete mucosal coverage and the elimination of pain. The risk assessment using the CTX value and disease severity were not correlated (r=-0.264, P=0.275). In addition, the risk assessment using CTX value and healing after surgery were not correlated (r=-0.147, P=0.547).
CONCLUSION
The serum CTX should be considered carefully by clinicians as part of overall management. Early surgical intervention is of benefit in the treatment of stage II BRONJ.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
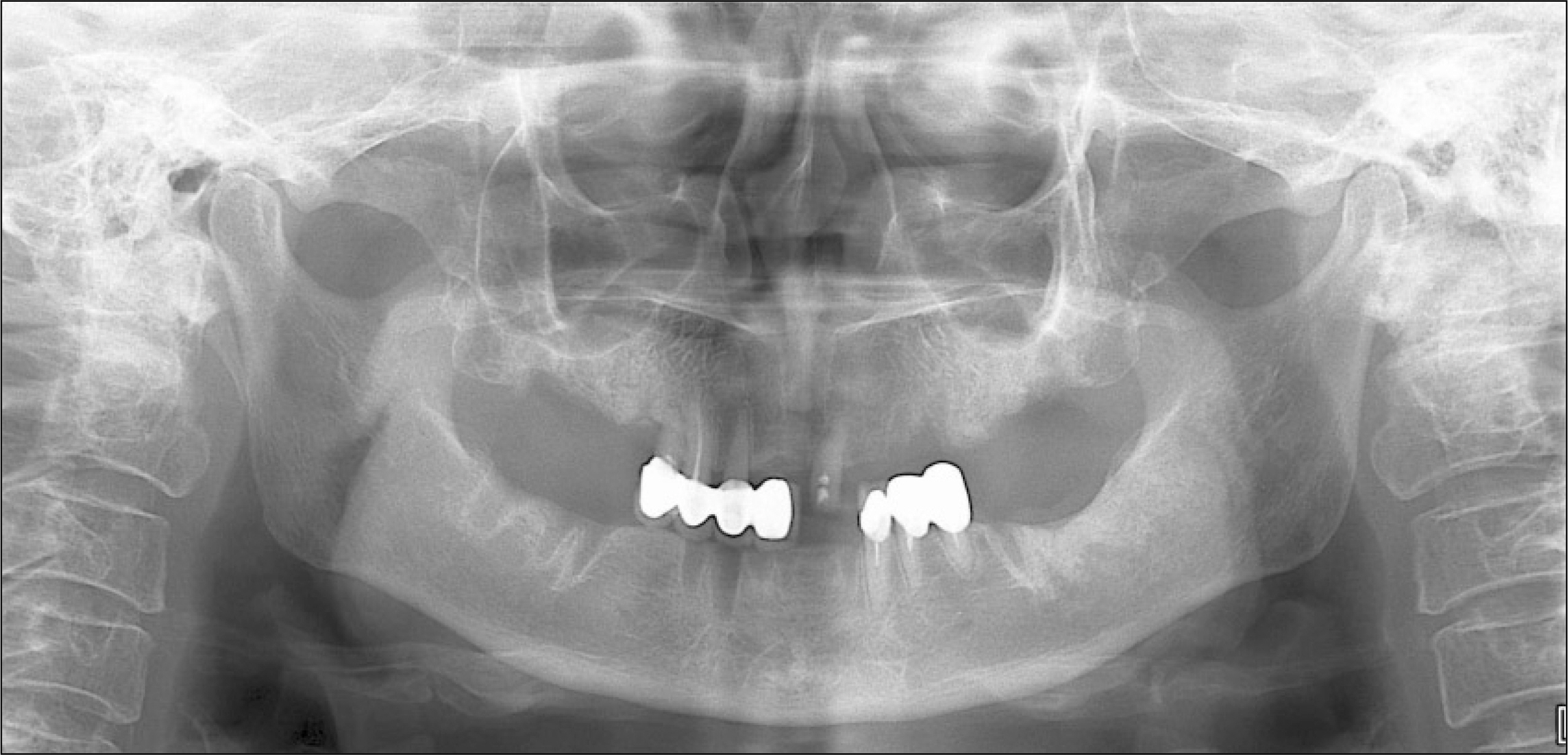
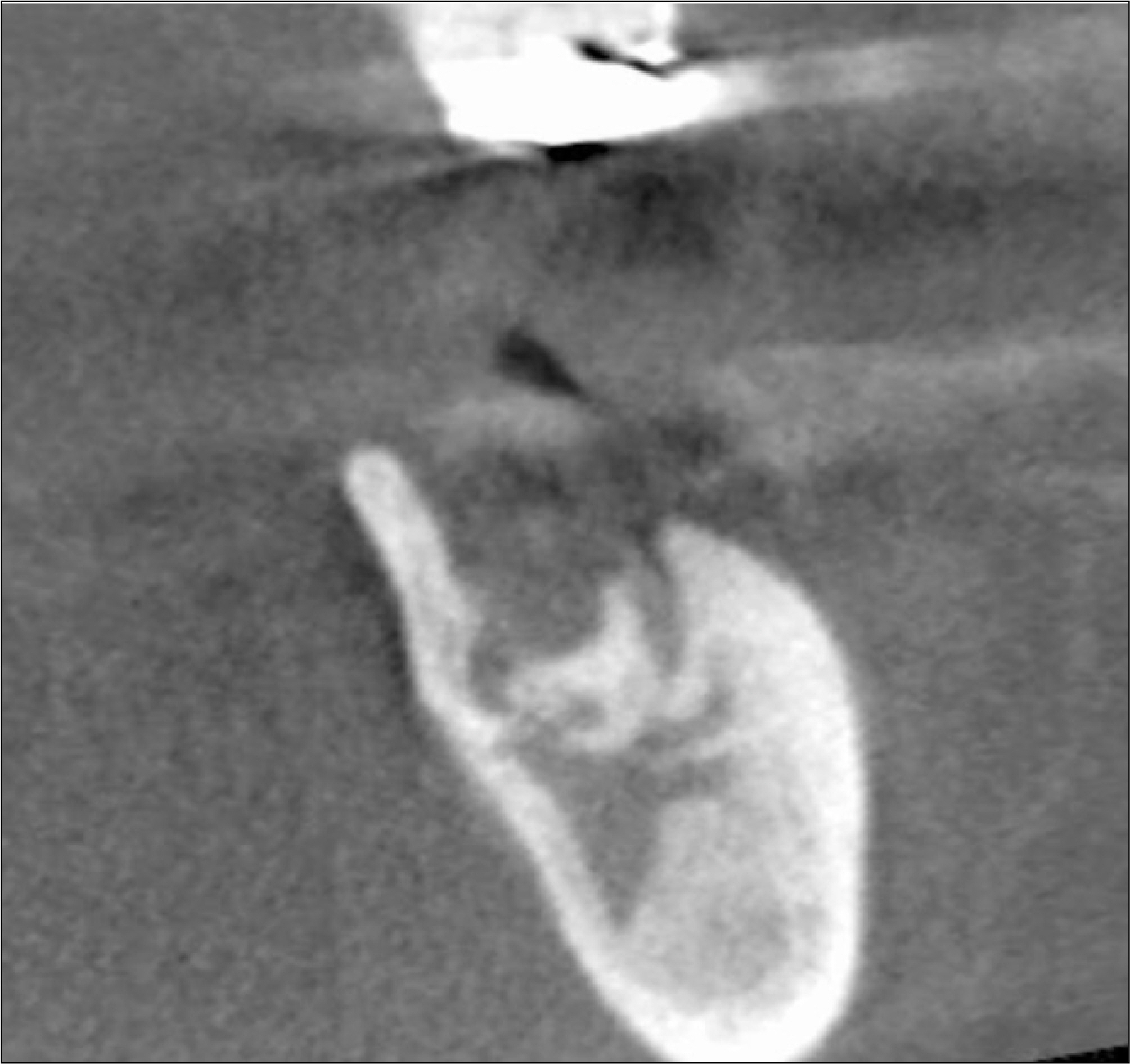
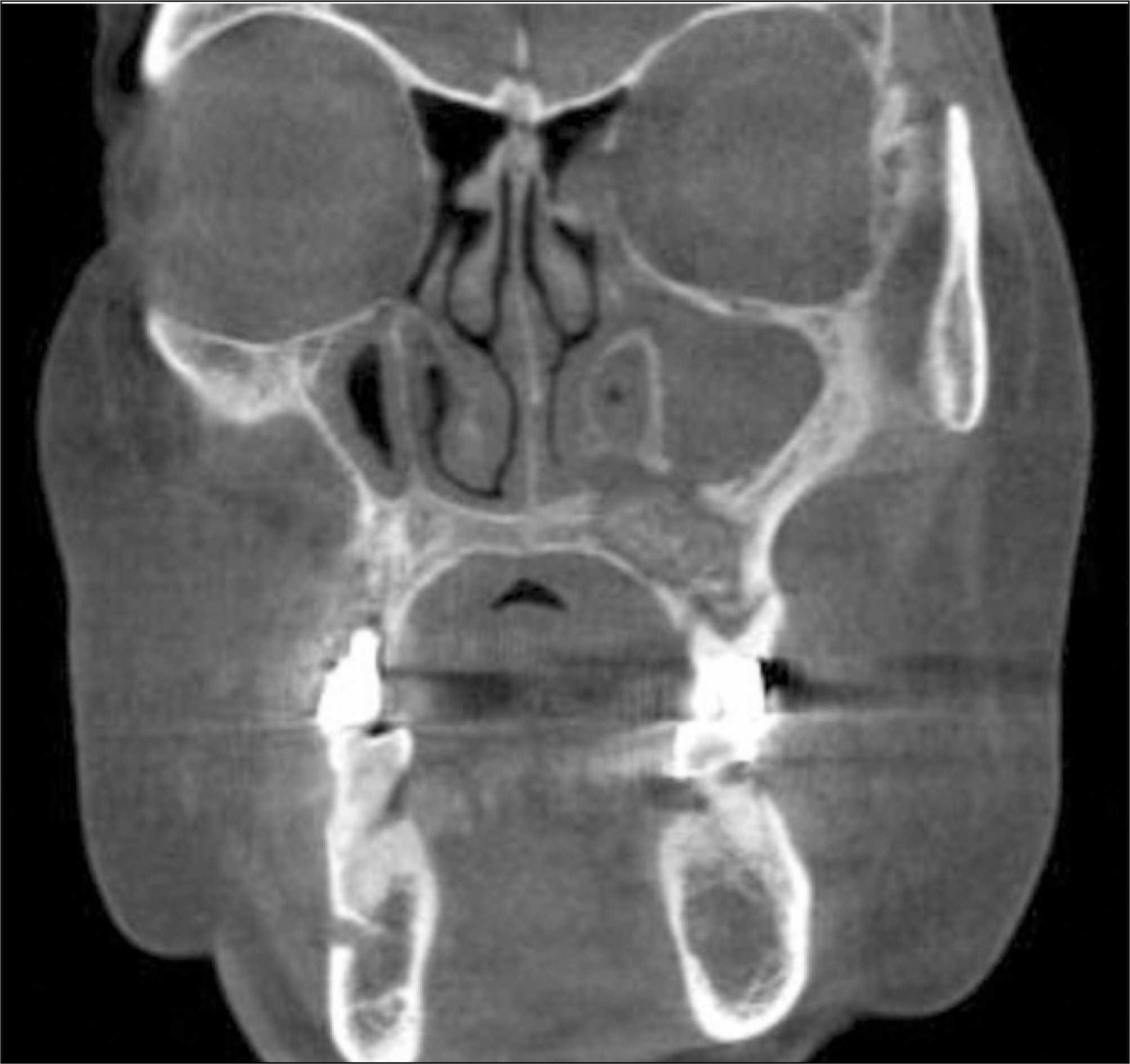
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Relationship between disease stage and renal function in bisphosphonate-related osteonecrosis of the jaw
Yun-Ho Kim, Han-Kyul Park, Na-Rae Choi, Seong-Won Kim, Gyoo-Cheon Kim, Dae-Seok Hwang, Yong-Deok Kim, Sang-Hun Shin, Uk-Kyu Kim
J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2017;43(1):16-22. doi: 10.5125/jkaoms.2017.43.1.16.
Reference
-
References
1. Marx RE. Pamidronate (Aredia) and zoledronate (Zometa) induced avascular necrosis of the jaws: a growing epidemic. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2003; 61:1115–7.
Article2. Saad F, Lipton A. Clinical benefits and considerations of bisphosphonate treatment in metastatic bone disease. Semin Oncol. 2007; 34(6 Suppl 4):S17–23.
Article3. Diel IJ, Bergner R, Gro ¨tz KA. Adverse effects of bisphosphonates: current issues. J Support Oncol. 2007; 5:475–82.4. Khosla S, Burr D, Cauley J, Dempster DW, Ebeling PR, Felsenberg D, et al. .;. American Society for Bone and Mineral Research. Bisphosphonate-associated osteonecrosis of the jaw: report of a task force of the American Society for Bone and Mineral Research. J Bone Miner Res. 2007; 22:1479–91.
Article5. Mavrokokki T, Cheng A, Stein B, Goss A. Nature and frequency of bisphosphonateassociated osteonecrosis of the jaws in Australia. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2007; 65:415–23.
Article6. Roelofs AJ, Coxon FP, Ebetino FH, Bala JF, Kashemirov BA, McKenna CE, et al. Use of a fluorescent analogue of risedronate to study localisation and cellular uptake of bisphosphonates in vivo. Bone. 2008; 42(Suppl 1):S85.
Article7. Marx RE, Cillo JE Jr, Ulloa JJ. Oral bisphosphonate-induced osteonecrosis: risk factors, prediction of risk using serum CTX testing, prevention, and treatment. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2007; 65:2397–410.
Article8. Advisory Task Force on Bisphosphonate-Related Ostenonecrosis of the Jaws, American Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons. American Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons position paper on bisphosphonate-related osteonecrosis of the jaws. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2007; 65:369–76.9. Marx RE. Oral and intravenous bisphosphonate-induced osteonecrosis of the jaws: history, etiology, prevention, and treatment. 1st ed.Chicago: Quintessence Pub. Co.;2007.10. Hansen T, Kunkel M, Springer E, Walter C, Weber A, Siegel E, et al. Actinomycosis of the jaws–histopathological study of 45 patients shows significant involvement in bisphosphonateassociated osteonecrosis and infected osteoradionecrosis. Virchows Arch. 2007; 451:1009–17.
Article11. Hansen T, Kirkpatrick CJ, Walter C, Kunkel M. Increased numbers of osteoclasts expressing cysteine proteinase cathepsin K in patients with infected osteoradionecrosis and bisphosphonateassociated osteonecrosis-a paradoxical observation? Virchows Arch. 2006; 449:448–54.
Article12. Rizzoli R, Burlet N, Cahall D, Delmas PD, Eriksen EF, Felsenberg D, et al. Osteonecrosis of the jaw and bisphosphonate treatment for osteoporosis. Bone. 2008; 42:841–7.
Article13. Chiandussi S, Biasotto M, Dore F, Cavalli F, Cova MA, Di Lenarda R. Clinical and diagnostic imaging of bisphosphonateassociated osteonecrosis of the jaws. Dentomaxillofac Radiol. 2006; 35:236–43.
Article14. Reid IR, Bolland MJ, Grey AB. Is bisphosphonateassociated osteonecrosis of the jaw caused by soft tissue toxicity? Bone. 2007; 41:318–20.
Article15. McDonald MM, Dulai S, Godfrey C, Amanat N, Sztynda T, Little DG. Bolus or weekly zoledronic acid administration does not delay endochondral fracture repair but weekly dosing enhances delays in hard callus remodeling. Bone. 2008; 43:653–62.
Article16. Li C, Mori S, Li J, Kaji Y, Akiyama T, Kawanishi J, et al. Longterm effect of incadronate disodium (YM-175) on fracture healing of femoral shaft in growing rats. J Bone Miner Res. 2001; 16:429–36.
Article17. Li J, Mori S, Kaji Y, Kawanishi J, Akiyama T, Norimatsu H. Concentration of bisphosphonate (incadronate) in callus area and its effects on fracture healing in rats. J Bone Miner Res. 2000; 15:2042–51.
Article18. Peter CP, Cook WO, Nunamaker DM, Provost MT, Seedor JG, Rodan GA. Effect of alendronate on fracture healing and bone remodeling in dogs. J Orthop Res. 1996; 14:74–9.
Article19. Allen MR, Burr DB. The pathogenesis of bisphosphonate-related osteonecrosis of the jaw: so many hypotheses, so few data. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2009; 67(5 Suppl):61–70.
Article20. Schwartz S, Joseph C, Iera D, Vu DD. Bisphosphonates, osteonecrosis, osteogenesis imperfecta and dental extractions: a case series. J Can Dent Assoc. 2008; 74:537–42.21. Vignery A, Baron R. Dynamic histomorphometry of alveolar bone remodeling in the adult rat. Anat Rec. 1980; 196:191–200.
Article22. Enlow DH. Functions of the Haversian system. Am J Anat. 1962; 110:269–305.
Article23. Marx RE, Sawatari Y, Fortin M, Broumand V. Bisphosphonate-induced exposed bone (osteonecrosis/osteopetrosis) of the jaws: risk factors, recognition, prevention, and treatment. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2005; 63:1567–75.
Article24. Product information sheet, Aredia. Pamidronatate sodium for injection for intravenous infusion. East Hanover, NJ: Novartis AG;2001.25. Bonewald LF. Osteocytes as dynamic multifunctional cells. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2007; 1116:281–90.
Article26. Product information sheet, Zometa. Zoledronic acid injection. East Hanover, NJ: Novartis AG;2004.27. Neff MJ. American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. ACOG releases guidelines for clinical management of osteoporosis. Am Fam Physician. 2004; 69:1558–1560.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Clinical study of diagnosis and treatment of bisphosphonate-related osteonecrosis of the jaws
- A clinical retrospective study of implant as a risk factor for medication‑related osteonecrosis of the jaw: surgery vs loading?
- Bisphosphonate related osteonecrosis of the jaws: report of two cases
- Clinical Study of Bisphosphonate-Induced Osteonecrosis of Mandibular and Maxillary Bone
- Medication-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaws: A Literature Review