J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg.
2015 Apr;41(2):84-89. 10.5125/jkaoms.2015.41.2.84.
A case report about the reconstruction procedures of the previously failed cylinderical implants site using distraction osteogenesis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Periodontology, Section of Dentistry, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea. periolee@gmail.com
- 2Department of Prosthodontics, Section of Dentistry, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea.
- 3Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Section of Dentistry, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea.
- KMID: 2189468
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5125/jkaoms.2015.41.2.84
Abstract
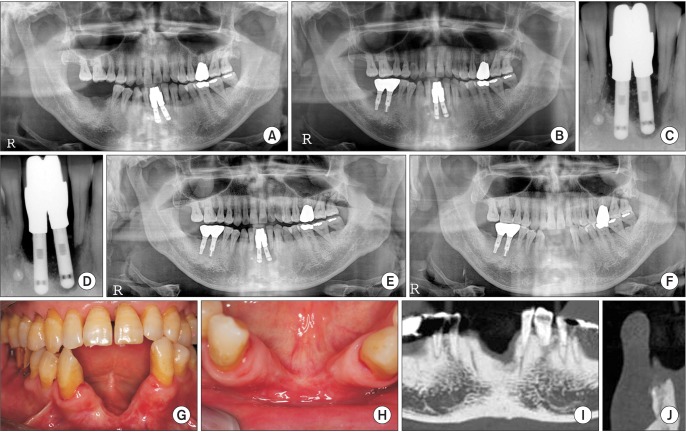
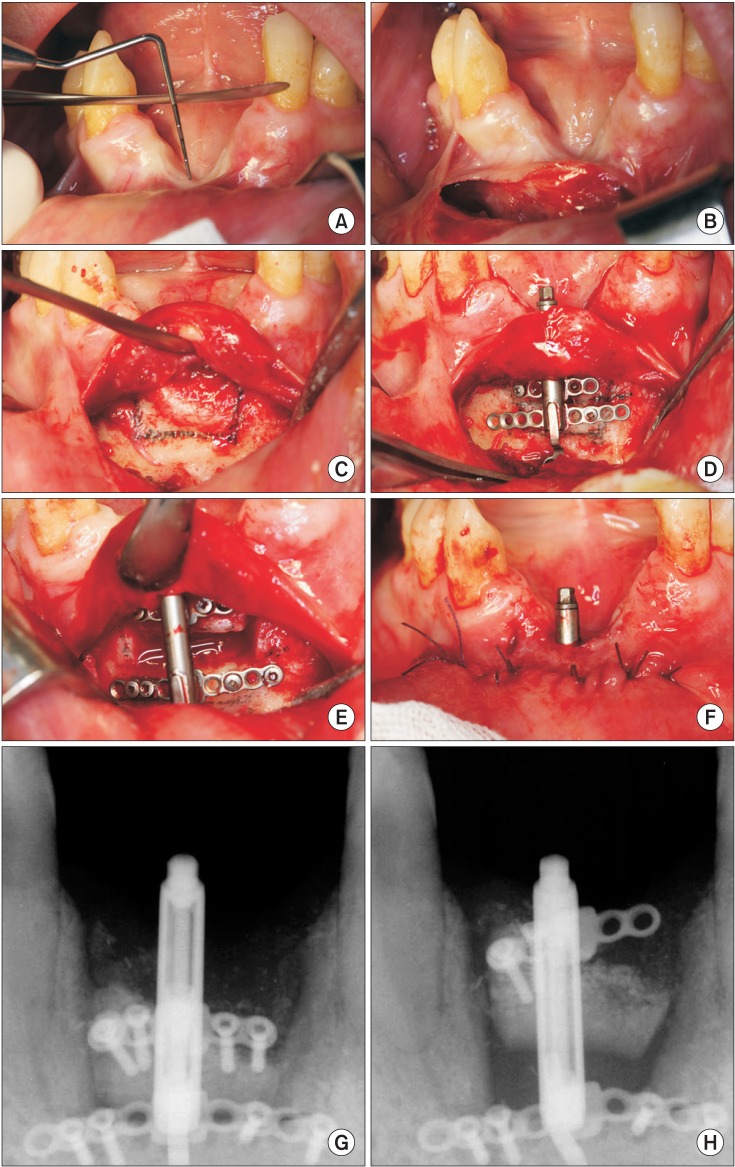
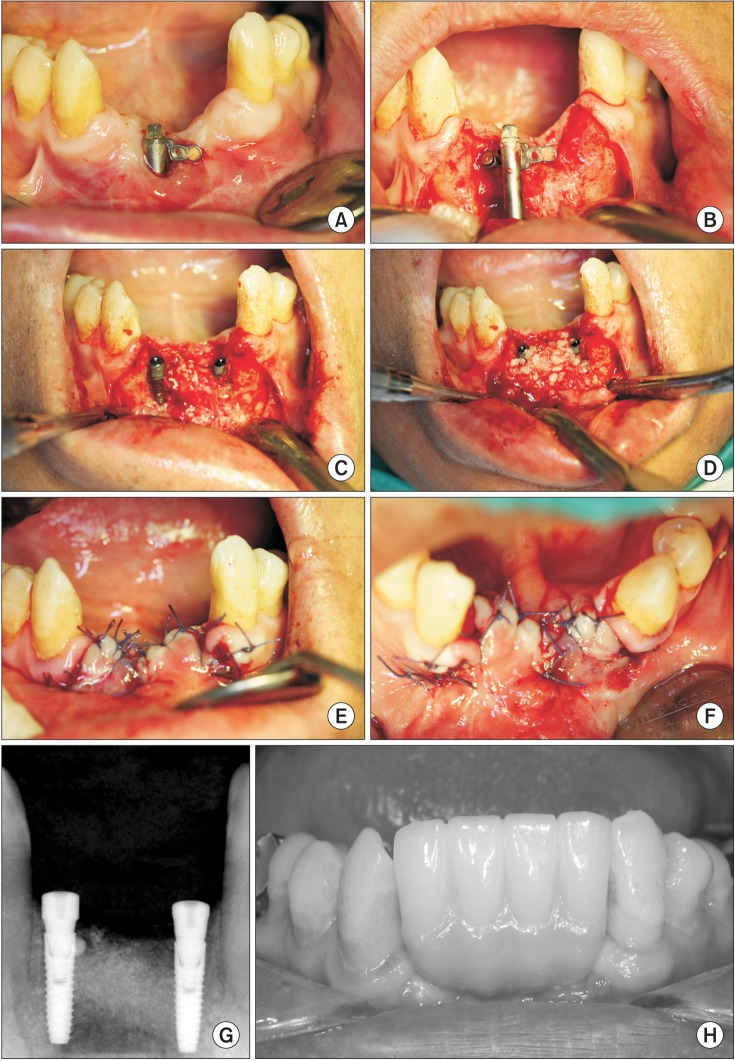
- We report the eventually successful treatment of a huge bone defect and peri-implantitis following reconstruction of a previously failed intra-mobile cylinder implant system (IMZ) implant site using distraction osteogenesis (DO). In the anterior mandible, two IMZ implants failed and surgical debridement was performed in accordance to the patient's needs. Thereafter, mobility and suppuration were decreased and the patient visited the dental clinic on a regular basis for oral health maintenance. However, the inflammation did not resolve, and the bone destruction around the implants progressed for 4 years. Finally, the implants failed and a severe bone defect remained after implant removal. To reconstruct the bone defects, we attempted bone graft procedures. Titanium mesh was unsuccessfully used to obtain bone volume regeneration. However, DO subsequently was used to obtain sufficient bone volume for implant placement. The new implants were then installed, followed by prosthetic procedures. In conclusion, progression of peri-implantitis could not be arrested despite surgical intervention and repeated maintenance care for 3 years. Reconstruction of the peri-implantitis site was complicated due to its horizontal and vertical bone defects. Lesions caused by implant failure require an aggressive regenerative strategy, such as DO. DO was successful in reconstruction of a peri-implantitis site that was complicated due to horizontal and vertical bone defects.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Mombelli A, Müller N, Cionca N. The epidemiology of periimplantitis. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2012; 23(Suppl 6):67–76. PMID: 23062130.
Article2. Willer J, Noack N, Hoffmann J. Survival rate of IMZ implants: a prospective 10-year analysis. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2003; 61:691–695. PMID: 12796880.
Article3. Rinke S, Ohl S, Ziebolz D, Lange K, Eickholz P. Prevalence of periimplant disease in partially edentulous patients: a practice-based cross-sectional study. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2011; 22:826–833. PMID: 21198898.
Article4. Leonhardt A, Renvert S, Dahlén G. Microbial findings at failing implants. Clin Oral Implants Res. 1999; 10:339–345. PMID: 10551058.
Article5. Renvert S, Roos-Jansåker AM, Lindahl C, Renvert H, Rutger Persson G. Infection at titanium implants with or without a clinical diagnosis of inflammation. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2007; 18:509–516. PMID: 17517058.
Article6. Roccuzzo M, Bonino F, Aglietta M, Dalmasso P. Ten-year results of a three arms prospective cohort study on implants in periodontally compromised patients. Part 2: clinical results. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2012; 23:389–395. PMID: 22092445.
Article7. Chrcanovic BR, Albrektsson T, Wennerberg A. Reasons for failures of oral implants. J Oral Rehabil. 2014; 41:443–476. PMID: 24612346.
Article8. Machtei EE, Frankenthal S, Blumenfeld I, Gutmacher Z, Horwitz J. Dental implants for immediate fixed restoration of partially edentulous patients: a 1-year prospective pilot clinical trial in periodontally susceptible patients. J Periodontol. 2007; 78:1188–1194. PMID: 17608572.
Article9. Levine RA, Clem D, Beagle J, Ganeles J, Johnson P, Solnit G, et al. Multicenter retrospective analysis of the solid-screw ITI implant for posterior single-tooth replacements. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2002; 17:550–556. PMID: 12182298.10. Spiekermann H, Jansen VK, Richter EJ. A 10-year follow-up study of IMZ and TPS implants in the edentulous mandible using barretained overdentures. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 1995; 10:231–243. PMID: 7744443.11. Esposito M, Hirsch JM, Lekholm U, Thomsen P. Failure patterns of four osseointegrated oral implant systems. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 1997; 8:843–847. PMID: 15348802.12. Wolvius EB, Scholtemeijer M, Weijland M, Hop WC, van der. Complications and relapse in alveolar distraction osteogenesis in partially dentulous patients. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2007; 36:700–705. PMID: 17604966.
Article13. Iizuka T, Hallermann W, Seto I, Smolka W, Smolka K, Bosshardt DD. Bi-directional distraction osteogenesis of the alveolar bone using an extraosseous device. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2005; 16:700–707. PMID: 16307577.
Article14. Polo WC, Cury PR, Sendyk WR, Gromatzky A. Posterior mandibular alveolar distraction osteogenesis utilizing an extraosseous distractor: a prospective study. J Periodontol. 2005; 76:1463–1468. PMID: 16171433.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Reconstruction using mandibular horizontal distraction osteogenesis and implant prosthesis in mandibular deficiency: a case report
- Case reports of antero-posteior movement with distraction osteogenesis in maxillary anterior segment
- Treatment of Infected Nonunion of the Femur with Marked Shortening by Compression and Gradual Distraction at the Nonunion Site: A Report of 2 cases
- Distraction osteogenesis in facial asymmetry patient
- Distraction Osteogenesis of Mandible using Short-Sagittal Osteotomy for the Patient with Hemifacial Microsomia