J Korean Orthop Assoc.
2007 Oct;42(5):653-658. 10.4055/jkoa.2007.42.5.653.
Treatment of the Femoral Shaft Nonunion Occurredafter Intramedullary Nailing
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Kwangju Christian Hospital, Gwangju, Korea. paedic@chol.com
- KMID: 2186473
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4055/jkoa.2007.42.5.653
Abstract
-
PURPOSE: To evaluate of efficacy of the treatment options for a femoral shaft nonunion occurring after intramedullary nailing.
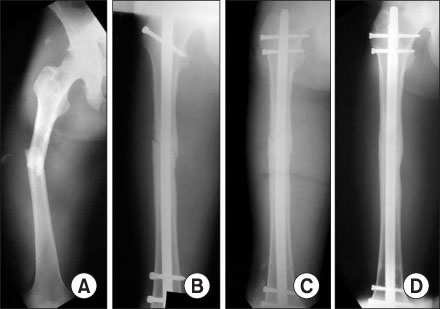
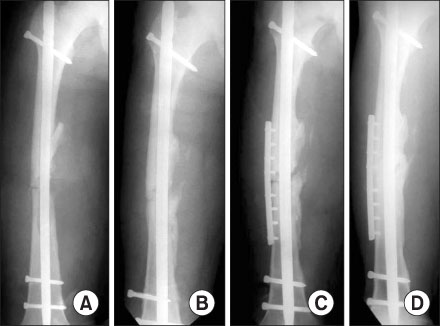
MATERIAL AND METHODS: Thirty-one patients with nonunion of a femoral shaft fracture, who had been treated with interlocking intramedullary nailing from January 1996 to December 2000, were examined. Twenty-six had oligotrophic nonunion and five were hypervascular. Forty-five procedures were performed for 31 nonunions; bone grafting for 14, exchange nailing for 13, plate augmentation and bone grafting for 14 and dynamization for 4 cases.
RESULTS
The success rate after a single procedure was only 58%. The four dynamization cases failed to unite. Seven of the 13 (54%) nonunion cases treated with nail exchange healed satisfactorily. All cases treated with plate augmentation and bone grafting achieved successful union. The mean period from fracture to union was 20 months.
CONCLUSION
Exchange nailing is not always a reliable procedure for treating nonunion of a femoral shaft fracture. Plate augmentation and bone grafting were found to be a successful mode of therapy for the femoral shaft nonunion without complications.
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Augmentative Locking Plate Fixation for the Treatment of Femoral Nonunion after Intramedullary Nailing
Ki-Chul Park, Chul-Woong Kim, Kyu-Tae Hwang, Ye-Soo Park
J Korean Fract Soc. 2013;26(4):268-274. doi: 10.12671/jkfs.2013.26.4.268.Results of Exchange Nailing in Hypertrophic Nonunion of Femoral Shaft Fracture Treated with Nailing
Suenghwan Jo, Gwang Chul Lee, Sang Hong Lee, Jun Young Lee, Dong Hwi Kim, Sung Hae Park, Young Min Cho
J Korean Fract Soc. 2019;32(2):83-88. doi: 10.12671/jkfs.2019.32.2.83.
Reference
-
1. Baixauli F, Baixauli EJ, Sánchez-Alepuz E, Baixauli F. Interlocked intramedullary nailing for treatment of open femoral shaft fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1998. 350:67–73.
Article2. Banaszkiewicz PA, Sabboubeh A, McLeod I, Maffulli N. Femoral exchange nailing for aseptic non-union: not the end to all problems. Injury. 2003. 34:349–356.
Article3. Basumallick MN, Bandopadhyay A. Effect of dynamization in open interlocking nailing of femoral fractures. A prospective randomized comparative study of 50 cases with a 2-year follow-up. Acta Orthop Belg. 2002. 68:42–48.4. Bellabarba C, Ricci WM, Bolhofner BR. Results of indirect reduction and plating of femoral shaft nonunions after intramedullary nailing. J Orthop Trauma. 2001. 15:254–263.
Article5. Brinker MR, O'Connor DP. Exchange nailing of ununited fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007. 89:177–188.
Article6. Cole JD. Browner BD, editor. The vascular response of bone to internal fixation. The science and practice of intramedullary nailing. 2nd ed. Williams and Wilkins;43–69.7. Hak DJ, Lee SS, Goulet JA. Success of exchange reamed intramedullary nailing for femoral shaft nonunion or delayed union. J Orthop Trauma. 2000. 14:178–182.
Article8. Heiple KG, Figgie HE, Lacey SH, Figgie MP. Femoral shaft nonunion treated by a fluted intramedullary rod. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1985. 194:218–225.
Article9. Johnson KD, Tencer AF, Blementhal S, August A, Johnston DW. Biomechanical performance of locked intramedullary nail systems in comminuted femoral shaft fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1986. 206:151–161.
Article10. Koval KJ, Seligson D, Rosen H, Fee K. Distal femoral nonunion: treatment with a retrograde inserted locked intramedullary nail. J Orthop Trauma. 1995. 9:285–291.
Article11. Mercado EM, Lim EV, Stern PJ, Aquino NJ. Exchange nailing for failure of initially rodded tibial shaft fractures. Orthopedics. 2001. 24:757–762.
Article12. Ueng SW, Chao EK, Lee SS, Shih CH. Augmentative plate fixation for the management of femoral nonunion after intramedullary nailing. J Trauma. 1997. 43:640–644.
Article13. Ueng SW, Shih CH. Augmentative plate fixation for the management of femoral nonunion with broken interlocking nail. J Trauma. 1998. 45:747–752.
Article14. Webb LX, Winquist RA, Hansen ST. Intramedullary nailing and reaming for delayed union or nonunion of the femoral shaft. A report of 105 consecutive cases. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1986. 212:133–141.15. Weresh MJ, Hakanson R, Stover MD, Sims SH, Kellam JF, Bosse MJ. Failure of exchange reamed intramedullary nails for ununited femoral shaft fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2000. 14:335–338.
Article16. Winquist RA, Hansen ST. Comminuted fractures of the femoral shaft treated by intramedullary nailing. Orthop Clin North Am. 1980. 11:633–648.
Article17. Wolinsky PR, McCarty E, Shyr Y, Johnson K. Reamed intramedullary nailing of the femur: 551 cases. J Trauma. 1999. 46:392–399.18. Wu CC, Chen WJ. Treatment of femoral shaft aseptic nonunions: comparison between closed and open bone-grafting techniques. J Trauma. 1997. 43:112–116.19. Zuckerman JD, Veith RG, Johnson KD, Bach AW, Hansen ST, Solvik S. Treatment of unstable femoral shaft fractures with closed interlocking intramedullary nailing. J Orthop Trauma. 1987. 1:209–218.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Use of Poller Screws in Nonunion of Femoral Shaft Following Intramedullary Nailing of Femoral Shaft Fracture: A Case Report
- Interlocking Intramedullary Nailing Versus conventional Kuntscher Intramedullary Nailing for Fracture of the Femoral Shaft
- Results of Exchange Nailing in Hypertrophic Nonunion of Femoral Shaft Fracture Treated with Nailing
- Analysis of Risk Factors for Nonunion after Intramedullary Nailing of Femoral Shaft Fracture in Adult
- Treatment of the Fractures of the Shaft of the Femur with Intramedullary Nailing