J Korean Orthop Assoc.
2009 Dec;44(6):651-660. 10.4055/jkoa.2009.44.6.651.
The Treatment of Nonunion of the Scaphoid with a Horse-Shoe Bone Graft and Fixation with Two Screws
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Haman Woori Hospital, Gyungnam, Korea. hoondeng@gmail.com
- KMID: 2186292
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4055/jkoa.2009.44.6.651
Abstract
- PURPOSE
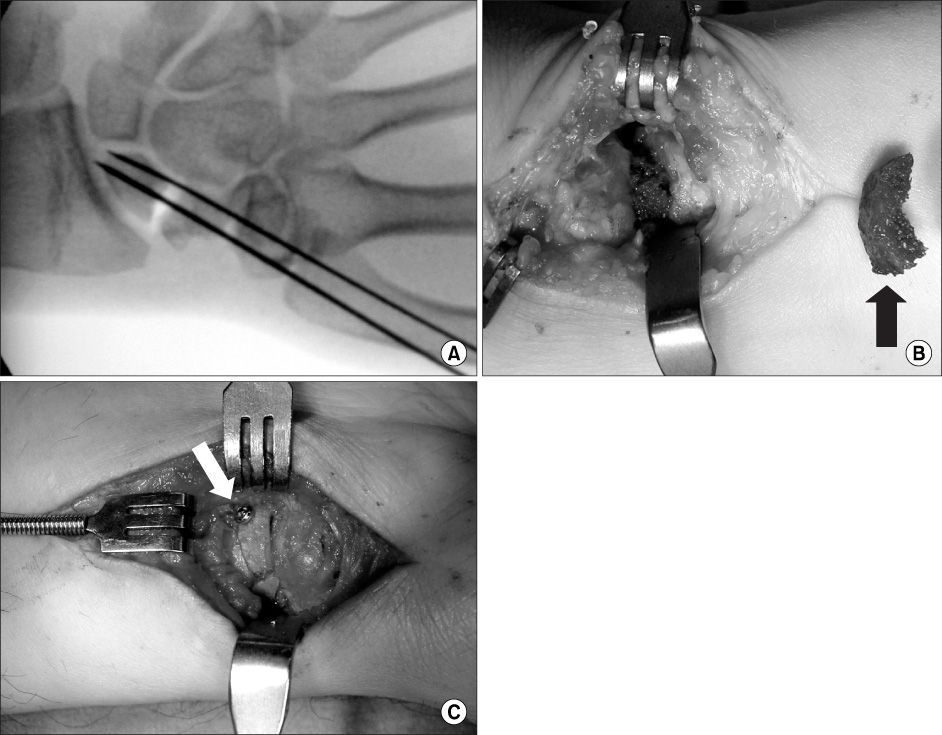
Three dimensional anatomical reconstruction of an old scaphoid nonunion injury with a humpback deformity is not an easy procedure. The single interpositional bone graft technique has its limitation for accurate anatomic reconstruction. We report here on the effect of a cortical interpositional horse-shoe graft using two screws and a volar cancellous chip bone graft for the treatment of scaphoid nonunion with a humpback deformity or a miss-match fracture surface in scaphoid nonunion.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
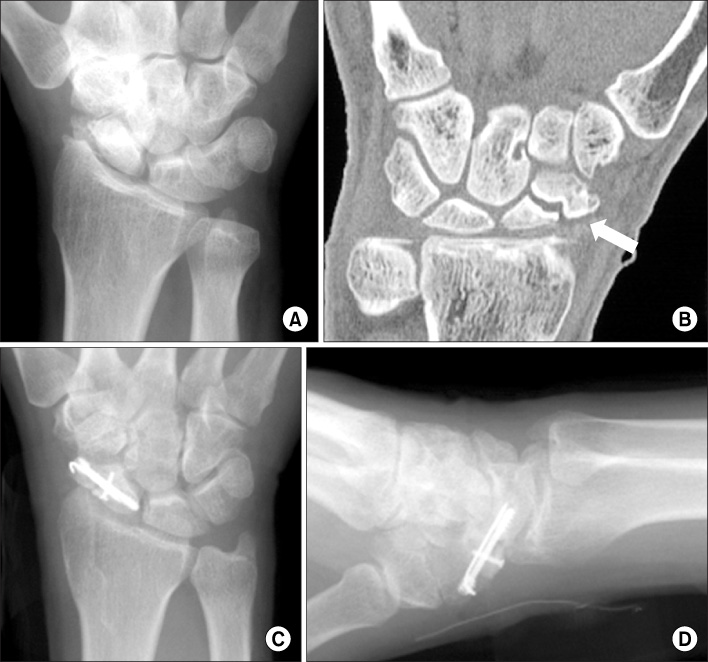
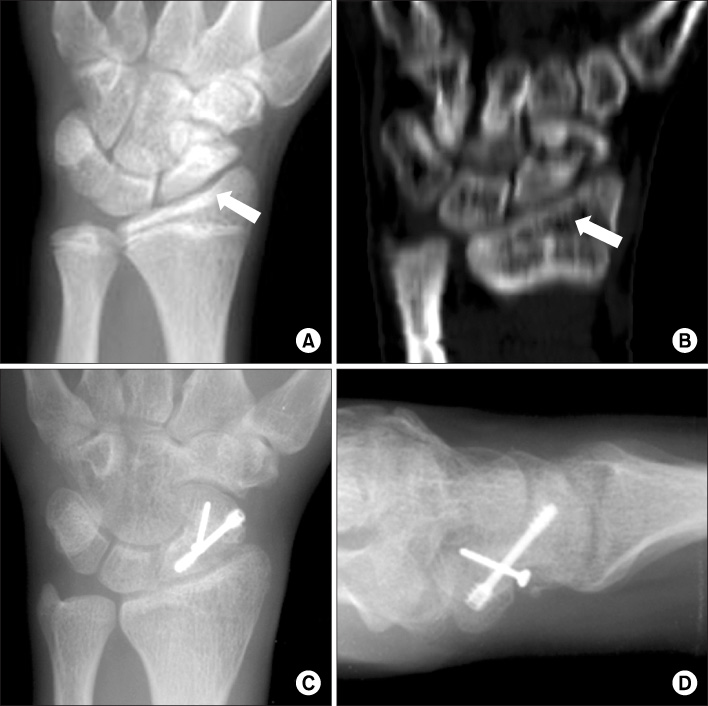
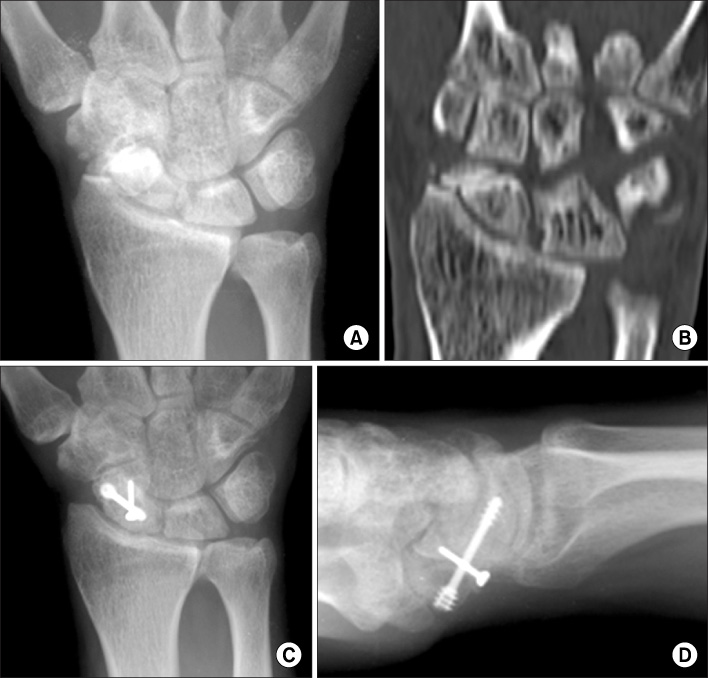
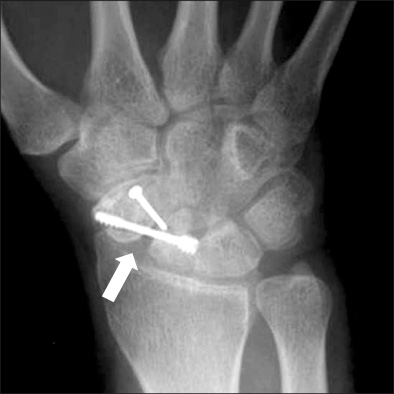
We retrospectively reviewed nineteen patients who were treated for scaphoid nonunion using a cancellous chip bone graft and a cortical interpositional horse-shoe graft with 2 screws (a Herbert's screw and a mini screw). The mean follow up period was 24 months (range: 14-36 months). The mean age was 30.5 years (range: 17-52 years) and 18 patients were male and 1 patient was female. The mean period between injury and operation was 6.7 years (range: 1 to 30 years). The nonunion sites were located in the waist in 15 wrists and in the distal third in 4 wrists. The volar approach was used in 18 cases and the dorsal approach was used in 1 case. In 2 cases, one additional kirschner's wire was used due to the instability of fixation. The clinical results were assessed by the criteria of Maudesley and Chen at the last follow-up.
RESULTS
Bony union was obtained in 18 (95%) cases. The average time for union was 13 weeks. There were improvements in the scapholunate angle (from 65.2 degrees to 49.5 degrees) and the intrascaphoid angle (from 43.5 degrees to 29.6 degrees). There are 3 cases with excellent results, 10 cases with good results and 6 cases with fair results. There was one complication. In 1 case, a nonunion gap was seen at 7 months after operation, but there were no clinical symptoms.
CONCLUSION
A cortical interpositional horse-shoe graft using two screws and a cancellous chip bone graft for treating scaphoid nonunion with a humpback deformity or a large defect seems to be an encouraging procedure for regaining the normal anatomy of the scaphoid.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Operative Treatment for Nonunion of the Distal Scaphoid
Sang-yun Lee, Jucheol Shin, Won-taek Oh, Yun-Rak Choi, Il-Hyun Koh, Ho-Jung Kang
Arch Hand Microsurg. 2018;23(1):35-45. doi: 10.12790/ahm.2018.23.1.35.
Reference
-
1. Cooney WP, Dobyns JH, Linscheid RL. Nonunion of the scaphoid: analysis of the result from bone grafting. J Hand Surg Am. 1980. 5:343–354.2. Cooney WP, Linscheid RL, Dobyns JH, Wood MB. Scaphoid nonunion: role of anterior interpositional bone grafts. J Hand Surg Am. 1988. 13:635–650.
Article3. Green PD. The effect of avascular necrosis on russe bone grafting for scaphoid nonunion. J Hand Surg Am. 1985. 10:597–605.
Article4. Berger RA. The anatomy of the scaphoid. Hand Clin. 2001. 17:525–532.
Article5. Taleisnik J, Kelly PJ. The extraosseous and intraosseous blood supply of the scaphoid bone. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1996. 48:1125–1137.
Article6. Herbert TJ, Fisher WE. Management of the fractured scaphoid using a new bone screw. J Bone Joint Surg. 1984. 66:114–123.
Article7. Russe O. Fracture of the carpal navicular. Diagnosis, nonoperative treatment and operative treatment. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1960. 42:759–768.8. Mack GR, Bosse MJ, Gelberman RH, Yu E. The natural history of scaphoid non-union. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1984. 66:504–509.
Article9. Maudsley RH, Chen SC. Screw fixation in the management of the fractured carpal scaphoid. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1972. 54:432–441.
Article10. Bunker TD, McNAmee PB, Scott TD. The herbert screw for scaphoid fractures. A multicentre study. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1987. 69:631–634.
Article11. Dias JJ, Taylor M, Thompson J, Brenkel IJ, Gregg PJ. Radiographic signs of union of scaphoid fractures. An analysis of inter-observer agreement and reproducibility. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1988. 70:299–301.
Article12. Kwon CS, Ko HS, Kim YU, Lee JH. Clinical analysis of carpsl scaphoid fracture. J Korean Orthop Assoc. 1991. 26:762–769.13. Gelberman RH, Wolock BS, Siegel DB. Fractures and nonunion of carpal scaphoid. J Bone Joint Surg. 1995. 77:883–893.14. McDonald G, Petrie D. Un-united fracture of the scaphoid. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1975. 108:110–114.
Article15. Gelberman RH, Wolock BS, Siegel DB. Fractures and non-union of carpal scaphoid. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1989. 71:1560–1565.16. Jiranek WA, Ruby LK, Millender LB, Bankoff MS, Newberg AH. Long-term results after Russe bone grafting: the effect of malunion of the scphoid. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1992. 74:1217–1228.17. Kang ES, Kang HJ, Lee JM, Shin SJ, Hahn SB. Comparison between Kirschner's wire and Herbert's screw fixation in Scaphoid nonunion. J Korean Soc Surg Hand. 1999. 4:149–156.18. Ruby LK, Stinson J, Belsky MR. The natural history of scaphoid nonunion. A review of fifty-five cases. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1985. 67:428–432.
Article19. Schneider LH, Aulicino P. Nonunion of the carpal scaphoid: the Russe procedure. J Trauma. 1982. 22:315–319.20. Stark HH, Rickard TA, Zemel NP, Ashworth CR. Treatment of ununited fractures of the scaphoid by iliac bone grafts and Kirschner-wire fixation. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1988. 70:982–991.
Article21. Adams JD, Leonard RD. Fracture of the carpal scaphoid. A new method of treatment with report of one case. New England J Med. 1928. 198:401–404.22. Matti H. Technik and resilte, meiner pseudoarthosen- operation. Z Chir. 1975. 63:1442–1453.23. Fisk GR. Nonunion of carpal scaphoid treated by wedge grafting. J Bone and Joint Surg. 1984. 66:277.24. Kawai H, Yamamoto K. Pronator quadratus pedicled bone graft for old scaphoid fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1988. 70:829–831.
Article25. Dooley BJ. Inlay bone grafting for non-union of the scaphoid bone by the anterior approach. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1968. 50:102–109.
Article26. Schuind F, Haentjens P, Van Innis F, Vander Maren C, Garcia-Elias M, Sennwald G. Prognostic factors in the treament of carpal scaphoid nonunions. J Hand Surg. 1999. 24:761–776.27. Ritter K, Giacchino AA. The treatment of pseudoarthrosis of the scaphoid by bone grafting and three methods of internal fixation. Can J Surg. 2000. 43:118–124.28. Merrell GA, Wolfe SW, Slade JF 3rd. Treatment of scaphoid nonunions: quantitative meta-analysis of the literature. J Hand Surg Am. 2002. 4:685–691.
Article29. Siegel DB, Gelberman RH. Radial styloidectomy: an anatomical study with special reference to radiocarpal intracapsular ligamentous morphology. J Hand Surg Am. 1991. 16:40–44.
Article30. Munk B, Larsen CF. Bone grafting the scaphoid nonunion: a systematic review of 147 publications including 5,246 cases of scaphoid nonunion. Acta Orthop Scand. 2004. 75:618–629.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Arthroscopic Bone Grafting and Kirschner-Wires Fixation for Scaphoid Nonunion
- Surgical Outcome of Stable Scaphoid Nonunion without Bone Graft
- Arthroscopic Bone Grafting and Percutaneous K-Wires Fixation for the Treatment of Scaphoid Nonunion: Surgical Technique
- Scaphoid Fractures and Nonunion
- Treatment of Scaphoid Fractures and Nonunions