J Korean Orthop Assoc.
2011 Jun;46(3):262-267. 10.4055/jkoa.2011.46.3.262.
Concomitant Fracture of the Lateral Process of the Talus and the Sustentaculum Tali of the Calcaneus
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, College of Medicine, Chungbuk National University, Cheongju, Korea. titanick25@yahoo.co.kr
- KMID: 2185468
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4055/jkoa.2011.46.3.262
Abstract
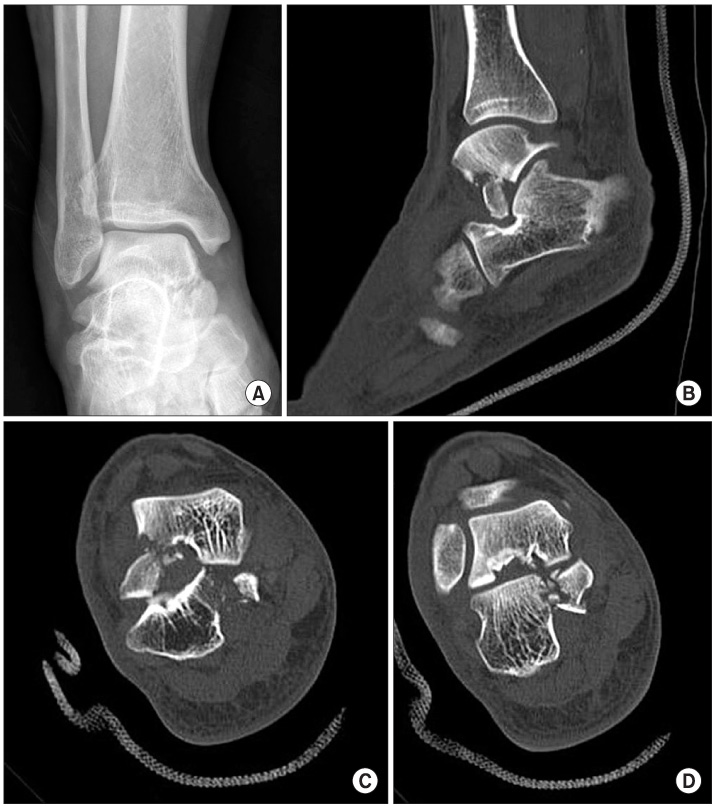
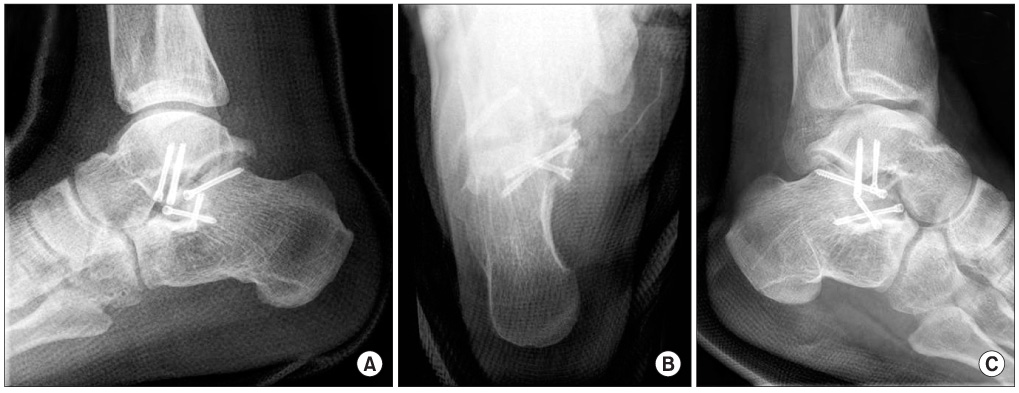
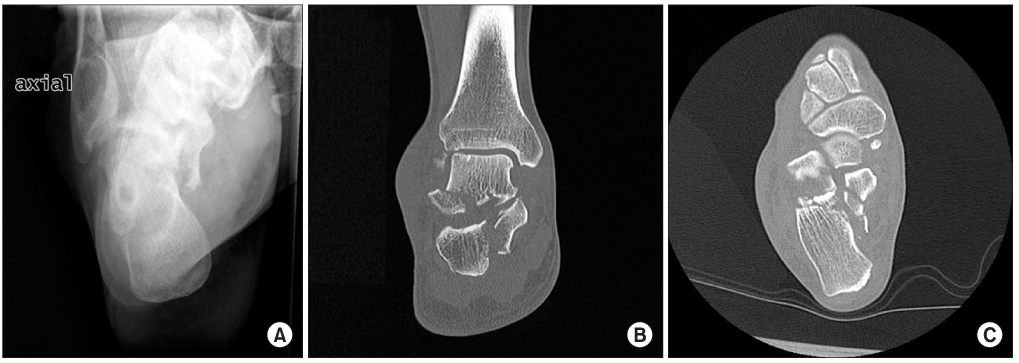
- Concomitant fracture of the lateral process of the talus and the sustentaculum tali of the calcaneus is a rare injury. There are few references in the literature that comment on the precise injury mechanism and the operative method for this type of fracture. We achieved satisfactory clinical results in 2 cases of concomitant fractures of the lateral process and the sustentaculum tali resulting from traffic accidents. We used a method of open reduction and internal fixation. We report these cases with a review of the relevant foreign literature because of no previous report in Korean literature.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Gatha M, Pedersen B, Buckley R. Fractures of the sustentaculum tali of the calcaneus: a case report. Foot Ankle Int. 2008. 29:237–240.
Article2. Della Rocca GJ, Nork SE, Barei DP, Taitsman LA, Benirschke SK. Fractures of the sustentaculum tali: injury characteristics and surgical technique for reduction. Foot Ankle Int. 2009. 30:1037–1041.
Article3. von Knoch F, Reckord U, von Knoch M, Sommer C. Fracture of the lateral process of the talus in snowboarders. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2007. 89:772–777.
Article4. McCrory P, Bladin C. Fractures of the lateral process of the talus: a clinical review. "Snowboarder's" ankle. Clin J Sport Med. 1996. 6:124–128.5. Boon AJ, Smith J, Zobitz ME, Amrami KM. Snowboarder's talus fracture. Mechanism of injury. Am J Sports Med. 2001. 29:333–338.6. Funk JR, Srinivasan SC, Crandall JR. Snowboarder's talus fractures experimentally produced by eversion and dorsiflexion. Am J Sports Med. 2003. 31:921–928.
Article7. Perera A, Baker JF, Lui DF, Stephens MM. The management and outcome of lateral process fracture of the talus. Foot Ankle Surg. 2010. 16:15–20.
Article8. Kirkpatrick DP, Hunter RE, Janes PC, Mastrangelo J, Nicholas RA. The snowboarder's foot and ankle. Am J Sports Med. 1998. 26:271–277.
Article9. Valderrabano V, Perren T, Ryf C, Rillmann P, Hintermann B. Snowboarder's talus fracture: treatment outcome of 20 cases after 3.5 years. Am J Sports Med. 2005. 33:871–880.10. Myerson MS, Berger BI. Nonunion of a fracture of the sustentaculum tali causing a tarsal tunnel syndrome: a case report. Foot Ankle Int. 1995. 16:740–742.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Concomitant Fracture of Lateral Process and Posteromedial Tubercle of Talus: A Case Report
- Irreducible Fracture of Calcaneus due to Flexor Hallucis Longus Tendon Interposition: A Case Report
- Peroneus Tendon Dislocation Associated with Fracture of Lateral Process of Talus: A Case Report
- Subtalar Dislocation: A Case Report
- Simultaneously Occurred Medial and Lateral Osteochondral Lesions of the Talus