J Korean Orthop Assoc.
2012 Dec;47(6):432-438. 10.4055/jkoa.2012.47.6.432.
Femoral Component Rotation of Total Knee Arthroplasty in Korean Subjects: A Study Using Grand Piano Sign and Computed Tomography
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, College of Medicine, Chungbuk National University, Cheongju, Korea. oseschoi@chungbuk.ac.kr
- KMID: 2185306
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4055/jkoa.2012.47.6.432
Abstract
- PURPOSE
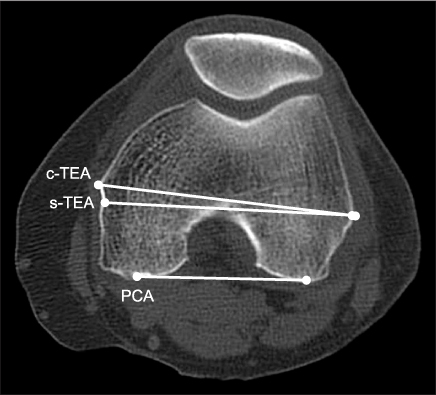
We aimed to obtain a reference for the optimal rotational alignment of femoral component in Koreans through an analysis of grand piano sign observed during total knee arthroplasty (TKA) and the angle between the clinical transepicondylar axis and the posterior condylar axis (TEA-PCA angle), by computed tomography.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
The study subjects included 24 patients (30 cases), who underwent the anterior femoral resection, which was applied at an external rotation 3degrees relative to the posterior condylar axis during TKA. The relationship between anterior femoral resection with external rotation of 3degrees and the morphological pattern of Grand piano sign was evaluated. On postoperative computed tomography images, we evaluated the relationship between the clinical transepicondylar axis, posterior condylar axis of femoral component and grand piano sign. Moreover, a total of 28 Korean patients with 41 arthritic knees scheduled for a TKA had a preoperative computed tomography. We measured the TEA-PCA angle to evaluate the normal range in Korean subjects.
RESULTS
The morphological pattern of grand piano sign observed after the anterior femoral resection, which was applied at an external rotation 3degrees, showed statistically significant correlation with TEA-PCA angle. On preoperative computed tomography images, the TEA-PCA angle was 6.01 degrees (range from 3.90 to 7.86).
CONCLUSION
The TEA-PCA angle of Koreans was different from that of the westerners. More external rotation was needed for the optimal femoral rotational alignment theoretically, and we could confirm the correlation between Grand piano sign and rotational alignment of femoral component by measurement of grand piano sign and computed tomography.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Rotational Alignment of the Distal Femur in Korean Female Patients with Osteoarthritis Using a Computer Image Program
Gyeong Min Kim, Sang-Rim Kim, Jong Hwan Bae, Yong-Geun Park
J Korean Orthop Assoc. 2017;52(3):272-278. doi: 10.4055/jkoa.2017.52.3.272.
Reference
-
1. Mochizuki RM, Schurman DJ. Patellar complications following total knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1979. 61:879–883.2. Moreland JR. Mechanisms of failure in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1988. (226):49–64.
Article3. Yoshii I, Whiteside LA, White SE, Milliano MT. Influence of prosthetic joint line position on knee kinematics and patellar position. J Arthroplasty. 1991. 6:169–177.
Article4. Arima J, Whiteside LA, McCarthy DS, White SE. Femoral rotational alignment, based on the anteroposterior axis, in total knee arthroplasty in a valgus knee. A technical note. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1995. 77:1331–1334.
Article5. Berger RA, Rubash HE, Seel MJ, Thompson WH, Crossett LS. Determining the rotational alignment of the femoral component in total knee arthroplasty using the epicondylar axis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1993. (286):40–47.
Article6. Whiteside LA, Arima J. The anteroposterior axis for femoral rotational alignment in valgus total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1995. (321):168–172.
Article7. Cui WQ, Won YY, Baek MH, Kim KK, Cho JH. Variations of the 'grand-piano sign' during total knee replacement. A computer-simulation study. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2006. 88:1441–1447.
Article8. Moyad TF, Hughes RE, Urquhart A. "Grand piano sign," a marker for proper femoral component rotation during total knee arthroplasty. Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ). 2011. 40:348–352.9. Shrout PE, Fleiss JL. Intraclass correlations: uses in assessing rater reliability. Psychol Bull. 1979. 86:420–428.10. Greenwald AS, Black JD, Matejczyk MB, Bryan RS, Insall JN, Wilde AH. Total knee replacement. Instr Course Lect. 1981. 30:301–341.11. Matsuda S, Matsuda H, Miyagi T, Sasaki K, Iwamoto Y, Miura H. Femoral condyle geometry in the normal and varus knee. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1998. (349):183–188.12. Laskin RS. Flexion space configuration in total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 1995. 10:657–660.
Article13. Griffin FM, Insall JN, Scuderi GR. The posterior condylar angle in osteoarthritic knees. J Arthroplasty. 1998. 13:812–815.
Article14. Cho WS, Park SS, Kim JH, Kim DH, Kim MY. The discrepancy between eipcondylar and posterior condylar axis of femur in total knee arthroplasty. J Korean Knee Soc. 1999. 11:8–12.15. Sohn SW, Jung MH. Measurement of the axial rotational axis of distal femur using different landmarks. J Korean Knee Soc. 1999. 11:129–133.16. Olcott CW, Scott RD. A comparison of 4 intraoperative methods to determine femoral component rotation during total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2000. 15:22–26.
Article17. Katz MA, Beck TD, Silber JS, Seldes RM, Lotke PA. Determining femoral rotational alignment in total knee arthroplasty: reliability of techniques. J Arthroplasty. 2001. 16:301–305.
Article18. Chang CB, Seong SC, Lee S, Yoo JH, Rhee SH, Lee MC. Anatomical assessment of distal femur for optimal femoral component rotational alignment in TKA. J Korean Orthop Assoc. 2005. 40:882–888.
Article19. Seon JK, Song EK, Park SJ, Cho SB, Choi NH. Rotational axes of the femoral componentin total knee arthroplasty. J Korean Orthop Assoc. 2006. 41:428–433.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Correlation of Postoperative Femoral Component Rotation Angle and Patella Tilt Angle with Clinical Results in Total Knee Arthroplasty
- How to Minimize Rotational Conflict between Femoral & Tibial Component in Total Knee Arthroplasty: The Use of Femoro-Tibial Axial Synchronizer (Linker)
- The Discrepancy between Eipcondylar and Posterior Condylar Axis of Femur in Total Knee Arthroplasty
- Rotational Alignment of Femoral Component for Minimal Medial Collateral Ligament Release in Total Knee Arthroplasty
- Influence of the Rotational Alignment of the Femoral and Patellar Components on Patellar Tilt in Total Knee Arthroplasty