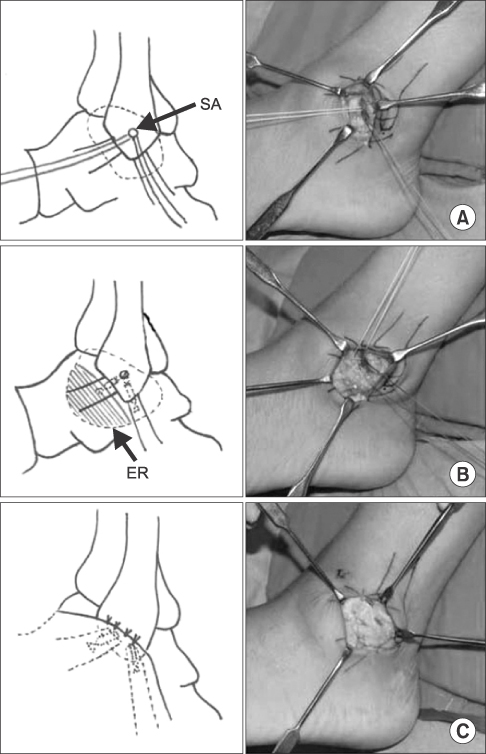
J Korean Orthop Assoc.
2014 Feb;49(1):13-21. 10.4055/jkoa.2014.49.1.13.
Anatomical Repair for Chronic Lateral Ankle Instability
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Sanggye Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. chunghj@dreamwiz.com
- KMID: 2185242
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4055/jkoa.2014.49.1.13
Abstract
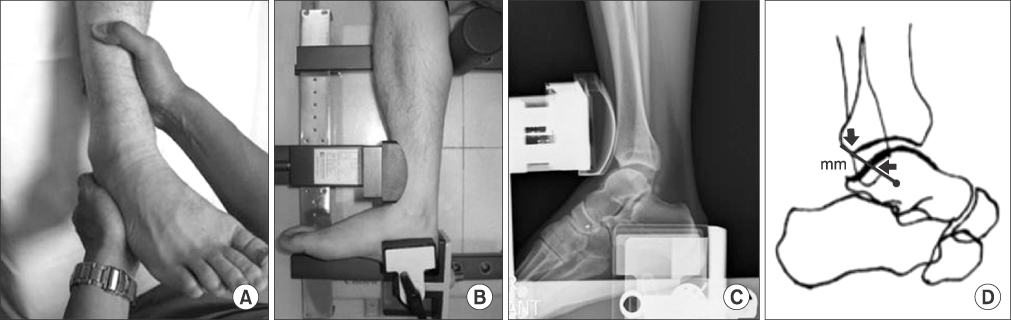
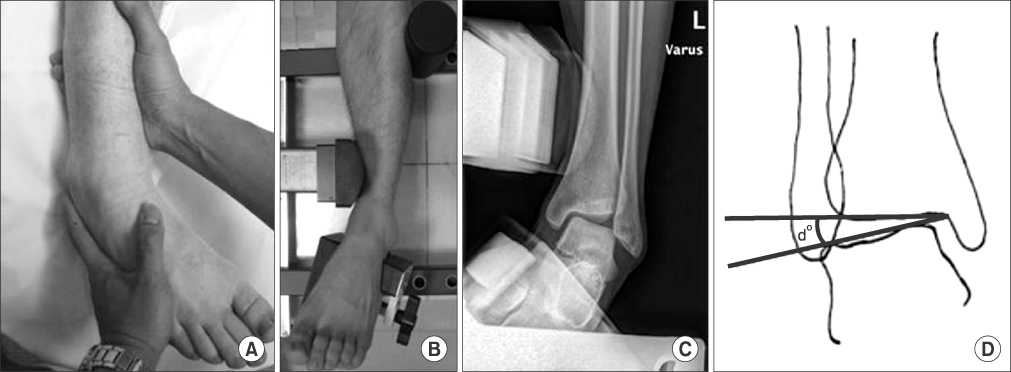
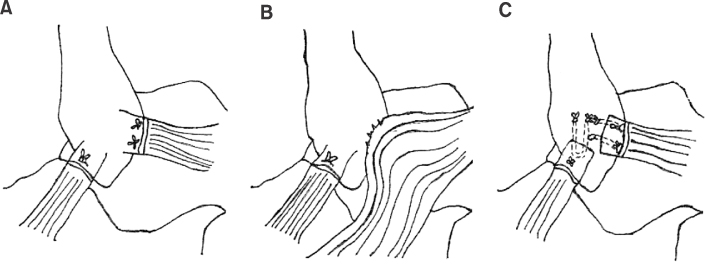
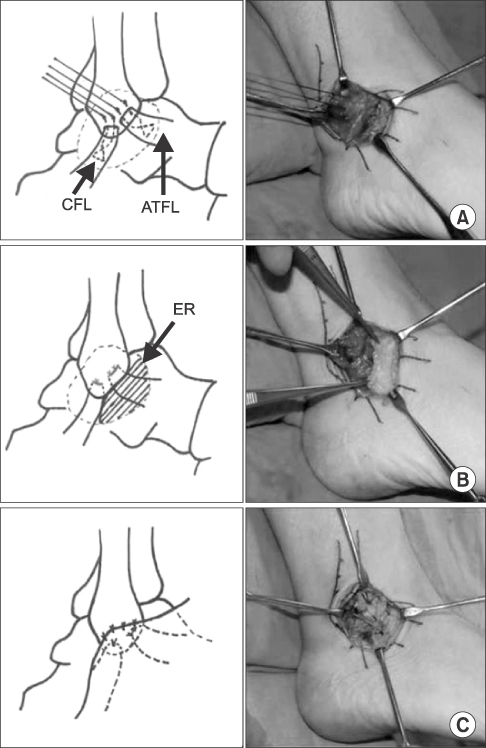
- Ankle sprain secondarily leads to chronic lateral ankle instability in 20%-30% of cases. Many surgical procedures have been presented for lateral ankle instability; however, controversy remains regarding the ideal surgical option. The Brostrom procedure or its modifications have been widely used; however, they have some limitations for the instabilities of over-weight, physically high demanding patients, generalized ligamentous laxity, and especially for significantly deficient or attenuated ligaments. This article reports on the difference between the bone tunnel technique and the suture anchor technique of the modified Brostrom procedure, and also provides a review of several recent debates.
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Ligament Repair in Chronic Lateral Ankle Instability: Efficacy and Technique of Brostr
ö m Procedures
Bi O Jeong, Yeok Gu Hwang
J Korean Foot Ankle Soc. 2018;22(3):83-90. doi: 10.14193/jkfas.2018.22.3.83.
Reference
-
1. Peters JW, Trevino SG, Renstrom PA. Chronic lateral ankle instability. Foot Ankle. 1991; 12:182–191.
Article2. McBride DJ, Ramamurthy C. Chronic ankle instability: management of chronic lateral ligamentous dysfunction and the varus tibiotalar joint. Foot Ankle Clin. 2006; 11:607–623.
Article3. Komenda GA, Ferkel RD. Arthroscopic findings associated with the unstable ankle. Foot Ankle Int. 1999; 20:708–713.
Article4. McKeon PO, Hertel J. Systematic review of postural control and lateral ankle instability, part II: is balance training clinically effective? J Athl Train. 2008; 43:305–315.
Article5. Molloy S, Solan MC, Bendall SP. Synovial impingement in the ankle. A new physical sign. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2003; 85:330–333.6. Chrisman OD, Snook GA. Reconstruction of lateral ligament tears of the ankle. An experimental study and clinical evaluation of seven patients treated by a new modification of the Elmslie procedure. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1969; 51:904–912.7. Safran MR, Benedetti RS, Bartolozzi AR 3rd, Mandelbaum BR. Lateral ankle sprains: a comprehensive review: part 1: etiology, pathoanatomy, histopathogenesis, and diagnosis. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 1999; 31:S429–S437.
Article8. DiGiovanni CW, Brodsky A. Current concepts: lateral ankle instability. Foot Ankle Int. 2006; 27:854–866.
Article9. DIGiovanni BF, Fraga CJ, Cohen BE, Shereff MJ. Associated injuries found in chronic lateral ankle instability. Foot Ankle Int. 2000; 21:809–815.
Article10. Gould N, Seligson D, Gassman J. Early and late repair of lateral ligament of the ankle. Foot Ankle. 1980; 1:84–89.
Article11. Karlsson J, Bergsten T, Lansinger O, Peterson L. Surgical treatment of chronic lateral instability of the ankle joint. A new procedure. Am J Sports Med. 1989; 17:268–273.12. Hess A, Caborn D, Rehak D, Harner CD, Fu FH. Surgical treatment of chronic lateral ankle instability using the mitek suture anchor system. Pittsburgh Orthop J. 1991; 2:54–59.13. Paden MH, Stone PA, McGarry JJ. Modified Brostrom lateral ankle stabilization utilizing an implantable anchoring system. J Foot Ankle Surg. 1994; 33:617–622.14. Hu CY, Lee KB, Song EK, Kim MS, Park KS. Comparison of bone tunnel and suture anchor techniques in the modified Broström procedure for chronic lateral ankle instability. Am J Sports Med. 2013; 41:1877–1884.
Article15. Glas E, Paar O, Smasal V, Bernett P. Periosteal flap reconstruction of the external ankle ligaments. Results of a follow-up study. Unfallchirurg. 1985; 88:219–222.16. Rudert M, Wülker N, Wirth CJ. Reconstruction of the lateral ligaments of the ankle using a regional periosteal flap. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1997; 79:446–451.
Article17. Lee JY, Kim TY, Gan XX, Kang SY, Hong SJ. Use of a recombinant Clonorchis sinensis pore-forming peptide, clonorin, for serological diagnosis of clonorchiasis. Parasitol Int. 2003; 52:175–178.
Article18. Cho BK, Kim YM, Kim DS, Choi ES, Shon HC, Park KJ. Comparison between suture anchor and transosseous suture for the modified-Broström procedure. Foot Ankle Int. 2012; 33:462–468.
Article19. Kim BS, Choi WJ, Kim YS, Lee JW. The effect of an ossicle of the lateral malleolus on ligament reconstruction of chronic lateral ankle instability. Foot Ankle Int. 2010; 31:191–196.
Article20. Chun TH, Park YS, Sung KS. The effect of ossicle resection in the lateral ligament repair for treatment of chronic lateral ankle instability. Foot Ankle Int. 2013; 34:1128–1133.
Article21. Baumhauer JF, O'Brien T. Surgical considerations in the treatment of ankle instability. J Athl Train. 2002; 37:458–462.22. Bell SJ, Mologne TS, Sitler DF, Cox JS. Twenty-six-year results after Broström procedure for chronic lateral ankle instability. Am J Sports Med. 2006; 34:975–978.
Article23. Karlsson J, Bergsten T, Lansinger O, Peterson L. Reconstruction of the lateral ligaments of the ankle for chronic lateral instability. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1988; 70:581–588.
Article24. Lee KT, Park YU, Kim JS, Kim JB, Kim KC, Kang SK. Long-term results after modified Bostrom procedure without calcaneo-fibular ligament reconstruction. Foot Ankle Int. 2011; 32:153–157.25. Lee KT. Soccer medicine. 1st ed. Seoul: Koonja Publish;2002. p. 119–133.26. Behrens SB, Drakos M, Lee BJ, et al. Biomechanical analysis of Brostrom versus Brostrom-Gould lateral ankle instability repairs. Foot Ankle Int. 2013; 34:587–592.
Article27. Maffulli N, Del Buono A, Maffulli GD, et al. Isolated anterior talofibular ligament Broström repair for chronic lateral ankle instability: 9-year follow-up. Am J Sports Med. 2013; 41:858–864.28. Kim ES, Lee KT, Park JS, Lee YK. Arthroscopic anterior talofibular ligament repair for chronic ankle instability with a suture anchor technique. Orthopedics. 2011; 34.
Article29. Sammarco VJ. Complications of lateral ankle ligament reconstruction. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2001; 391:123–132.
Article30. Chan KW, Ding BC, Mroczek KJ. Acute and chronic lateral ankle instability in the athlete. Bull NYU Hosp Jt Dis. 2011; 69:17–26.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Ligament Repair in Chronic Lateral Ankle Instability: Efficacy and Technique of Broström Procedures
- Surgical Treatment of Chronic Ankle Lateral Instability: Reconstruction with Tenodesis or Tendon Graft
- Arthroscopic Procedure in the Treatment of Chronic Lateral Ankle Instability
- Surgical Treatment of Chronic Lateral Ankle Instability: Repair versus Reconstruction
- Chronic Lateral Ankle Instability