J Korean Orthop Assoc.
2014 Apr;49(2):172-176. 10.4055/jkoa.2014.49.2.172.
Mechanical Failure in Distraction Osteogenesis Using the Intramedullary Skeletal Kinetic Distractor
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, CHA Bundang Medical Center, Seongnam, Korea. orthopaedee@naver.com
- 2Department of Orthopedic Surgery, CHA Gumi Medical Center, CHA University, Gumi, Korea.
- KMID: 2185224
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4055/jkoa.2014.49.2.172
Abstract
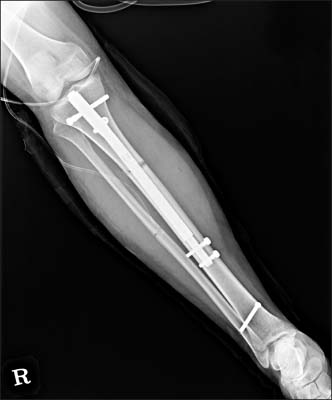
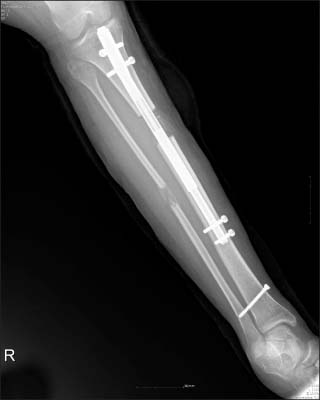
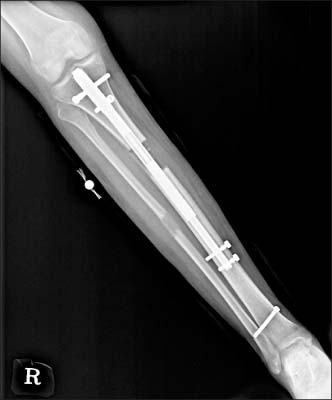
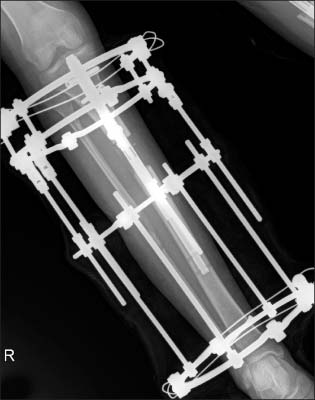
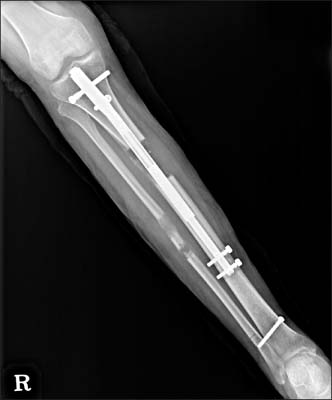
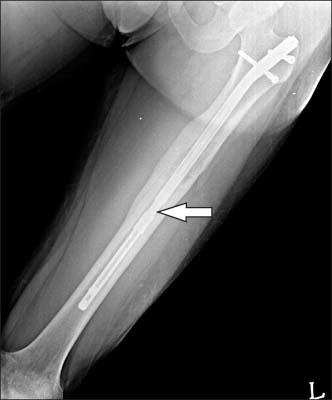
- In an effort to overcome the drawbacks of distraction osteogenesis using the Ilizarov external fixator, intramedullary lengthening devices have been developed and applied for long bone distraction osteogenesis. Several successful cases have been reported, leading to the next generation of distraction osteogenesis. However, intramedullary lengthening devices have their own problems, such as device failure, difficulty of control of the lengthening degree. The authors report on a case of device failure during distraction osteogenesis using ISKD(R) (Orthofix Inc.) in the distraction phase, and the strategy that involved switching to a lengthening over nail system, which uses the Ilizarov external fixator, in order to obtain the target length.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Paley D. Problems, obstacles, and complications of limb lengthening by the Ilizarov technique. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1990; 250:81–104.
Article2. Faber FW, Keessen W, van Roermund PM. Complications of leg lengthening. 46 procedures in 28 patients. Acta Orthop Scand. 1991; 62:327–332.
Article3. Paley D, Herzenberg JE, Paremain G, Bhave A. Femoral lengthening over an intramedullary nail. A matched-case comparison with Ilizarov femoral lengthening. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1997; 79:1464–1480.
Article4. Cole JD, Justin D, Kasparis T, DeVlught D, Knobloch C. The intramedullary skeletal kinetic distractor (ISKD): first clinical results of a new intramedullary nail for lengthening of the femur and tibia. Injury. 2001; 32:Suppl 4. SD129–SD139.
Article5. Hankemeier S, Gösling T, Pape HC, Wiebking U, Krettek C. Limb lengthening with the Intramedullary Skeletal Kinetic Distractor (ISKD). Oper Orthop Traumatol. 2005; 17:79–101.6. Simpson AH, Shalaby H, Keenan G. Femoral lengthening with the Intramedullary Skeletal Kinetic Distractor. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2009; 91:955–961.
Article7. Mahboubian S, Seah M, Fragomen AT, Rozbruch SR. Femoral lengthening with lengthening over a nail has fewer complications than intramedullary skeletal kinetic distraction. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2012; 470:1221–1231.
Article8. Burghardt RD, Herzenberg JE, Specht SC, Paley D. Mechanical failure of the Intramedullary Skeletal Kinetic Distractor in limb lengthening. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2011; 93:639–643.
Article9. Wang K, Edwards E. Intramedullary skeletal kinetic distractor in the treatment of leg length discrepancy--a review of 16 cases and analysis of complications. J Orthop Trauma. 2012; 26:e138–e144.
Article10. Kubiak EN, Strauss E, Grant A, Feldman D, Egol KA. Early complications encountered using a self-lengthening intramedullary nail for the correction of limb length inequality. Jt Dis Relat Surg. 2007; 18:52–57.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Distraction Osteogenesis Of The Midface With A Rigid External Distractor (RED)
- Reports of mandibular symphysis widening with distraction osteogenesis
- Case reports of antero-posteior movement with distraction osteogenesis in maxillary anterior segment
- Distraction osteogenesis on mandible symphysis widening with a bone-borne type distractor
- Vertical Distraction Of Alveolar Bone For Placement Of Dental Implant