J Korean Orthop Assoc.
2014 Apr;49(2):118-125. 10.4055/jkoa.2014.49.2.118.
Distal Femoral Varization Osteotomy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Ewha Womans University Mokdong Hospital, Seoul, Korea. koreanknee@gmail.com
- KMID: 2185216
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4055/jkoa.2014.49.2.118
Abstract
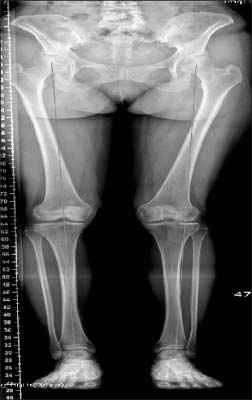
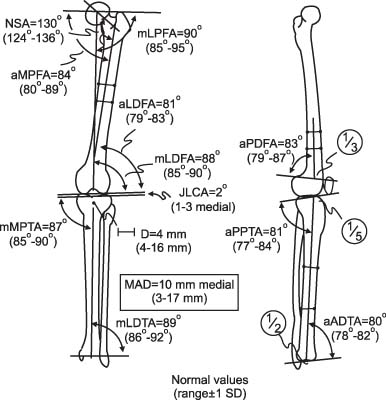
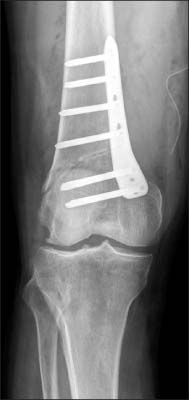
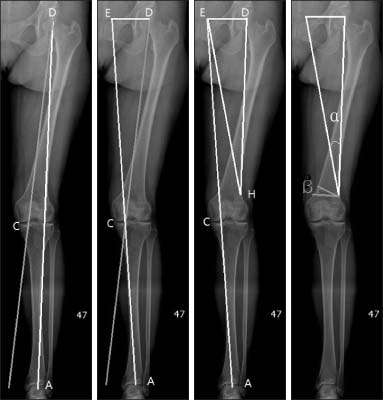
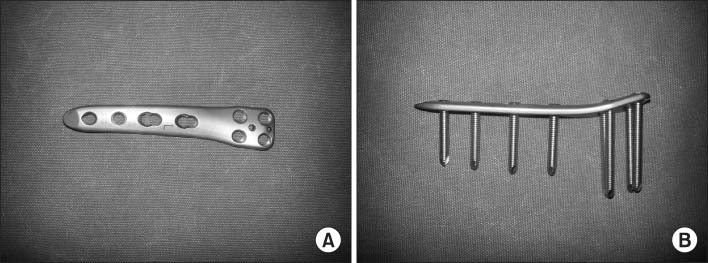
- Distal femoral varization osteotomy is performed for treatment of lateral compartment osteoarthritis of the knee associated with valgus deformity for relief of pain and improvement of functional status. Careful selection of patients is the key to the success of this procedure. Distal femoral varus osteotomy is indicated for patients with isolated lateral compartment knee arthritis with a valgus deformity; candidates must have a range of motion arc of at least 90 degrees and less than 20 degrees of flexion-contracture. The indications of distal femoral varization osteotomy must be considered before surgery. Contraindications include patients with diffuse and nonspecific knee pain, primary complaint of patellofemoral pain, history of medial meniscectomy, and bicompartmental degeneratvie osteoarthritis. The success of an osteotomy is dependent on adequate correction of limb malalignment; therefore, accurate determination of the desired angle of correction is essential during preoperative planning. In recent years with the advent of new anatomical locking plate designs, medial closed wedge osteotomy has become popular. Compared to lateral opening wedge osteotomy, with medial closing wedge osteotomy, earlier union is expected and it provides stable fixation even with poor bone quality. Nevertheless, arthroplasty offers rapid pain relief and short-term rehabilitation period; however, risk of wear, difficulty and poor outcome of revision surgery, possible complication of infection or prosthetic failure in young and active patients, demanding high functional loading, is a cause for concern. Because this joint preserving procedure is not associated with prosthesis-related complication, it can be a good alternative option for young and active patients.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Osteotomy around the Knee: Indication and Preoperative Planning
Seung Wan Lim, Seung Min Ryu, Oog Jin Shon
J Korean Orthop Assoc. 2018;53(4):283-292. doi: 10.4055/jkoa.2018.53.4.283.
Reference
-
1. Shoji H, Insall J. High tibial osteotomy for osteoarthritis of the knee with valgus deformity. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1973; 55:963–973.
Article2. Gross AE, Hutchison CR. Realignment osteotomy of the knee-Part 1: distal femoral varus osteotomy for osteoarthritis of the Valgus knee. Oper Tech Sports Med. 2000; 8:122–126.
Article3. Coventry MB. Proximal tibial varus osteotomy for osteoarthritis of the lateral compartment of the knee. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1987; 69:32–38.
Article4. Hunter DJ, Sharma L, Skaife T. Alignment and osteoarthritis of the knee. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2009; 91:Suppl 1. 85–89.
Article5. Lobenhoffer P, Van Heerwaarden RJ, Staubli AE, Jakob RP. Osteotomies around the knee: indications, planning, surgical techniques using plate fixators. New York: AO Foundation, Thieme;2008. p. 150–152.6. Aglietti P, Menchetti PP. Distal femoral varus osteotomy in the valgus osteoarthritic knee. Am J Knee Surg. 2000; 13:89–95.7. Learmonth ID. A simple technique for varus supracondylar osteotomy in genu valgum. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1990; 72:235–237.
Article8. McDermott AG, Finklestein JA, Farine I, Boynton EL, MacIntosh DL, Gross A. Distal femoral varus osteotomy for valgus deformity of the knee. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1988; 70:110–116.
Article9. Thein R, Bronak S, Thein R, Haviv B. Distal femoral osteotomy for valgus arthritic knees. J Orthop Sci. 2012; 17:745–749.
Article10. Wang JW, Hsu CC. Distal femoral varus osteotomy for osteoarthritis of the knee. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005; 87:127–133.
Article11. Franco V, Cipolla M, Gerullo G, Gianni E, Puddu G. Open wedge osteotomy of the distal femur in the valgus knee. Orthopade. 2004; 33:185–192.12. Mathews J, Cobb AG, Richardson S, Bentley G. Distal femoral osteotomy for lateral compartment osteoarthritis of the knee. Orthopedics. 1998; 21:437–440.
Article13. Finkelstein JA, Gross AE, Davis A. Varus osteotomy of the distal part of the femur. A survivorship analysis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1996; 78:1348–1352.
Article14. Backstein D, Morag G, Hanna S, Safir O, Gross A. Long-term follow-up of distal femoral varus osteotomy of the knee. J Arthroplasty. 2007; 22:2–6.
Article15. Kosashvili Y, Safir O, Gross A, Morag G, Lakstein D, Backstein D. Distal femoral varus osteotomy for lateral osteoarthritis of the knee: a minimum ten-year follow-up. Int Orthop. 2010; 34:249–254.
Article16. Edgerton BC, Mariani EM, Morrey BF. Distal femoral varus osteotomy for painful genu valgum. A five-to-11-year follow-up study. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1993; 288:263–269.17. Nelson CL, Saleh KJ, Kassim RA, et al. Total knee arthroplasty after varus osteotomy of the distal part of the femur. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2003; 85:1062–1065.
Article18. Morrey BF, Edgerton BC. Distal femoral osteotomy for lateral gonarthrosis. Instr Course Lect. 1992; 41:77–85.19. Scott WN, Cushner FD, Diduch DR, et al. Insall & Scott surgery of the knee. 5th ed. Philadelphia: Elsevier;2012. p. 923–925.20. Saithna A, Kundra R, Modi CS, Getgood A, Spalding T. Distal femoral varus osteotomy for lateral compartment osteoarthritis in the valgus knee. A systematic review of the literature. Open Orthop J. 2012; 6:313–319.
Article21. Magyar G, Toksvig-Larsen S, Alkstedt J, et al. Frequent complications in distal femoral osteotomy: a retrospective 8 year multicenter follow-up. Chir Organi Mov. 1999; 84:19–26.22. Terry GC, Cimino PM. Distal femoral osteotomy for valgus deformity of the knee. Orthopedics. 1992; 15:1283–1289.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Surgical Technique for Distal Femur Varization Osteotomy
- Distal Femoral Medial Opening Wedge Osteotomy for Post-Traumatic, Distal Femoral Varus Deformity
- Subtrochanteric Varization Osteotomy with Open Wedge Technic in a Legg-Calve-Perthes Disease
- Deformity Correction by Femoral Supracondylar Dome Osteotomy with Retrograde Intramedullary Nailing in Varus Deformity of the Distal Femur after Pathologic Fracture of Giant Cell Tumor
- Medial Plating of Distal Femoral Fracture with Locking Compression Plate-Proximal Lateral Tibia: Cases' Report