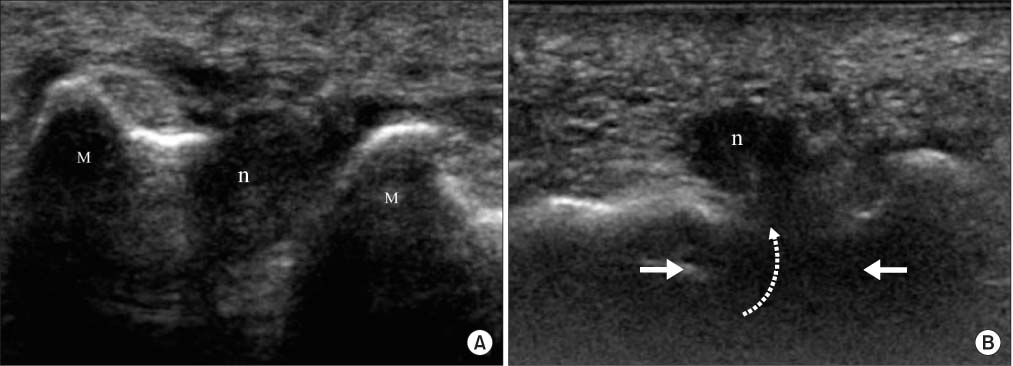
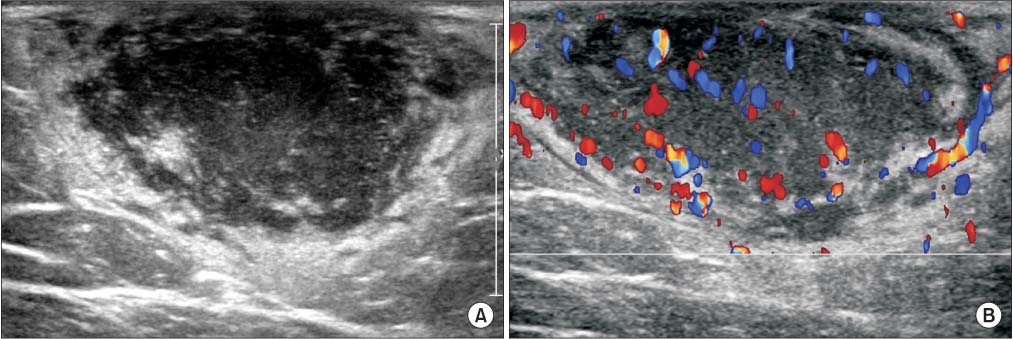
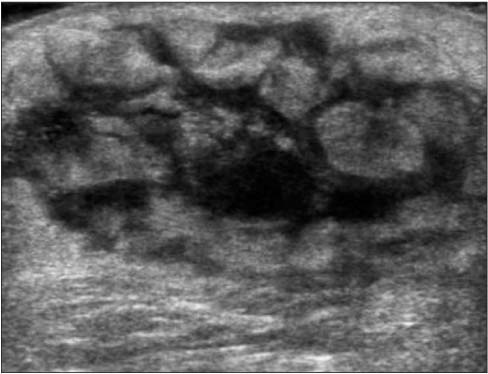
J Korean Orthop Assoc.
2014 Dec;49(6):422-430. 10.4055/jkoa.2014.49.6.422.
Sonographic Features of Common Soft Tissue Masses in the Extremities
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. dalnara3@gmail.com
- KMID: 2185155
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4055/jkoa.2014.49.6.422
Abstract
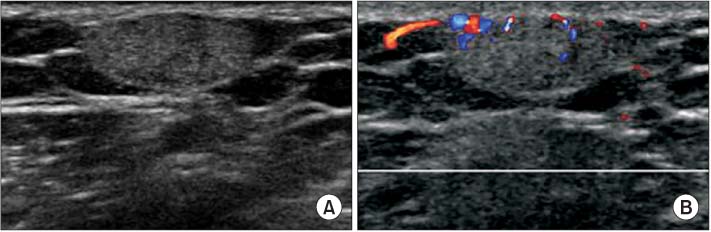
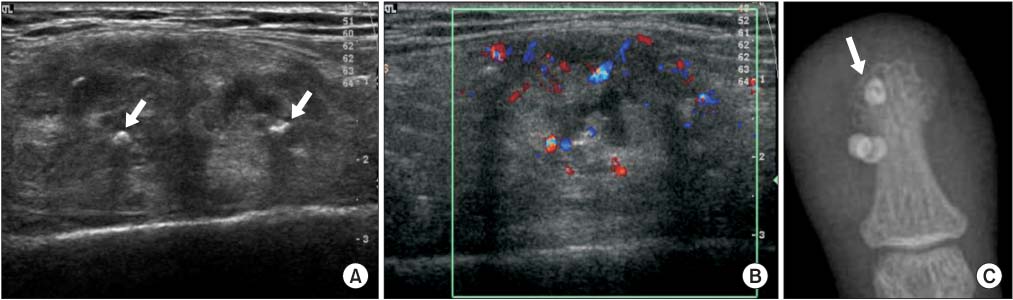
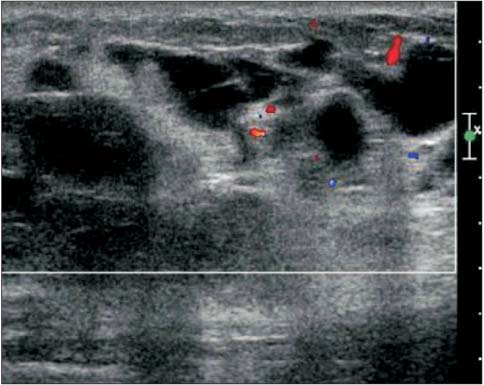
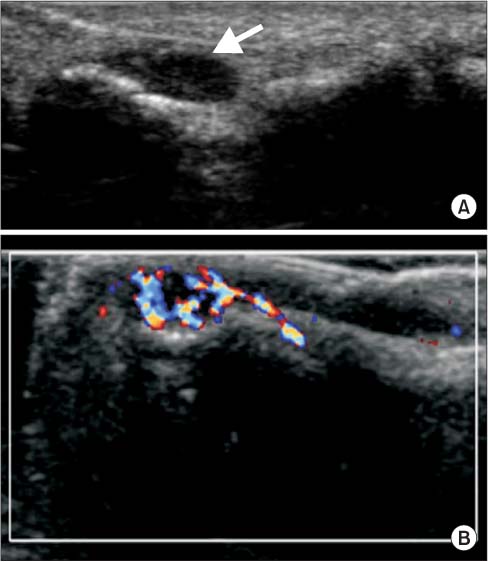
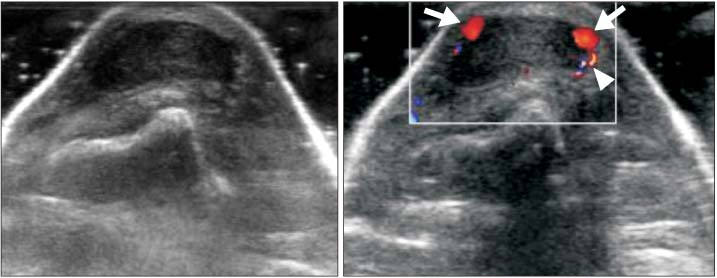
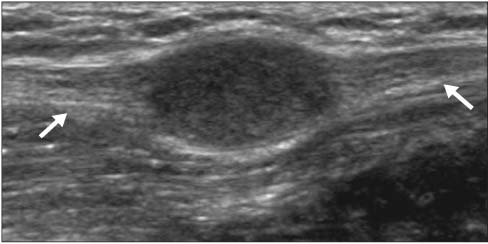
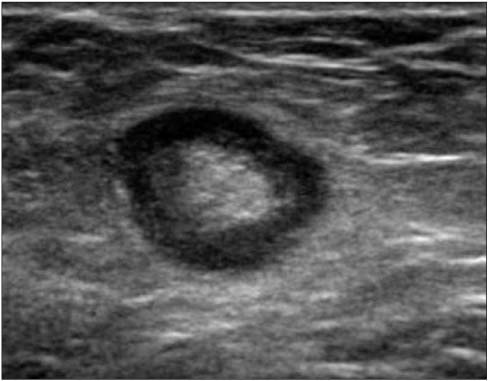
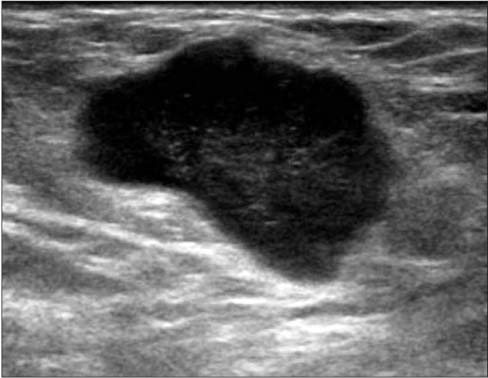
- A wide variety of superficial soft tissue masses may be seen in clinical practice and imaging modalities can be helpful in achievement of a definitive diagnosis or limit a differential diagnosis. Among them, ultrasonography is well suited for screening soft tissue masses because of its safety, low cost, and real-time dynamic imaging. The purpose of this article is to review the characteristic sonographic appearance of soft tissue masses in the extremities.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
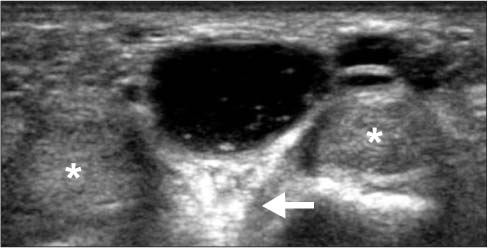
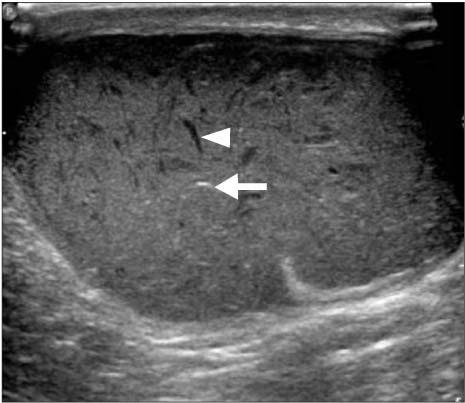
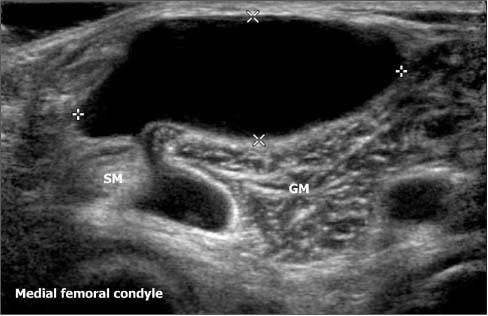
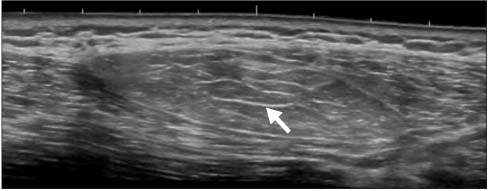
Figure
Reference
-
1. Lachenmayer A, Yang Q, Eisenberger CF, et al. Superficial soft tissue sarcomas of the extremities and trunk. World J Surg. 2009; 33:1641–1649.
Article2. Kransdorf MJ. Imaging of soft tissue tumours. 2nd ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins;2006.3. Bianchi S, Martinoli C. Ultrasound of the musculoskeletal system. Berlin; New York: Springer;2007.4. Lakkaraju A, Sinha R, Garikipati R, Edward S, Robinson P. Ultrasound for initial evaluation and triage of clinically suspicious soft-tissue masses. Clin Radiol. 2009; 64:615–621.
Article5. Chiou HJ, Chou YH, Chiou SY, Wang HK. High-resolution ultrasonography in superficial soft tissue tumors. J Med Ultrasound. 2007; 15:152–174.
Article6. Wu S, Tu R, Liu G, Shi Y. Role of ultrasound in the diagnosis of common soft tissue lesions of the limbs. Ultrasound Q. 2013; 29:67–71.
Article7. Widmann G, Riedl A, Schoepf D, Glodny B, Peer S, Gruber H. State-of-the-art HR-US imaging findings of the most frequent musculoskeletal soft-tissue tumors. Skeletal Radiol. 2009; 38:637–649.
Article8. Wu JS, Hochman MG. Soft-tissue tumors and tumorlike lesions: a systematic imaging approach. Radiology. 2009; 253:297–316.
Article9. Teefey SA, Middleton WD, Boyer MI. Sonography of the hand and wrist. Semin Ultrasound CT MR. 2000; 21:192–204.
Article10. Horcajadas AB, Lafuente JL, de la Cruz Burgos R, et al. Ultrasound and MR findings in tumor and tumor-like lesions of the fingers. Eur Radiol. 2003; 13:672–685.
Article11. Dudea SM, Lenghel M, Botar-Jid C, Vasilescu D, Duma M. Ultrasonography of superficial lymph nodes: benign vs. malignant. Med Ultrason. 2012; 14:294–306.12. Ahuja AT, Ying M. Sonographic evaluation of cervical lymph nodes. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2005; 184:1691–1699.
Article13. Chiou HJ, Chou YH, Chiu SY, et al. Differentiation of benign and malignant superficial soft-tissue masses using grayscale and color doppler ultrasonography. J Chin Med Assoc. 2009; 72:307–315.
Article