J Korean Fract Soc.
2011 Apr;24(2):174-177. 10.12671/jkfs.2011.24.2.174.
Usefulness of Kyphoplasty in Sacral Insufficiency Fracture: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopeadic Surgery, School of Medicine, Wonkwang University, Iksan, Korea. oschae68@hanmail.net
- KMID: 2183861
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2011.24.2.174
Abstract
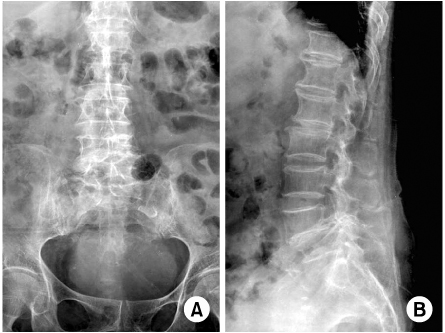
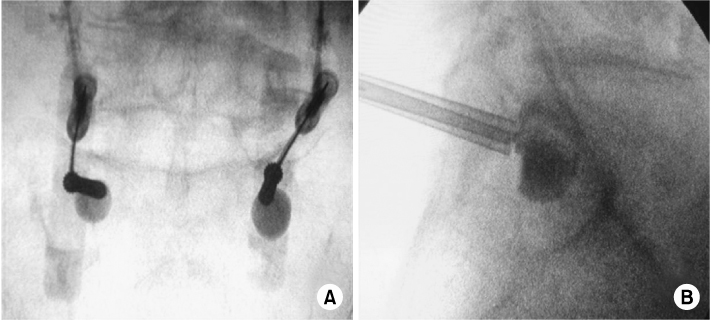
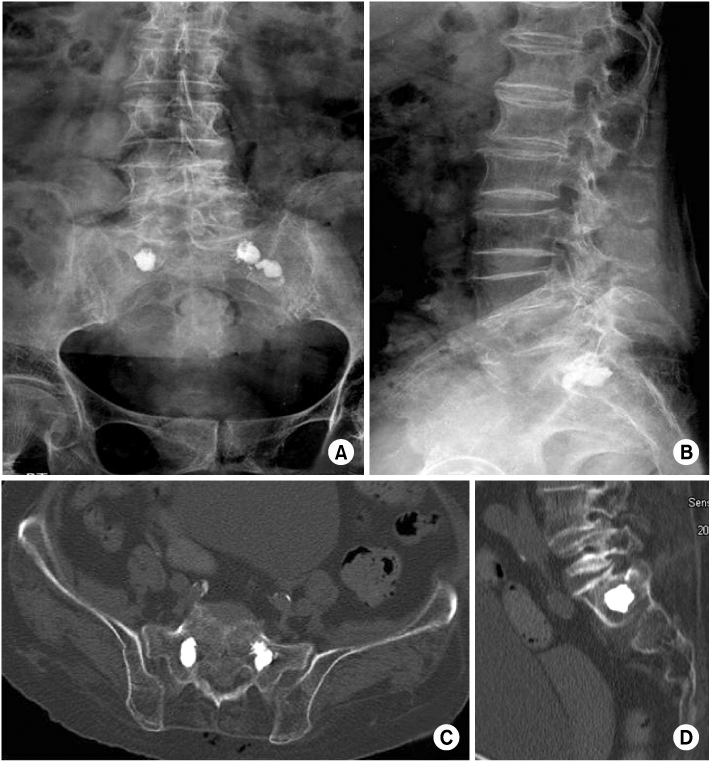
- Kyphoplasty has recently attended as a potential treatment for sacral insufficiency fracture. We report a 85-years-old female patient with osteoporotic S1 insufficiency fracture with absence of trauma history treated with kyphoplasty which has no symptom improve with conservative treatment. Kyphoplasty is an effective and useful procedure in the treatment of the sacral insufficiency fracture, additionally reviewed of the literatures.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Pelvic Insufficiency Fracture in Severe Osteoporosis Patient
Woong Chae Na, Sang Hong Lee, Sung Jung, Hyun Woong Jang, Suenghwan Jo
Hip Pelvis. 2017;29(2):120-126. doi: 10.5371/hp.2017.29.2.120.
Reference
-
1. Atalay B, Caner H, Yilmaz C, Altinors N. Sacral kyphoplasty for relieving pain caused by sacral hemangioma. Spinal Cord. 2006. 44:196–199.
Article2. Bayley E, Srinivas S, Boszczyk BM. Clinical outcomes of sacroplasty in sacral insufficiency fractures: a review of the literature. Eur Spine J. 2009. 18:1266–1271.
Article3. Frey ME, Depalma MJ, Cifu DX, Bhagia SM, Carne W, Daitch JS. Percutaneous sacroplasty for osteoporotic sacral insufficiency fractures: a prospective, multicenter, observational pilot study. Spine J. 2008. 8:367–373.
Article4. Garant M. Sacroplasty: a new treatment for sacral insufficiency fracture. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2002. 13:1265–1267.
Article5. Lee SE, Nam IH, Lee SS, Lee DH, Woo DH. Insufficiency fracture of the sacrum: a case report. J Korean Soc Spine Surg. 2001. 8:172–175.6. Lourie H. Spontaneous osteoporotic fracture of the sacrum. An unrecognized syndrome of the elderly. JAMA. 1982. 248:715–717.
Article7. Lyders EM, Whitlow CT, Baker MD, Morris PP. Imaging and treatment of sacral insufficiency fractures. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2010. 31:201–210.
Article8. Smith DK, Dix JE. Percutaneous sacroplasty: long-axis injection technique. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2006. 186:1252–1255.
Article9. Waites MD, Mears SC, Richards AM, Mathis JM, Belkoff SM. A biomechanical comparison of lateral and posterior approaches to sacroplasty. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2008. 33:E735–E738.
Article10. Whitlow CT, Yazdani SK, Reedy ML, Kaminsky SE, Berry JL, Morris PP. Investigating sacroplasty: technical considerations and finite element analysis of polymethylmethacrylate infusion into cadaveric sacrum. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2007. 28:1036–1041.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Therapeutic Considerations of Percutaneous Sacroplasty for the Sacral Insufficiency Fracture
- A Case of S1 Radiculopathy in Sacral Insufficiency Fracture without Fracture Line
- Sacral Insufficiency Fracture, Usually Overlooked Cause of Lumbosacral Pain
- Sequential Sacral Insufficiency Fracture After Unilateral Pubic Fractures: A Case Report
- Osteoporotic Compression Fracture of the Thoracolumbar Spine and Sacral Insufficiency Fracture: Incidence and Analysis of the Relationship according to the Clinical Factors