J Korean Fract Soc.
2013 Oct;26(4):333-337. 10.12671/jkfs.2013.26.4.333.
Breakage of Reamer during Tibia Intramedullary Nailing: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Eulji General Hospital, Eulji University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. jins33@eulji.ac.kr
- 2Dr. Choi's Orthopedic Surgery, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2183836
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2013.26.4.333
Abstract
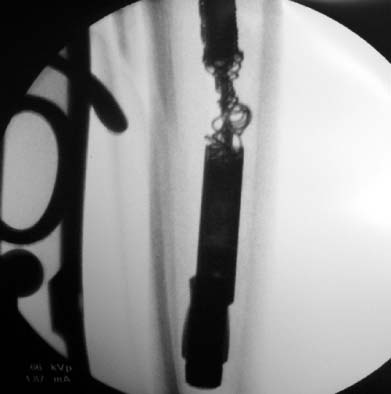
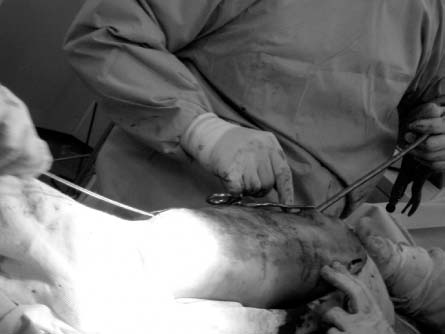
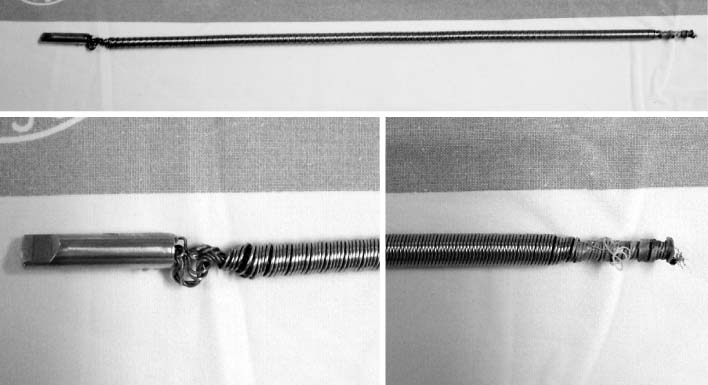
- The reamer crack, followed by breakage at its distal part occurred during intramedullary nailing of tibial shaft fracture. The broken reamer was trapped in the intramedullary canal, making it very difficult to pull out. We successfully extracted the broken reamer by retrograde impaction through the fracture site and completed intramedullary nailing procedure. Thus, we present this case with a review of the literature.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Bhandari M, Guyatt GH, Swiontkowski MF, et al. Surgeons' preferences for the operative treatment of fractures of the tibial shaft. An international survey. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2001; 83-A:1746–1752.2. Bisbinas I, Ho YM, Learmonth DJ. Reamer breakage in the femoral medulla during total knee arthroplasty: should reamers have a finite life? J Arthroplasty. 2004; 19:501–503.3. Coles CP, Gross M. Closed tibial shaft fractures: management and treatment complications. A review of the prospective literature. Can J Surg. 2000; 43:256–262.4. Darowish M, Gorczyca JT. Catastrophic intramedullary fragmentation of a tinel reamer. J Trauma. 2009; 67:E36–E40.
Article5. Hooper GJ, Keddell RG, Penny ID. Conservative management or closed nailing for tibial shaft fractures. A randomised prospective trial. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1991; 73:83–85.
Article6. Hwang SK, Yoo JM. Complication related to interlocking nailing of the tibia fracture. J Korean Soc Fract. 1995; 8:823–829.
Article7. Moreland JR, Marder R, Anspach WE Jr. The window technique for the removal of broken femoral stems in total hip replacement. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1986; (212):245–249.
Article8. Noh JH, Yang BK, Park JT, Je MS. Breakage of core reamer during anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction -A case report-. J Korean Arthrosc Soc. 2010; 14:33–35.9. Pape HC, Giannoudis P. The biological and physiological effects of intramedullary reaming. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2007; 89:1421–1426.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Extraction of Misplaced Endcap during Tibia Intramedullary Nailing by 'Fish-Hook' Technique: Technical Note
- Clinical Results of Unreamed Static Interlocking Intramedullary Nailing In Clsed Tibial Shaft Fractures
- Screw breakage in tibial interlocking nailing
- Interlocking Intramedullary Nailing Versus conventional Kuntscher Intramedullary Nailing for Fracture of the Femoral Shaft
- Thermal Injury Complicating Improperly Reamed Intramedullary Nailing of the Tibia: A Case Report