J Korean Fract Soc.
2013 Oct;26(4):241-247. 10.12671/jkfs.2013.26.4.241.
Analysis of Risk Factors for the Posterolateral Articular Depression and Status of Posterolateral Fragment in Lateral Condylar and Bicondylar Tibial Plateau Fractures with Joint Depression
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Inje University Sanggye Paik Hospital, Seoul, Korea. woonysos@paik.ac.kr
- KMID: 2183823
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2013.26.4.241
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To evaluate risk factors of posterolateral articular depression and characteristics of the posterolateral fragment in lateral condylar and bicondylar tibial plateau fractures with joint depression.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
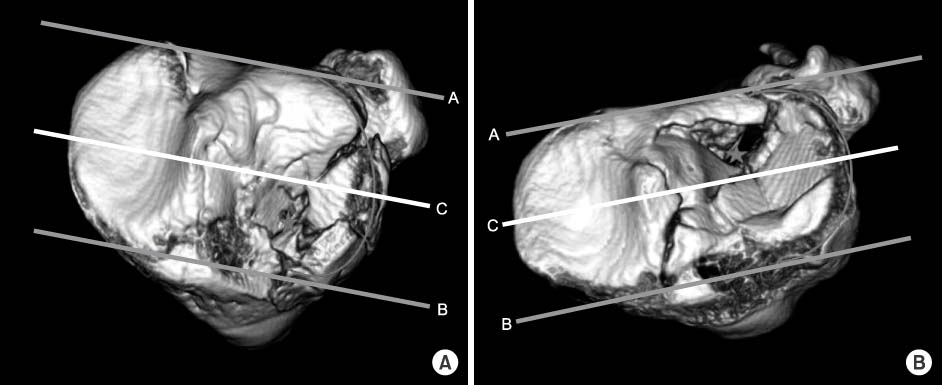
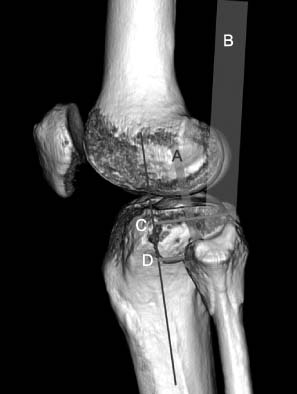
We reviewed 48 patients of Schatzker type II and type V (type II 34, type V 14) and evaluated risk factors of posterolateral articular depression according to the posterolateral fragment, fibular fracture, and Schatzker classification. We evaluated the position of articular depression and anterolateral fracture line of the posterolateral fragment and measured anterior to posterior lengths of the posterolateral fragment.
RESULTS
Posterolateral articular depression was found in 20 of 34 cases (59%) with coexisting posterolateral fragment and in 16 of 21 cases (76%) with coexisting fibular fracture. There was a significant difference in the occurrence of posterolateral articular depression with the existence of the posterolateral fragment and fibular fracture (p<0.001). Multivariate regression analysis revealed that fibular fracture increased the occurrence of posterolateral articular depression (odds ratio 24.5, 95% confidence interval 2.2-267.2). Fifty-seven percentage of the anterolateral fracture line of the posterolateral fragment existed posterior to the anterior margin of the fibular head.
CONCLUSION
This study showed that fibular fracture affects posterolateral articular depression in Schatzker type II and V tibial plateau fractures. Selecting a fixation device and performing fracture reduction requires a careful consideration since the anterolateral fracture line of the posterolateral fragment exists posterior to the anterior margin of the fibular head.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Current Concepts in Management of Tibia Plateau Fracture
Sang Hak Lee, Kang-Il Kim
J Korean Fract Soc. 2014;27(3):245-260. doi: 10.12671/jkfs.2014.27.3.245.
Reference
-
1. Barei DP, O'Mara TJ, Taitsman LA, Dunbar RP, Nork SE. Frequency and fracture morphology of the posteromedial fragment in bicondylar tibial plateau fracture patterns. J Orthop Trauma. 2008; 22:176–182.
Article2. Bozkurt M, Turanli S, Doral MN, et al. The impact of proximal fibula fractures in the prognosis of tibial plateau fractures: a novel classification. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2005; 13:323–328.
Article3. Brunner A, Honigmann P, Horisberger M, Babst R. Open reduction and fixation of medial Moore type II fractures of the tibial plateau by a direct dorsal approach. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2009; 129:1233–1238.
Article4. Chan PS, Klimkiewicz JJ, Luchetti WT, et al. Impact of CT scan on treatment plan and fracture classification of tibial plateau fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 1997; 11:484–489.
Article5. Chang SM, Zheng HP, Li HF, et al. Treatment of isolated posterior coronal fracture of the lateral tibial plateau through posterolateral approach for direct exposure and buttress plate fixation. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2009; 129:955–962.
Article6. Fakler JK, Ryzewicz M, Hartshorn C, Morgan SJ, Stahel PF, Smith WR. Optimizing the management of Moore type I postero-medial split fracture dislocations of the tibial head: description of the Lobenhoffer approach. J Orthop Trauma. 2007; 21:330–336.
Article7. Fernandez DL. Anterior approach to the knee with osteotomy of the tibial tubercle for bicondylar tibial fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1988; 70:208–219.
Article8. Gosling T, Schandelmaier P, Muller M, Hankemeier S, Wagner M, Krettek C. Single lateral locked screw plating of bicondylar tibial plateau fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2005; 439:207–214.
Article9. Huang YG, Chang SM. The posterolateral approach for plating tibial plateau fractures: problems in secondary hardware removal. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2012; 132:733–734.
Article10. Kennedy JC, Bailey WH. Experimental tibial-plateau fractures. Studies of the mechanism and a classification. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1968; 50:1522–1534.11. Lobenhoffer P. Posterolateral transfibular approach to tibial plateau fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2011; 25:e31.
Article12. Oh JK. Treatment of complex tibial plateau fractures. J Korean Fract Soc. 2005; 18:349–358.
Article13. Partenheimer A, Gösling T, Müller M, et al. Management of bicondylar fractures of the tibial plateau with unilateral fixed-angle plate fixation. Unfallchirurg. 2007; 110:675–683.14. Sarmiento A, Kinman PB, Latta LL, Eng P. Fracutres of the proximal tibia and tibial condyles: a clinical and laboratory comparative study. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1979; (145):136–145.15. Savolainen VT, Pajarinen J, Hirvensalo E, Lindahl J. Hybrid external fixation in treatment of proximal tibial fractures: a good outcome in AO/ASIF type-C fractures. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2010; 130:897–901.
Article16. Tao J, Hang DH, Wang QG, et al. The posterolateral shearing tibial plateau fracture: treatment and results via a modified posterolateral approach. Knee. 2008; 15:473–479.
Article17. Zhang W, Luo CF, Putnis S, Sun H, Zeng ZM, Zeng BF. Biomechanical analysis of four different fixations for the posterolateral shearing tibial plateau fracture. Knee. 2012; 19:94–98.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Meniscal Incision to Approach for Lateral Tibial Plateau Fractures
- Evaluation of the Patterns of Fractures and the Soft Tissue Injury Using MRI in Tibial Plateau Fractures
- Restoration of Lateral Tibial Plateau Widening and Articular Depression Is Necessary to Prevent Valgus Deformities after Arthroscopic Reduction and Internal Fixation in AO/OTA 41.B2 or B3 Fractures
- Lateral Locked Plating or Dual Plating: A Comparison of Two Methods in Simple Bicondylar Tibial Plateau Fractures
- The Treatment of Posterolateral Malleolar Fractures using Percutaneous Reduction Technique